The Spiders, Mites and Scorpions ClipArt gallery includes 149 illustrations of spiders, mites, scorpions, and other members of the arachnid class.
Acarida
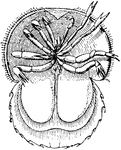
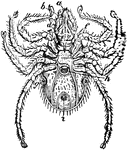
"An order of the class Arachinida, includes those insects, as the mites, ticks, itch-insects, etc.,…
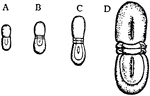
Agnostus Nudus
"Four stages in the development of the trilobite Agnostus nudus. A, Youngest stage with no mesosomatic…

Arachnid Scorpion
The name of animals of the class Arachnida. Scorpions have an elongated body, suddenly terminated by…
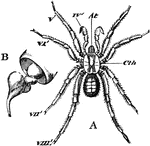
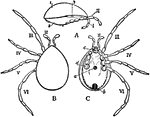
Araneida
"Mygale cæmentaria, typical of Araneida. A, female, natural size: At, cheliceræ; IV', pedipalpi;…
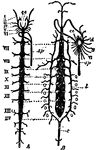
Arterial System
"Diagram of the arterial system of A, Scorpio, and B, Limulus. The Roman numerals indicate the body…
Cheese-mite
"The Cheese-mite, Acarus domesticus, and others are parasitic upon or beneath the skin of man…
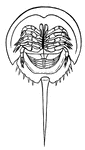
Horseshoe Crab
Horseshoe crabs represent an order called Xiphosura, from the fact that the end of the abdomen is furnished…

Horseshoe Crab (Adult)
An illustration of an adult horseshoe crab from the dorsal aspect. The horseshoe crab or Atlantic horseshoe…
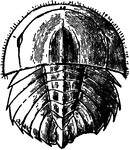
Horseshoe Crab (Young)
An illustration of a young horseshoe crab from the dorsal aspect. The horseshoe crab or Atlantic horseshoe…
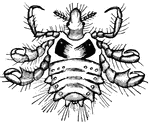
Crab-louse
The crab louse can live in almost any form of human hair, leading to its other common name of pubic…

Scorpion
Scorpions are any arachnid of the order Scorpionida. Unlike the majority of arachnid species, scorpions…
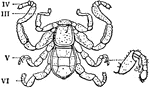
Cryptostemma Karschii
"Cryptostemma Karschii, one of the Podogona. Dorsal view of male. III to VI, The third, fourth, fifth…
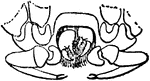
Cryptostemma Karschii
"Cryptostemma Karschii, anterior aspect of the prosoma with the "hood" removed. I to IV, first to fourth…
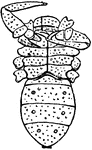
Cryptostemma Karschii
"Cryptostemma Karschii, one of the Podogona. Vental view. I to VI, The six pairs of appendages of the…
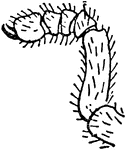
Cryptostemma Karschii
"Cryptostemma Karschii. Extremity of the fifth pair of appendages of the female for comparison with…
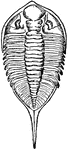
Dalmanites
"Dalmanites limulurus, Green. One of the Phacopidae, from the Silurian, New York." — The Encyclopedia…
Deiphon
"Deiphon Forbesii, Barr. One of the Cheiruridae. Silurian Bohemia." — The Encyclopedia Britannica,…
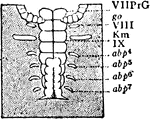
Embryo
"Portion of a similar embryo at a later stage of growth. The praegenital somite, VII PrG, is still present,…
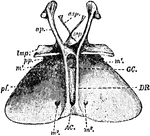
Entosternum
"Entosternum of scorpion (Palamnaeus indus, de Geer); dorsal surface. asp, Paired anterior process of…
Entosternum
"Entosternum of one of the mygalomorphous spiders; ventral surface. Ph.N., pharyngeal notch. The posterior…
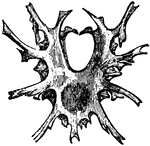
Entosternum
"Dorsal surface of an entosternum. Ph.N., pharyngeal notch." — The Encyclopedia Britannica, 1910
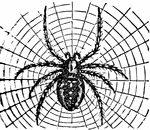
Epeira Diadema
"A genus of spiders, the type of a family called Epeirdae. They are of those spiders which have only…
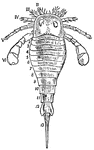
Eurypterus Fischeri
"Eurypterus Fischeri, Eichwald. Silurian of Rootzikil. Restoration after Schmidt. The dorsal aspect…
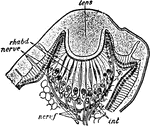
Euscorpius Italicus
"Section through the lateral eye of Euscorpius italicus. lens, Cuticular lens. nerv.c, Retinal cells…

Galeodes
"Galeodes sp., one of the Solifugae. Ventral view to show legs and somites. I to VI, The six leg-bearing…

