Search for "diana"

Phoebus Apollo
Apollo was the son of Zeus and Leto, twin brother of Diana, one of the principal gods of the Greeks,…

Diana
Diana was a goddess of the Romans. She was the daughter of Zeus and Leto, twin sister of Apollo, and…

Rescue of Iphigenia
"When she was about to be slain at the altar, Artemis intervened and carried her off in a cloud to be…
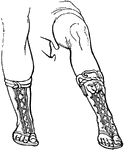
Cothurnus
"A boot. Its essential distinction was its height; it rose above the middle of the leg, so as to surround…
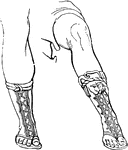
Cothurnus
"The cothurnus or buskin, rose above the midddle of the leg so as to surround the calf (sura),…

Venus and Diana
"Venus and Diana are generally represented with their hair dressed in the simple style of the young…
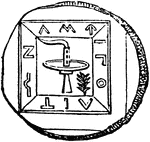
Lampadephoria
"Lampadedromia, torch-race, and often simply, Lampas, was a game common throughout Greece. At Athens…

Sacrifice of Iphigenia
"The cut represents a painting from a wall at Pompeii, the subject of which is the sacrifice of Iphigenia,…

Leto or Latona
"The persecution which Latona experienced from Juno is alluded to in the story. The tradition was that…

Chiron
"Chiron was instructed by Apollo and Diana, and was renowned for his skill in hunting, medicine, music,…

Sacrifice of Iphigenia
"When she was about to be sacrificed the goddess relented and snatched her away, leaving a hind in her…

Diana Monkey
A large African monkey. So called from a fancied resemblance of its white coronet to the silver bow…

Façade Tile from the Temple of Diana at Ephesus
On the apex and two lower angles of the pediment were introduced acroteria, sometimes ornaments of flowers…

Temple of Diana at Ephesus
"The temple of Diana was the chief glory of the city. The style was Grecian. The length of the ground-plan…

Fortune
A female depiction of Fortune with many iconic symbols, such as the rudder, the cornucopia, and ears…
![Drawing of the Diana of Versailles, a 2nd-century Roman version in the Greek tradition of iconography. In Roman mythology, Diana ([djana]) was the goddess of the hunt, the moon and childbirth, being associated with wild animals and woodland, and having the power to talk to and control animals.](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/188200/188203/188203-diana-of-versailles_mth.gif)
Diana of Versailles
Drawing of the Diana of Versailles, a 2nd-century Roman version in the Greek tradition of iconography.…

























