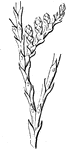The Leaf Shapes ClipArt gallery offers 310 examples of the various shapes, margins, and arrangements of leaves. For leaves of specific shrubs or trees, please see our Flowers and Shrubs selections, or our Trees gallery.
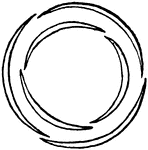
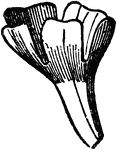
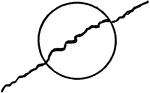
Imbricate
Overlapping as the segments of some perianths in the bud. At least one segment must be wholly outside…
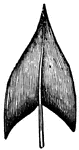
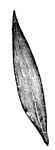
Lanceolate
Shaped like a spear head, broadest near base, tapering to apex, and several times as long as broad.
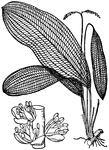
Lattice Leaf
Lattice Leaf is the popular name of a water plant, 'Aponogeton jenestralis', belonging to the order…

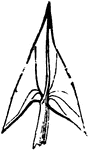
Leaf
Leaves are arranged in a great many different ways on their stems. Here are three leaves together on…

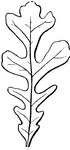
Leaf
Leaves are arranged in a great many different ways on their stems. Here the leaf-stem has three little…
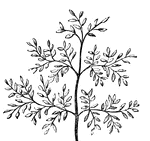
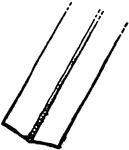
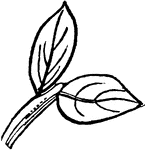
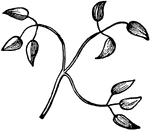
Leaf
Leaves are arranged in a great many different ways on their stems. On this leaf-stem are a great many…

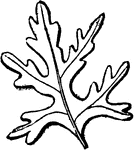
Leaf
One of the three principal parts or organs of vegetation, generally flattened in shape, and greenish…
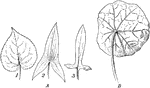
Leaf Bases
"A, Shapes of bases of leaves; B, Peltate leaf of Tropaeolum. 1, heart-shaped; 2, arrow-shaped; 3, halberd-shaped."…
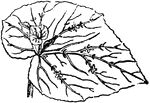
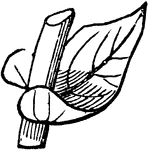
Leaf Cuttings
"Many plans may be propagated by planting their leaves or portions of their leaves as cuttings, as,…

Leaf Indentations
An illustration of a fossil of a toothed fern. Ferns are vascular plants differing from the more primitive…

Leaf Margins
"Shapes of margins of leaves. a (1), finely serrate; (2), coarsely serrate; (3), doubly serrate. b (1),…
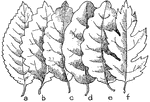
Leaf Margins
"Marginal forms of leaves: a- serrate, or saw-toothed. b- dentate, or toothed. c- crenate, or scalloped.…
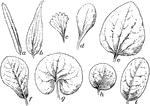
Leaf Shapes
"General outline of leaves. a, linear; b, lanceolate; c, wedge-shaped; d, spatulate; e, ovate; f, obovate;…
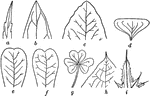
Leaf Tips
"Tips of leaves. a, acuminate or taper-pointed; b, acute; c, obtuse; d, truncate; e, retuse; f, emarginate…
Cut Leaf Veins
"Showing the effect of cutting across the veins on the removal of food from the leaf. A, all of the…
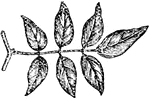
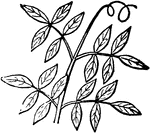
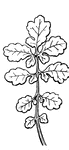
Compound Leaf
This is an example of a compound leaf. Pinnate leaves have their leaflets arranged along the sides of…
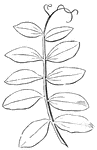
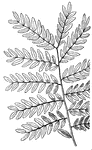
Compound Leaf
This is an example of a compound leaf. Pinnate leaves have their leaflets arranged along the sides of…
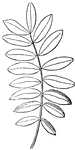
Compound Leaf
This is an example of a compound leaf. Pinnate leaves have their leaflets arranged along the sides of…
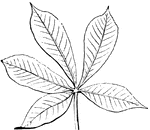
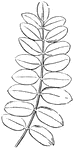
Compound Leaf
This is an example of a compound leaf. Palmate leaves have their leaflets arranged on the very end of…