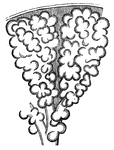
Bronchioles
This diagram shows the bronchial tubes, with clusters of cells. The bronchioles are the first airway…

Raphides
This is an illustration of raphides, or acicular crystals, from the stalk of the Rhubarb: three of the…
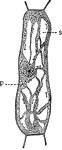
Protoplasm
The circulation of protoplasm (p) in a cell of the stamen-hair of Tradescania. In the channels the granules…
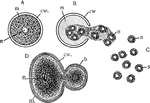
Cell Reproduction
Modes of cell reproduction. A, B, and C, stages in the reproduction of the Infusorian, Colpoda, by the…
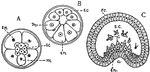
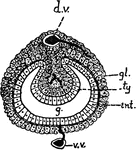
Mesoderm
"Modes of forming mesoderm. A and B, special mesoblasts distinguishable early in egmentation (annelid):…
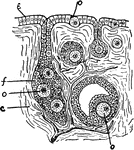
Ovary
"Section through ovary of a young Mammal. The eggs (o) are seen to be formed from the epithelium. c,…
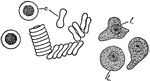
Blood Corpuscles
"Blood corpuscles (human). c, colored; l, leucocytes. The red cells tend to collect in rows with the…
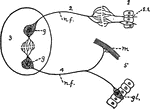
Nervous System
"Scheme showing the essential relations of the parts of a nervous system: 1, the sensory end organ (epithelial);…
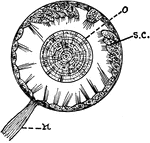
Otocyst
"Otocyst in a mollusk. n, nerve; ;o, otolith; s.c., sensory cells in wall of otocyst." — Galloway
Hydra
"Nettling cells of Hydra. A, unexploded; B, exploded; b, barbs; c, the nettling cell in which the nettling…
Earthworm
"Transverse section of the intestine of the Earthworm. ty, typhlosole, an infolded longitudinal ridge…
Nerve Cells
"Nervous tissue is either gray, which is a mass of tailed cells suppoted by a fine connective tissue."…

Non-Striated Muscle
"Non-striped spindle-shaped cells which branch and join with one another." — Richardson, 1906
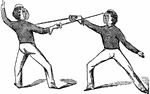
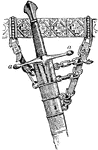
Carte
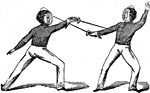
"Carte, Guard. Turn wrist with nails upwards; hand on a line with lower part of breast; arm somewhat…
Tierce
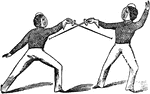
"Tierce, Guard. As in carte, the nails and wrist being somewhat more downward, and the arm stretched…
Seconde
"Seconde, Parade. Nails and wrist downward, hand opposed outward, and blade, pointing low, should form…

Prime
"Prime, Parade. In using prime to parry the thrust in seconde, pass your point over the adversary's…
Quinte
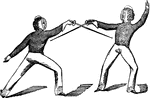
"Quinte, Parade. Wrist in high carte, sword-point low, and oppose adversary from the forte of the outside…

Pinus Sylvestris
"Radial longitudinal section of wood of Pinus Sylvestris. a, cambium; b, c, d, e, f, wood cells; f,…

Bamboo
"Section of Bamboo, showing an angular network of cells, and the round apertures of pitted vessels."…
Pondweed Leaf
"Vertical section of the leaf of Potamogeton or Pondweed, showing air cavities or lecunae l, and parenehymatous…
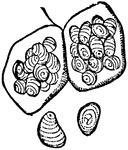
Starch Cells
"a, Starch cells of the Pea, showing grains of starch in the interior. b, Seperate starch grains, with…
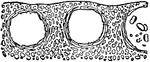
Orange Rind
"Vertical section of part of the rind of the Orange, showing glands containing volatile oil, R, R, R,…
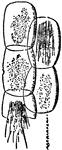
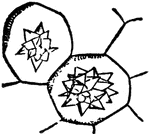
Rumex
"Cells of Rumex c, containing raphides r. The cells are called Raphidian. The raphides are acicular…
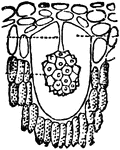
Urostigma Elasticum
"Cellular tissue from leaf of Urostigma elasticum. c, a large cell; r, cystolith, an agglomeration of…

