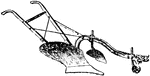
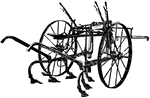
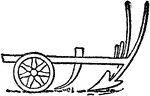
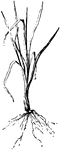Manure Spreader
A manure spreader in operation. The manure was pitched from the stable to the spreader, handled only…

Buckwheat field
A farmer standing waist-deep in a field of buckwheat on land that was plowed early and well fitted.

Buckwheat field
Farmer standing in a sparse and stunted field of buckwheat, which was on land that was plowed late.

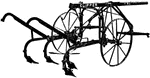
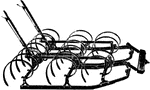
Check-Row Corn-Planter
A check-row corn-planter, which plants two rows at once and rows the corn both ways.

Pasture with Trees
White pines coming into a pasture. On this land trees pay better than the poor pasture.

Grove of black-locust trees
A grove of black-locust trees. Contrast with the brush in the background on an adjoining farm.

Side View of Farmhouse
Scattered planting of trees pruned in artificial shapes in front of a farmhouse.

Farmhouse
A well-planted farmyard, with trees at the sides, flowers in the corners and about the house, and an…

City House
A city house in the country. A low house would be better suited to sitting alone on a hill.

Battle-ground
This view is taken from near the house of Mr. Neilson, looking northwest. In the foreground, on the…

Liberty Hall
Liberty Hall. Some time after the death of Governor Livingston this property was purchased by Lord Blingbroke,…

Dining-Hall
"The dining-hall, or room with seven doors. In the December number of the New York Mirror for 1834,…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Moore's House
"This is a view from the lawn, looking south. It is a frame building with a brick foundation. At the…

stockade
"A stockade. Those settlers who lived outside of Roston and the few seaport villages built palisades…
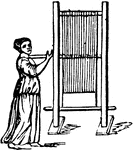
Tela
"Tela, a loom. Although weaving was among the Greeks and Romans a distinct trade, carried on by a separate…
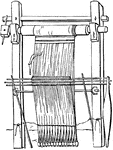
Tela
"Tela, a loom. Although weaving was among the Greeks and Romans a distinct trade, carried on by a separate…

Triangular coop
"This triangular shape is a good one also for a movable poultry-house in its simplest form." —…

Triangular coop
"This triangular shape is a good one also for a movable poultry-house in its simplest form." —…