Clipart tagged: ‘tapeworm’
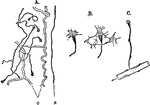
Protonephridium
Structure of the protonephridium (excretory organ) of a flatworm. A, part of the excretory apparatus…
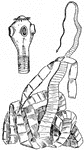
Tapeworm
Probably the most widely known of the flatworms are the tapeworms. These are parasites in the digestive…
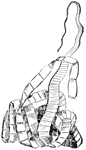
Tapeworm
Tapeworms are parasites in the digestive tube of various vertebrates, including man. this is the much…
Tapeworm
"The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length…
!["The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length is from 5 to 15 yards, and its breadth from two lines at the narrowest part to four or five at the other or broader extremity. At the narrow end is the head, which is terminated anteriorly by a central rostellum, surrounded by a crown of small recurved hooks, and behind them four suctorial depressions; then follow an immense number of segments, each full of microscopic ova. The segments are capable of being detached when mature, and reproducing the parasite. There is no mouth; but nutrition appears to take place through the tissues of the animal, as algæ derive nourishment from the sea water in which they float. The digestive system consists of two tubes or lateral canals, extending from the anterior to the posterior end of the body, and a transverse canal at the summit of each joint. [Pictured] A single segment or proglottis magnified; 1, generating pore; 2, water vessels; 3, dendritic ovary."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16500/16595/tapeworm2_16595_mth.gif)
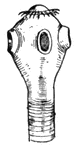
Tapeworm
"The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length…
!["The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length is from 5 to 15 yards, and its breadth from two lines at the narrowest part to four or five at the other or broader extremity. At the narrow end is the head, which is terminated anteriorly by a central rostellum, surrounded by a crown of small recurved hooks, and behind them four suctorial depressions; then follow an immense number of segments, each full of microscopic ova. The segments are capable of being detached when mature, and reproducing the parasite. There is no mouth; but nutrition appears to take place through the tissues of the animal, as algæ derive nourishment from the sea water in which they float. The digestive system consists of two tubes or lateral canals, extending from the anterior to the posterior end of the body, and a transverse canal at the summit of each joint. [Pictured] Head of tænia solium (enlarged)."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16500/16599/tapeworm3_16599_mth.gif)
Tapeworm
"The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length…
!["The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length is from 5 to 15 yards, and its breadth from two lines at the narrowest part to four or five at the other or broader extremity. At the narrow end is the head, which is terminated anteriorly by a central rostellum, surrounded by a crown of small recurved hooks, and behind them four suctorial depressions; then follow an immense number of segments, each full of microscopic ova. The segments are capable of being detached when mature, and reproducing the parasite. There is no mouth; but nutrition appears to take place through the tissues of the animal, as algæ derive nourishment from the sea water in which they float. The digestive system consists of two tubes or lateral canals, extending from the anterior to the posterior end of the body, and a transverse canal at the summit of each joint. [Pictured] A, ovum with contained embryo, B, Cystericus longicollis."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16600/16600/tapeworm4_16600_mth.gif)
Tapeworm
"The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length…
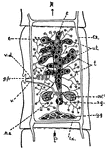
Tapeworm
This diagram shows some stages in the life history of the tapeworm. A, Cysticercus or Bladderworm stage,…