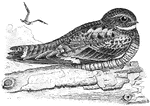
Nighthawk
Nighthawks are birds of the nightjar family in the New World subfamily Chordeilinae. They are medium-sized…
Army Worm
The Fall Army Worm (Spodoptera frugipeda) is part of the order of Lepidoptera and are the caterpillar…
![Smilax is a genus of about 300-350 species, found in the tropics and subtropics worldwide. In China for example about 80 are found (39 of which are endemic), while there are 20 in North America north of Mexico[1]. They are climbing flowering plants, many of which are woody and/or thorny, in the monocotyledon family Smilacaceae, native throughout the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. Common names include catbriers, greenbriers, prickly-ivys and smilaxes. "Sarsaparilla" (also zarzaparrilla, sarsparilla) is a name used specifically for the Jamaican S. regelii as well as a catch-all term in particular for American species. Occasionally, the non-woody species such as the Smooth Herbaceous Greenbrier (S. herbacea) are separated as genus Nemexia; they are commonly known by the rather ambiguous name "carrion flowers"](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/57000/57029/57029_smilax_mth.gif)
Smilax
Smilax is a genus of about 300-350 species, found in the tropics and subtropics worldwide. In China…

Juniper
Junipers are coniferous plants in the genus Juniperus of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending…

Vassar College from the Lake
The first institution for imparting a full collegiate education to women established in the world; founded…

Giovanni da Verrazzano
Giovanni da Verrazzano (c. 1485 – c. 1528) was an Italian explorer of North America, in the service…

Anoa
Anoa are a subgenus of buffalo comprising two species native to Indonesia: the Mountain Anoa (Bubalus…

North American Bison
The American Bison (Bison bison) is a bovine mammal, also commonly known as the American buffalo. 'Buffalo'…
Maria Pia Bridge
The Maria Pia bridge (Ponte Maria Pia) is a railway bridge built in 1877 by Gustave Eiffel in Porto,…
Forth Bridge
The Forth Bridge is a cantilever railway bridge over the Firth of Forth in the east of Scotland, to…

Dromedary
The Dromedary camel (Camelus dromedarius) is a large even-toed ungulate. It is often referred to as…

Chess Board
Chess is a recreational and competitive game played between two players. Sometimes called Western chess…
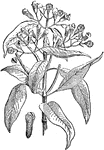
Clove Plant and Seed
Cloves (Syzygium aromaticum, syn. Eugenia aromaticum or Eugenia caryophyllata) are the aromatic dried…

Scaly Ground Dove
The scaly ground dove (Scardafella squamosa) is a species of New World doves in the Columbidae family.

Cotton
An illustration of a ripe cotton capsule after dehiscence. Dehiscence is the spontaneous opening at…

Cotton Seed
An illustration of a cotton seed. Cotton is a soft, staple fiber that grows around the seeds of the…

Cotton Plant
An illustration of a cotton plant. Cotton is a soft, staple fiber that grows around the seeds of the…
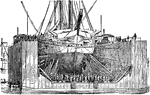
Floating-dock
A floating dock is a platform or ramp supported by pontoons. These are usually joined to the shore with…

Plover
Plovers are a widely distributed group of wading birds belonging to the subfamily Charadriinae. They…

Great Horned Owl
The American horned owls and the Old World eagle-owls make up the genus Bubo, at least as traditionally…

John Bassett Moore
John Bassett Moore (December 3, 1860 – November 12, 1947) was an American authority on international…

Eland
The common eland (Taurotragus oryx, also known as the southern eland) is a savannah and plains antelope…

Hops
The hop (Humulus) is a small genus of flowering plants, native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere.…

Madder
Madder is the common name of the plant genus Rubia, the type genus of the madder family Rubiaceae. The…

Tanner's Sumac Branch
Sumac is any one of approximately 250 species of flowering plants in the genus Rhus and related genera,…

Wildcat
The Wildcat (Felis silvestris), sometimes Wild Cat or Wild-cat, is a small felid native to Europe, the…

Death of Major Richard Waldron
On September 7, 1676, Waldron invited about 400 Indians to participate in a mock battle against the…

