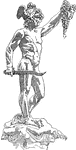Search for "medusa"
Acaleph
"One of the Acalephae; a name given to a large number of marine animals; and redpresenyted chiefly by…
Terebella medusa
"Distinguished by their habit of forming a tube or case, within which the soft parts of the animal can…
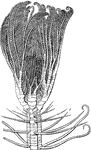
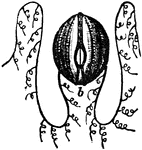
Medusa's head pentacrinus
"This may be considered as one of the greatest wonders of nature, it being a real animal, having blood,…
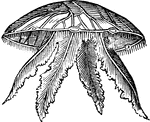
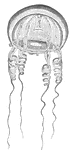
Medusa, aurita
"One of the commonest species, and must have been observed by those who frequent the sea-shore. In the…

Endoderm Cell
"Vacnolated endoderm cells of eartilaginous consistence from the axis of the tentacle of a Medusa (Cunina)."…
Ocellus
"Ocellus of a medusa (Lizzia Koellikeri). oc, pigmented ectodermal cells; l, lens." — Encyclopedia…
Sporosae
"Gradual degeneration of the medusa bud into the form of a sporosae. The black represents the enteric…
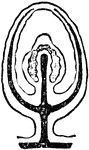
Sporosae
"Gradual degeneration of the medusa bud into the form of a sporosae. The black represents the enteric…
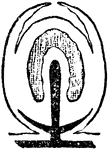
Sporosae
"Gradual degeneration of the medusa bud into the form of a sporosae. The black represents the enteric…
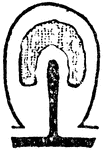
Sporosae
"Gradual degeneration of the medusa bud into the form of a sporosae. The black represents the enteric…
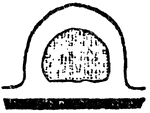
Sporosae
"Gradual degeneration of the medusa bud into the form of a sporosae. The black represents the enteric…
Sporosac
"Two female sporosacs (degenerate medusae) of Hydraetinia echinata. a, ectoderm; b, endoderm; o, eggcella;…
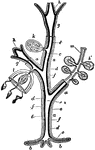
Hydromedusa
"Diagram showing possible modifications of persons of a gymnoblastic Hydromedusa. a, hydrocaulus (stem);…
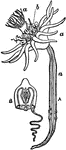
Corymorpha
"A, a hydriform person giving rise to medusiform persons by budding from the margin of the disc; B,…

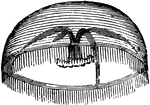
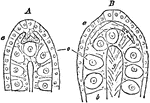
Acalephae
"The under surface, showing the mouth in the center, surrounded by the tentacula, and overial chambers…
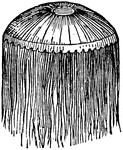
Acalephae
"Side-view, showing the tentacula hanging down in their natural position." — Chambers' Encyclopedia,…
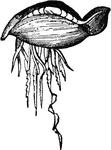
Physalia
"Physalia has no proper mouth, but the food is conveyed to the digestive cavity through a number of…
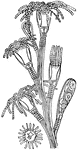
Polyp
"A hydroid colony of six polyps; f, feeding polyp; r, reproductive polyp; m, a medusa." —Davison,…
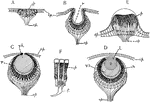
Invertebrate Simple Eye
"Diagrams showing some of the stages in the increasing complexity of the simple eye in Invertebrates.…
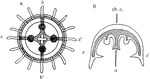
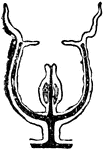
Medusa
"Diagram of Medusa, illustrating radial symmetry. A, viewed from the oral end of the principal axis;…
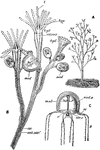
Bougainvillea Ramosa
"Bougainvillea ramosa. A, entire colony, natural size; B, portion of the same magnified; C, immature…

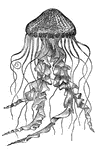
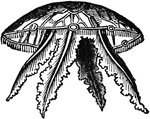
Fleet of Medusa
"They usually inhabit the deep seas. They are rarely solitary, but seem to wander about in considerable…
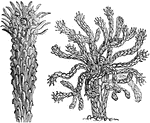
Medusa's Head Spurge
Euphorbia caputmedusae or the Medusa's Head is a spurge from the diverse genus, Euphorbia.

Farnese Medusa Head Dish
The Farnese Dish Medusa Head is an onyx patera, or black dish. It is a Roman design.

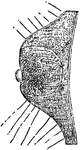
Antique Patera Medusa Head
The Antique Patera Medusa Head design comes from the center of a dish. It is a Roman design.

Tympanum Medusa Head
The Tympanum Medusa Head is found in the arch of the entrance of the Royal Palace of Tuileries in Paris,…
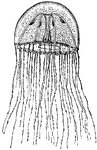
Medusa of a Hydroid
Colonial, plant-like animals closely related to jellyfish, with stinging cells, Any member of the invertebrate…

Perseus of Macedonia Coin
An illustration of a coin with the face of Perseus of Macedonia. Perseus the legendary founder of Mycenae…

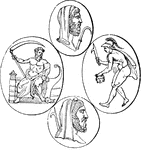
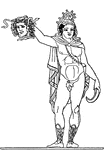
Perseus
Perseus, the legendary founder of Mycenae and of the Perseid dynasty there, was the first of the mythic…