Entablature
The Entablature ClipArt gallery provides 17 examples of entablatures, the horizontal structure of classical buildings that rests on columns and supports the pediment above. Entablatures usually consist of the architrave, the frieze, and the cornice.

Capital and Entablature from the Rock Tomb of Darius
The columns in the ruins of Persepolis are circular and slender, and have capitals and bases. The capital…
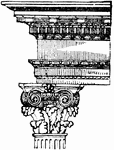
Composite Order
A mised order, combining the volutes of the Ionic order with the leaves of the Corinthian order.

Corinthian Order
One of the three orders of classical architecture. It was said to have been invented by an architect,…
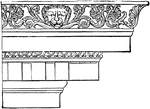
Ionic Cornice from the Temple of Minerva Polias at Priene
The entablature resting on the columns has three parts: a plain architrave divided into two, or more…

Cornice of Entablature over Doorway at the Great Temple at Philæ
An entablature refers to the superstructure of moldings and bands which lie horizontally above columns,…
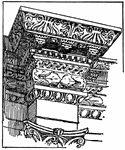
Palace of Diocletian Detail
Architectural detail from the Palace of Diocletian at Spalato, A.D. 300.
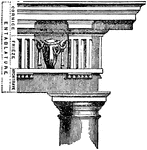
Entablanture
An entablature refers to the superstructure of moldings and bands which lie horizontally above columns,…
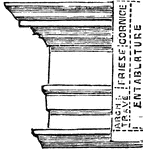
Entablature
"The horizontal portion of an order, including cornice, frieze, and architrave, which is supported by…
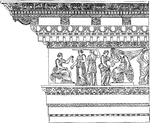
Corinthian Entablature from the Nerva at Rome
Simple styles, such as the Doric, which accorded so intimately with the whole disposition of the Grecian…
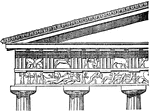
Doric Entablature
"Doric Entablature. E, entablature: a, epistyle or architrave; b, frieze; c, cornice." -Whitney, 1911

Doric Order Frieze in the Parthenon at Athens
The frieze of the Doric order is not taken up with sculpture in uninterrupted succession, but it occurs…

Roman-Doric Frieze
"A Frieze, in architecture, is that portion of the entablature which is between the architrave and the…

Friezes at Venice
In architecture the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain or—in…
Friezes at Venice
In architecture the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain or—in…
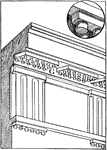
Gutta in Doric Architecture
"Guttae in Doric Architecture. A, form of gutta beneath regula; G, G, guttae beneath mutules and regulae.…
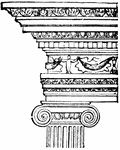
Ionic Order
One of the three orders of classical architecture. It originated in the mid-6th century BC.
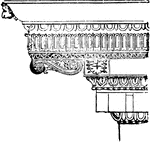
Modillion
"An ornamental bracket (a), much used in classic architecture, especially in the cornices of the Corinthian…