General External Views
This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 33 general external views.
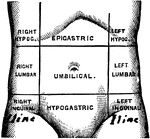
Regions of the Abdomen
Regions of the abdomen. The abdomen is divided into 9 regions by two horizontal planes, one at the level…
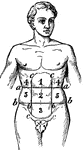
Abdominal
"In human anatomy, certain regions into which the abdomen is arbitrarily divided for the purpose of…

Back View of the Parts of the Human Body Labeled in English and Latin
Back view of a man. On one lateral the names of the parts are given in English, on the other in Latin.
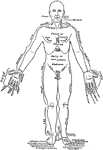
Front View of the Parts of the Human Body Labeled in English and Latin
Front view of a man in the anatomical position. On one lateral half the parts are labeled in English,…

Diagram of the Body Plan
Plan of the body in cross-section. The systems in the body are arranged in a certain way which is the…
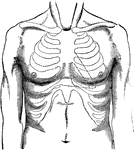
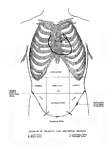
Breast Surface
Surface of the breast in a normal condition; contours or cardial torpor to the left of the breast bone.…
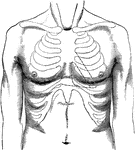
Surface of Normal Chest
Surface of normal chest; outlines of cardiac dulness to the left of the sternum. The spaces enclosed…
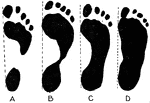
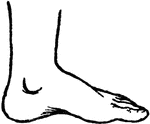
Various Forms of Footprints
Various forms of footprints. A, normal foot with high arch; B, normal foot also with high arch; C, normal…
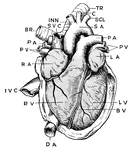
Anatomy of Heart
A complex anatomical view of the heart. RA is the right atrium, or auricle, which receives the deoxygenated…
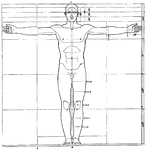
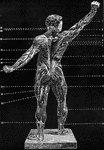
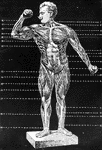
Proportions of human figure
"The proportions of the human figure. As handed down to us by Vitruvius and described by Joseph Bonomi."…

Neanderthal Man
The head of a Neanderthal man during the Early Paleolithic Age. The Neanderthal men are an extinct race.
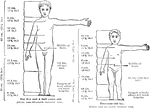
Proportions of a Healthy Child's Body at 2 and 5 Years of Age
Proportions of a health child's body and head size at 2 and 5.5 years of age.

Proportions of a Healthy Child's Body at Birth and Birth and One Year
Proportions of a health child's body and head size at birth and at one year of age.
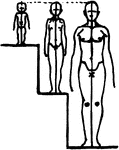
Relation of Head to Height by Age
At birth the head measures about 4 times into height. At 5 years the head measures about 6 times into…
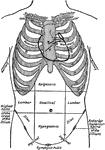
Thoracic and Abdominal Regions
Diagram of the thoracic and abdominal regions. Labels: A, aortic valve; P, pulmonary valve; M, mitral…