Epidermis
"Vertical section of epidermis, from the lower surface of the leaf of Madder, showing the intimate union…
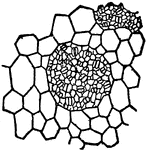
Saxifraga Sarmentosa
"Epidermis of leaf of Saxifraga Sarmentosa, showing clusters of stomata s, surrounded by large epidermal…
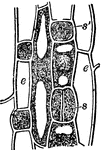
Hyacinth
"Formation of stomata from leaf of Hyacinth, seen from the surface. e, epidermis cells; s', mother-cell…
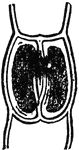
Sachs
"Splitting of partition wall between guard-cells to form the stoma (Sachs.)" — Encyclopedia Britanica,…
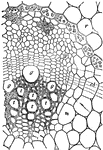
Cambium
"Transverse section of an open fibro-vascular bundle. c, cambium; cb, continuation of cambium between…
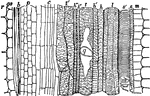
Fibro-vascular Bundle
"Longitudinal section of an open fibro-vascular bundle. c, cambium; s, spiral vessels with fibers which…
Fibro-vascular Bundle
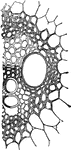
"Transverse section of a closed fibro-vascular bundle. r, annular vessel; s, spiral vessel; I, inter-cellular…
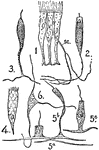
Tentacles
"1, Portion of epithelium from the tentacle of an Actinian, showing three supporting cells and one sense…

Connective Tissue
"Presently in the production of ordinay connective tissue, fibers of two kinds make their appearance…
Connective Tissue
"Presently in the production of ordinay connective tissue, fibers of two kinds make their appearance…

Epiderm Cels
"Epidermo-muscular cells of Hydra m, muscular-fiber processes." — Encyclopedia Britannica, 1893
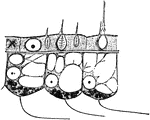
Body-wall
"Portion of the body-wall of Hydra, showing ectoderm cells above, separated by "structureless lamelia"…

Endoderm Cell
"Vacnolated endoderm cells of eartilaginous consistence from the axis of the tentacle of a Medusa (Cunina)."…
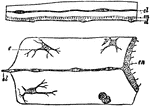
Medusae
"Portions of sections through the disc of medusae. The upper one of Lizzia, the lower of Aurelia. el,…
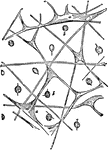
Aurelia
"Gelatinous substance of the disc of Aurelia, showing-a, fibrous trabeculae, and b, wandering endoderm…
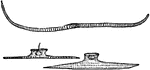
Muscular Cells
"Muscular cells of medusae (Lizzia). The uppermost is a purely muscular cell from the sub-umbrella;…
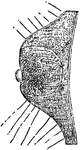
Ocellus
"Ocellus of a medusa (Lizzia Koellikeri). oc, pigmented ectodermal cells; l, lens." — Encyclopedia…
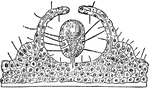
Trachomedusae
"Simple tentaculocyst of one of the Trachomedusae (Rhopalonema velatum). The process carrying the otolith…

Carmarina
"Carmarina (Geryonia) hastata, one of the Trachomedusae. a, nerve-ring; a', radial nerve; b, tentaculocyst;…
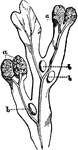
Fucus Vesiculosus
"Fucus vesiculosus: showing the receptacles of the fructification a, a, at the ends of the branching…
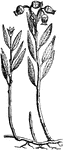
Andromeda
"A genus of Andromeda polifolia of plants of the natural order Ericaceae, distinguished by a 5-valve…

Cloves
"Cloves are the flower-buds of the Clove-tree. The genus to which this tree belongs is of the natural…

Cress
"A name given to many plants, of which the foliage has a pungent, mustard-like taste, and is used as…
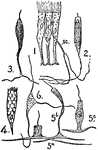
Epithelium
"Portion of epithelium from the tentacle of an Actinian, showing three supporting cells and one sense…
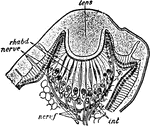
Euscorpius Italicus
"Section through the lateral eye of Euscorpius italicus. lens, Cuticular lens. nerv.c, Retinal cells…
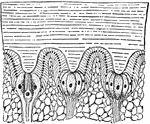
Limulus
"Section through a portion of the lateral eye of Limulus, showing three ommatidia—A, B and C.…
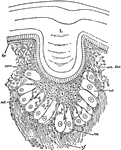
Limulus
"Section through one of the central eyes of a young Limulus. L, Cuticular or corneous lens. hy, Epidermic…
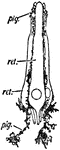
Retinula
"Diagram of a retinula of the central eye of a scorpion consisting of five retina-cells (ret), with…
Limulus
"Transverse section of a retinula of the lateral eye of Limulus, showing ten retinula cells (ret), each…
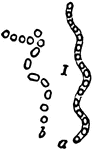
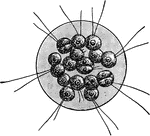
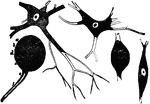
Spirillum
"Spirillum containing many spores (a), which are liberated at b by the breaking up of the parent cells."…
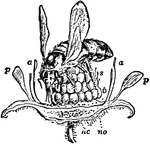
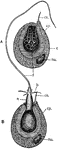
Raspberry Fertilization
"Raspberry (Rubus idaeus, order Rosaceae), being fertilized. A, Flower. p, p, Petals. a, a, Anthers.…