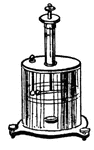
Coulomb’s torsion balance
Coulomb's torsion balance is in the shape of a cylinder with the pan inside.
Smooth Caterpillar
The body is cylinder and divided by rings into thirteen segments. The smooth caterpillars don't have…

Hairy Caterpillar
Caterpillars are an insect that is cylinder and is divided by rings into 13 segments. The hairy caterpillar…
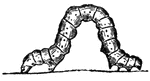
Spanner Caterpillar
Caterpillars are insects that are cylinder and are divided by rings into 13 segments. The spanner caterpillar…
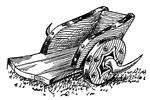
Roman Military Chariot
A vehicle used for pleasure and war by the early Assyrians, Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans. The vehicle…

Interior View of Fort Beauregard
Fort Beauregard, at Bay Point, on the point opposite Fort Walker, was built of sand and palmetto logs…

Fort Hatteras
View of the camp of the twentieth Indiana Regiment; also of Fort Hatteras and the anchorage at Hatteras…

General John Sedgewick
While directing the placing of some pieces of artillery in position in front of Spottslyvania Courthouse…
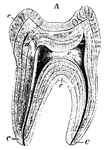
Human Tooth
A tooth is generally described as possessing a crown, neck, and root. Side view of a tooth.
Human Tooth
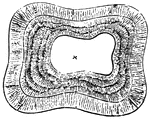
A tooth is generally described as possessing a crown, neck, and root. Top view of a tooth.; 1. Central…
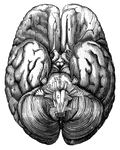
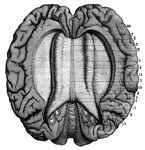
Human Brain
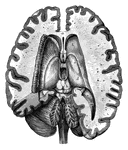
A top view of a dissection of the human brain showing the lateral fourth and fifth ventricles.

Sixth Regiment
"Gallant charge of the Sixth Regiment, United States Regular Cavalry, upon the Confederate Stuart's…

77th Pennsylvania Regiment
"Captain Muller's Battery Company of the Seventy-seventh Pennsylvania Regiment making fascines and gabions…

George Custer
"General George A. Custer, born in New Rumley, Harrison County, Ohio, December 5th, 1839, died in Montana,…

First naval battle
"First naval battle in Hampton Roads between the Confederate iron-plated steamers Merrimac, Yorktown,…

Fort Hatteras
"General view of Forts Hatters and Clark, N. C., captured on the 29th of August, 1861, by the Federal…

Seventy-ninth Regiment
"Taking away the colors of the Seventy-ninth New York Regiment for insubordination and mutiny, Washington,…

View of Grafton
"View of Grafton, West Virginia, occupied by the Federal Troops, under the command of General McClellan,…

Battle of Gaines's Mill
"Battle of Gaines's Mill, Friday, June 27th, 1862. At eleven o'clock each division, brigade, regiment…
Occupation of Norfolk
"Occupation of Norfolk, VA., by the Federal troops- view of the city- Federal vessels at anchor." —Leslie,…
Federal Fleet
"Panoramic view of the Federal fleet passing the forts of the Mississippi, on its way to New Orleans,…

Camp of Ninth Massachusetts
"Camp of the Ninth Massachusetts Regiment in the woods, one mile from the Confederate fortifications,…

Mortar Practice - Rear View
"Mortar practice- rear view of 13-inch mortar, with its usual complement of seven gunners. The mortar…

Fort Thompson
"View of New Berne, N. C., from the interior of Fort Thompson after its capture by the Federal forces-…

Battle of Secessionville
"Battle of Secessionville, James Island, S. C.- bayonet charge of Federal troops, commanded by General…

Battle of Cedar Mountain
"Battle of Cedar Mountain, fought Saturday, August 9th, 1862, between the Federal troops commanded by…

Pulaski Monument
"Review of Confederate troops on their march to Virginia, in front of the Pulaski Monument, Monument…

Battle of Cross Keys
"Battle of Cross Keys, Sunday June 8th, 1862- centre and front of the Federal army in the engagement.…

Commencement of Bull Run
"The Confederate forces under General Jackson advancing upon the Rapphannock Station at the river. Federal…

Landing at Parkersburg
"Landing of Federal troops at Parkersburg, Western Virginia. Parkersburg, Va., in 1861 was a thriving…

Frederick City
"General McClellan and the Federal troops passing through Frederick City, Md., in pursuit of the Confederate…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Fort Runyon
"Section of Fort Runyon, Va., guarding the road to Alexandria, occupied by the Twenty-first Regiment,…

View of Strasburg
"View of the town of Strasburg, valley of the Shenandoah, occupied by the Federal forces under General…