Galeodes
"Galeodes sp., one of the Solifugae. Ventral view with the appendages cut off at the base. I to VI,…
Galeodes
"Galeodes sp., one of the solifugae. Dorsal view. I to VI, Bases of the prosomatic appendages. o, Eyes.…
Galeodes
"Galeodes sp., one of the Solifugae. I to VI, The six prosomatic limbs cut short. o, The eyes. b, c,…
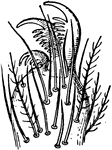
Foot of a garden spider
"Closeup of a garden spider's foot, showing the 'combs' for clinging to webs."—Finley, 1917

Garden-spider and trap-door spider
"Some spiders, like the Ctenizae, close the mouth of their subterranean resdence with a most…

Garden-spiders
"Some, of which the Common Garden Spider, Epeira diadema is an excellent example, construct…
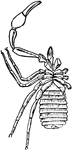
Garypus Litoralis
"Garypus litoralis, one of the Pseudoscorpiones. Ventral view. I to VI, Prosomatic appendages. o, Sterno-coxal…
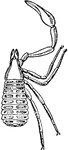
Garypus Litoralis
"Garypus litoralis, one of the Pseudoscorpiones. Dorsal view. I to VI, The prosomatic appendages. o,…
Garypus Litoralis
"Garypus litoralis, one of the Pseudoscopions. Lateral view. I to VI, Basal segments of the six prosomatic…
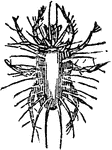
Harvest-tick
"The true ticks attach themselves parasitically to the bodies of various mammals, as sheep, oxen, dogs,…
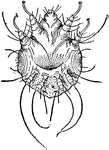
Holothyrus Nitidissimus
"Holothyrus nitidissimus, one of the Acari; ater Thorell. A, Lateral view with appendages III to VI…
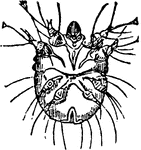
Itch Mite
The itch mite (Sarcoptes) is a genus of skin parasites, and part of the larger family of mites collectively…
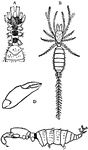
Itch-mite
"Of the true mites, the domestic or cheese mite and the itch-mite are examples." — Williams, 1889
Koenenia Mirabilis
"Koenenia Mirabilis, Grassi, one of the Palpigradi. A, Ventral view of prosoma and of anterior region…
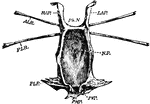
Limulus
"Ventral surface of the entosternum of Limulus polyphemus, Latr. NF, neural fossa protecting the aggregated…
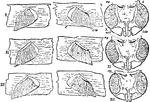
Limulus
"The remaining three pairs of mesosomatic appendages of Scorpio and Limulus. l130 indicates that there…
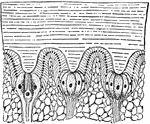
Limulus
"Section through a portion of the lateral eye of Limulus, showing three ommatidia—A, B and C.…
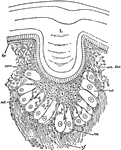
Limulus
"Section through one of the central eyes of a young Limulus. L, Cuticular or corneous lens. hy, Epidermic…
Limulus
"Transverse section of a retinula of the lateral eye of Limulus, showing ten retinula cells (ret), each…
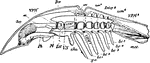
Limulus
"Diagram of a lateral view of a longitudinal section of Limulus. Suc, Suctorial pharynx. al, Alimentary…
Limulus Longispina
"Section through an early embryo of Limulus longispina, showing seven transverse divisions in the region…
Limulus Polyphemus
"Diagram of the dorsal surface of Limulus polyphemus. oc, Lateral compound eyes. oc', Central monomeniscous…
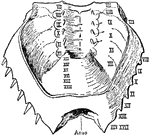
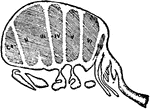
Limulus Polyphemus
"Ventral view of the posterior carapace or meso-metasomatic (opisthosomatic) fusion of Limulus polyphemus.…
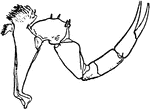
Limulus Polyphemus
"Third leg of Limulus polyphemus, showing the division of the fourth segment of the leg by a groove…
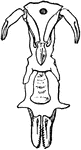
Limulus Polyphemus
"View of the ventral surface of the mid-line of the prosomatic region of Limulus polyphemus. The coxae…
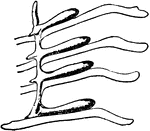
Limulus Polyphemus
"The right coxal gland of Limulus polyphemus, Latr. a2 to a5, Posterior borders of the chitinous bases…
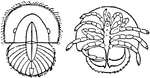
Limulus Polyphemus
"So-called "trilobite stage" of Limulus polyphemus. A, Dorsal; B, ventral view." — The Encyclopedia…
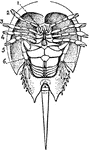
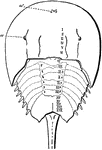
Limulus Polyphemus
"Ventral view of Limulus polyphemus. 1 to 6, The six prosomatic pairs of appendages. abd, the solid…
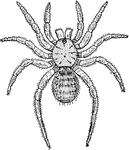
Liphistius Desultor
"Liphistius desultor, Schiodte, one of the Araneae Mesothelae. Dorsal view. I to VI, the prosomatic…