This ClipArt gallery offers 209 illustrations of ancient Greek architecture.

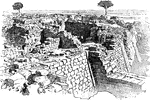
Sepulchral Heroon
"The following example of Sepulchral Heroon will give a general idea of monuments of this kind." —…
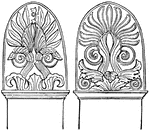
Sepulchral Stelai
"The Sepulchral Stelai were frequently ornamented with a kind of arabesque work." — Smith, 1873.

Stele-Crest
The Stele-crest is a Greek tomb-tone. It is an upright tablet that bears an inscription with decoration…
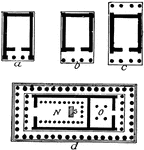
Types of Greek Temple Plans
A, in antis; B, prostyle; C, amphiprostyle; D, peripteral (The Parthenon); N, Naos; O, Opisthodomus;…

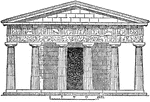
Tetrastyle
"Elevation of a Greek Ionic attached Tetrastyle in Antis." — Encyclopedia Britanica, 1893

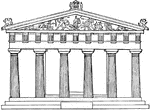
The Parthenon
The Parthenon is a temple of the Greek Goddess Athena, who was considered as the protector of the city…
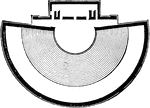
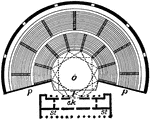
Ground Plan of the Theatre at Iassus
The theatres were originally built on a very large scale to accommodate the large number of people on…
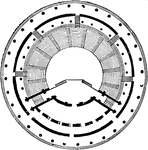
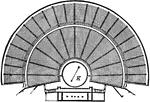
Ground Plan of the Theatre of Herodes Atticus
The Odeon of Herodes Atticus is a stone theatre structure located on the south slope of the Acropolis…
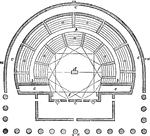
Theatrum
"Theatrum, a theatre. The Athenians before the time of Aeschylus had only a wooden scaffolding on which…

Thebes
The principal city of Baeotia, in ancient Greece, was situated in the south part of the country, onm…
Thesium restored
"The Theseum is situated on a height to the north of the Areopagus, and was built to receive the bones…

Façade Tile from the Temple of Diana at Ephesus
On the apex and two lower angles of the pediment were introduced acroteria, sometimes ornaments of flowers…

Tower of the Winds
The Tower of the Winds, also called horologion (timepiece), is an octagonal Pentelic marble clocktower…
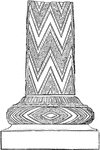
Pillar Fragment from the Treasury of Atreus
Peculiar vaulted buildings often existed in connection with the palaces for the preservation of valuables;…

Section of the Treasury of Atreus
Peculiar vaulted buildings often existed in connection with the palaces for the preservation of valuables;…
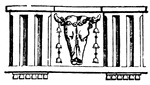
Triglyph
A triglyph is an ornament on a Doric frieze, consisting of three square projections, or parallel nicks,…

Section of a Volute of an Ionic Capital
These volutes, or scrolls, when viewed from the side, appear to meet in the middle, and form a wavy…
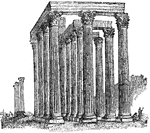
Temple of the Olympian Zeus
"Athens is said to have derrived its name from the prominence given to its worship of Athena by its…