Eleazar Williams
A dark mystery shrouds the fate of the eldest son of Louis XVI of France and Marie Antoinette, who was…

Dormouse
Dormice are rodents of the family Gliridae. (This family is also variously called Myoxidae or Muscardinidae…

Fennel
Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) is a plant species in the genus Foeniculum (treated as the sole species…
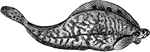
Flounder
Flounder (also; fluke) are flatfish that live in ocean waters ie., Northern Atlantic and waters along…

Moray Eel
Moray eels are large cosmopolitan eels of the family Muraenidae. There are approximately 200 species…

Gold Fish
The Goldfish, Carassius auratus, was one of the earliest fish to be domesticated, and is still one of…

Halibut
A halibut is a type of flatfish from the family of the right-eye flounders (Pleuronectidae). This name…

Mackerel
Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of fish, mostly, but not exclusively,…

Blowfish
Tetraodontidae is a family of primarily marine and estuarine fish. The family includes many familiar…

Mackerel
Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of fish, mostly, but not exclusively,…

John Winthrop
John Winthrop (12 January 1588 – 26 March 1649) led a group of English Puritans to the New World,…
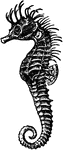
Seahorse
Seahorses are a genus (Hippocampus) of fish belonging to the family Syngnathidae, which also includes…
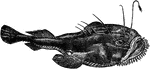
Anglerfish
Anglerfish are the members of the order Lophiiformes. They are bony fish named for their characteristic…

Stickleback
The three-spined stickleback Gasterosteus aculeatus aculeatus, common in Northern Temperate Climates…

Channel-Billed Cuckoo
The Channel-Billed Cucko (Scythrops novaehollandiae) is the largest species of cuckoo and the largest…

Juan Ponce de Leon
Juan Ponce de León (1474 – July 1521) was a Spanish conquistador. He accompanied Christopher Columbus…

Seal of Texas
The Seal of Texas. The seal has simply a star which is a common symbol of Texas, an olive branch, and…

Seal of Wyoming
The Great Seal of the State of Wyoming. The seal shows two men symbolizing livestock and mining next…

A View of Jerusalem
Jerusalem is the capital of Israel and its largest city in both population and area. Located in the…

Roanoke Island
Roanoke Island was the site of the 16th century Roanoke Colony, the first English colony in the New…

Orca
The Orca or Killer Whale (Orcinus orca), less commonly, Blackfish or Seawolf, is the largest species…

Gudgeon
Gudgeon is a common name for a number of small freshwater fishes of the families Cyprinidae, Eleotridae…

Polygonal Masonry
Polygonal masonry is a technique of stone construction of the ancient Mediterranean world. True polygonal…
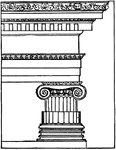
Greek Ionic Order
The Ionic order column originated in the mid-6th century BC in Ionia. The Ionic order column was being…

Greek Ionic Order (Side View)
The Ionic order column originated in the mid-6th century BC in Ionia. The Ionic order column was being…
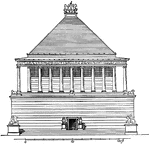
Mausoleum at Halicarnassus
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus was a tomb built between 353 and 350 BC at Halicarnassus (present Bodrum,…
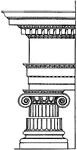
Roman Ionic Order
The Ionic order column originated in the mid-6th century BC in Ionia. The Ionic order column was being…

Viper
An illustration of an atheris burtoni, a species of viper. These snakes are found all over the world,…

Discovery of Santo Domingo
Bartholomew Columbus, brother of Christopher Columbus, founded the Santo Domingo and named it after…

New York Waterthrush
The New York Waterthrush (Seiurus naevius) is a passerine bird of the New World warblers.
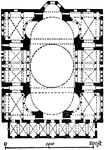
Plan of Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia is a former patriarchal basilica, later a mosque, now a museum in Istanbul, Turkey. Famous…

Section of Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia is a former patriarchal basilica, later a mosque, now a museum in Istanbul, Turkey. Famous…