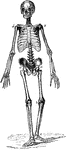
Overhand Swimming
"The overhead movement enables the swimmer to throw himself forward on the water, and to move his arms…
Side-Stroke Swimming
"An improvement on the foregoing for long distances is the known as the side stroke. In this method,…

Large Beetle
"Under surface of large beetle, with deeply concave and comparatively small wings, shows that the nervures…
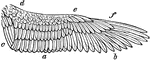
Right Wing of Kestrel
"Right wing of the Kestrel, drawn from the specimen, while being held against the light."—Pettigrew,…

Northern Lapwing
"The Lapwing with one wing fully extended, and forming a long lever; the other being in a flexed condition…

Dragonfly
An insect characterized by large multifaceted eyes, two pairs of strong transparent wings, and an elongated…

The Pigeon
"The Pigeon flying downwards and turning prior to alighting. The pigeon expands its tail both in ascending…
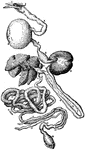
Fowl Digestion
The digestive system of a fowl. 1 is the tongue, 3 is the crop, 6 is the gizzard, 10 is the small intestine,…
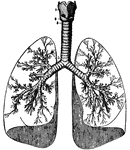
Human Lungs
Human lungs. 1 and 2 make up the larynx, or voice box. 1 is thyroid cartilage, 2 is cricoid cartilage.…
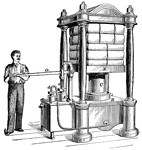
Hydraulic Press
A hydraulic press which uses a hydraulic cylinder to generate force. The inventor of the device, Joseph…
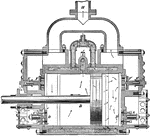
Air Compressor
An air compressor. They come in many forms, most commonly in cylinder form - as shown. This image shows…
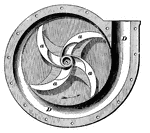
Centrifugal Pump
This image is a centrifugal pump with one half of the casing removed. S is a hollow hub, a is a curved…
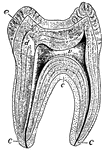
Human Tooth
A sectional view of a human molar. The roots, or fangs, are shown covered by a layer of bone called…
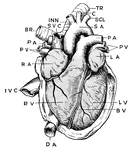
Anatomy of Heart
A complex anatomical view of the heart. RA is the right atrium, or auricle, which receives the deoxygenated…
Striated Muscle
Striped, or striated, muscle which quickly contracts causing the alternating black and white lines.…
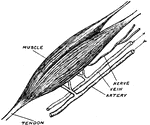
Bicep Muscle
The upper bicep of the right arm. Included are the tendons, blood vessels, and its nerve.
Nerve Cell
A simple nerve cell, or neuron. N is the nucleus of the cell, NC is the cytoplasm, D are dendrites which…
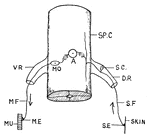
Reflex Action
Illustration of the reflex action of an animal. SE is the sensory nerve-ending. A stimulus passes through…
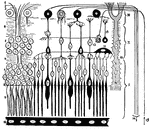
Eye Retina
Diagram of the retina, aka percipient layer of the eye. 1: inner limiting membrane, which is next to…
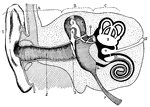
Human Ear
A diagram of the human ear. It is divided into the outer ear - A, middle ear - B, and inner ear - C.…
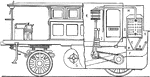
Hancock Coaches
A Hancock Coach cross-sectioned in order to display the engine and driving connections. (A) is the exhaust…
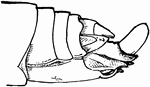
Locust Anatomy
Enlarged end of the female, showing oviposition: the oviduct, the egg guide, and the egg issuing from…
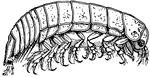
Limnoria Lignorum (Flabellifera)
Flabellifera are a tribe of isopods. Their bodies end in a tail fan, made by the last pair of appendages…
Nerve Ganglia (Spinal)
Nerve Ganglia, or Knots (sing. Ganglion; Knot) occur as collections of nerve cells on the course of…
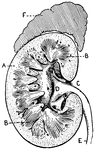
Section of Human Kidney
This illustration shows a section of a human kidney (A, Cortical substance; B, Pyramids; C, Hilum; D,…
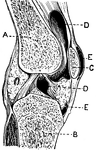
Section of the Knee
This illustration shows a section on the knee (A, Femur; B, Tibia; C, Patella; D, Synovial sac; E, bursæ).…
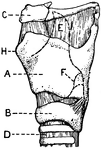
Lateral Aspect of Larynx
This illustration shows a lateral aspect of the larynx and its multiple parts (A. Thyroid Cartilage;…
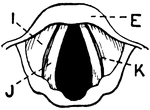
Vertical Section of Larynx
This illustration shows a vertical section of the larynx and its many parts (A. Thyroid Cartilage; B.…
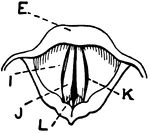
Vocal Cords Seen from above During Quiet Breathing
This illustration shows the vocal cords, seen from above during quiet breathing (A. Thyroid Cartilage;…
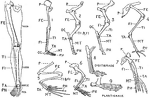
Human Leg (Front View), and Comparative Diagrams showing Modifications of the Leg
This illustration shows a human leg (front view), and comparative diagrams showing modifications of…
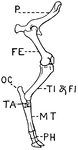
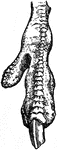
Leg of Ox
This illustration shows the leg of an Ox. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA. Tarsus, MT.…
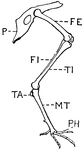
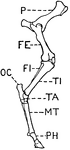
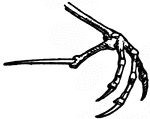
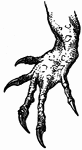
Leg of Bird
This illustration shows the leg of a bird. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA. Tarsus,…
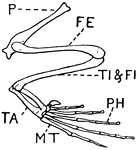
Leg of Frog
This illustration shows the leg of a frog. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA. Tarsus,…
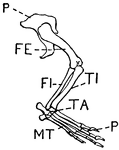
Leg of Crocodile
This illustration shows the leg of a crocodile. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA. Tarsus,…
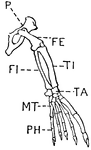
Leg of Seal
This illustration shows the leg of a seal. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA. Tarsus,…
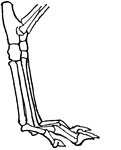
Leg of Dog
This illustration shows the leg of a dog. This leg is digitigrade. Animals with digitigrade legs walk…
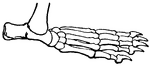
Leg of Bear
This illustration shows the plantigrade leg of a bear. Plantigrade means that the animal walks flat…

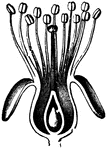
Common Mushroom
Common mushroom (agaricus campestris). A, young fructification on mycelium, in section; b, c, later…
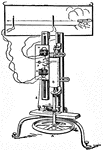
Bashforth Chronograph
Bashforth Chronograph. A, flywheel turning cylinder B on which the record is marked; C, toothed wheel…