Nelson's Ferry
"View at Nelson's Ferry, the spot here portrayed, was an important locality during the Revolution. It…

Frederica
"Ruins of Oglethorpe's Barracks at Frederica. This is from a sketch made by W. W. Hazzard, Esq., in…

Turtle Bay
"View at Turtle Bay. Turtle Bay is a small rock-bound cove of the East River, at the foot of Forty-seventh…

Woodhull's Grave
"Woodhull's Grave. Nathaniel Woodhull was born at Mastic, Long Island, December 30, 1722. Agriculture…

Chatterton's Hill
"Chatterton's Hill, from the rail-way station. This is a view of the southeastern side of Chatterton's…

Fort Washington
"View at Fort Washington. This is a view from the site of the interior works at Fort Washington from…

Death of Becket
"Death of Becket. During the early years of the reign Thomas A. Becket, as the king's chancellor, had…
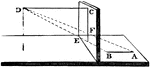
Accidental Point
"That point in which a right line drawn from the eye parallel to another given right line cuts the picture…
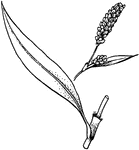
Polygonum
Stems with a sheath just above attachment point of leaf; flowers individually small, white to pink.
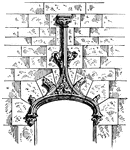
Accolade
"An ornament composed of two ogee curves meeting in the middle, each concave toward its outer extremity…

George III, King of England
"George III (1760-1815). The first two Hanoverian kings were ignorant of English politics and obliged…
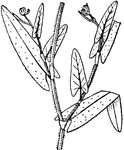
Polygonum
Sheaths around stem above each point of leaf-attachment; flowers white to red, not fragrant.
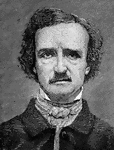
Edgar Allan Poe
"Edgar Allan Poe, the son of a Baltimore gentleman and an actress, Elizabeth Arnold, was born in Boston,…

George B. McClellan
"George Brinton McClellan was born at Philadelphia, December 3, 1826. He was for two years a student…

George Armstrong Custer
"George Armstrong Custer, a brilliant cavalry officer, was born at New Rumley, Ohio, December 5, 1839.…

Anamorphosis
"A method of drawing which gives a distorted image of the object represented when it is viewed from…
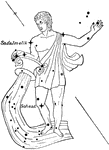
Aquarius
"A zodiacal constellation, supposed to represnt a man standing with his left hand extended upward, and…
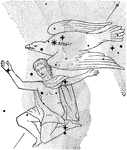
Aquila
"A northern constellation situated in the Milky Way, nearly south of Lyra, and containing the bright…
Filipino Bolo
"A Bolo is a short, broad, lance-shaped weapon; used by the Filiinos in their operations against the…

Filipino Bolo Sheath
"A Bolo is a short, broad, lance-shaped weapon; used by the Filiinos in their operations against the…

Underside of a starfish
"The organs of motion are similar, consisting of a multitude of small feet called ambulacra,…

Common brittle-star
Among the several species of Brittle-Star found in the British seas is the Common Brittle-Star, Ophicoma…

Five-fingered jack
"In this family the arms appear to be merely prolongations of the disc; they are suaully five in number,…

Common European sea-star
"The colors in this are variable but brilliant - red, purple, green, and white. It measures from nine…
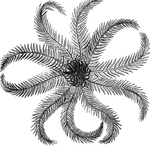
Rosy feather-star
"The body is flattened and covered with several cacareous plates; the lower, or entral surface, bears…
!["The largest diamond ever found in Brazil weighed 254 and a half carats, and was discovered in 1853 by a [African-American] in the river Bogageno; it is known as the "Star of the South." It was sold to the Gaekwar of Baroda for $450,000."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/15100/15121/starsouth_15121_mth.gif)
Star of the South Diamond
"The largest diamond ever found in Brazil weighed 254 and a half carats, and was discovered in 1853…

The Great Mogul Diamond
"Another important diamond is the one at the point of the scepter of the Russian empire, known as the…
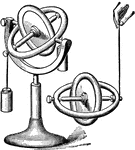
Gyroscope
"The Gyroscope is an instrument constructed by M. Foucault to make the rotation of the earth visible.…

Heron
"Heron is the common name of birds of the genus Ardea. The herons are distinguished by having a long…
Bedouin Lance Heads
"The Lance is a weapon consisting of a long shaft with a sharp point, much used, particularly before…
Bedouin Lance Heads
"The Lance is a weapon consisting of a long shaft with a sharp point, much used, particularly before…
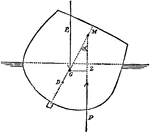
Metacenter
"The Metacenter is the point of intersection of the vertical line passing through the center of gravity…
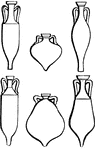
Amphorae
"A vessel used for holding wine, oil, honey. The following cut represents amphorae in the British Museum.…
!["Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the Atlantic coasts. The body is more or less star shaped, and consists of a central portion, or disk, surrounded by five or more lobes, or arms, radiating from the body and containing prolongations of the viscera. The mouth is situated in the center of the lower surface of the body, and the anus is either absent or on the upper surface. Locomotion is effected by means of peculiar tube-like processes, which are protruded from the under surface of the arms. They possess in a high degree the power of reproducing lost members and abound in all seas. [Pictured] Lesser Sand-star (Ophiura albida)"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16200/16266/starfish1_16266_mth.gif)
Lesser Sand-Star Starfish
"Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the…
!["Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the Atlantic coasts. The body is more or less star shaped, and consists of a central portion, or disk, surrounded by five or more lobes, or arms, radiating from the body and containing prolongations of the viscera. The mouth is situated in the center of the lower surface of the body, and the anus is either absent or on the upper surface. Locomotion is effected by means of peculiar tube-like processes, which are protruded from the under surface of the arms. They possess in a high degree the power of reproducing lost members and abound in all seas. [Pictured]Common Starfish, reproducing rays"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16200/16277/starfish2_16277_mth.gif)
Common Starfish
"Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the…
!["Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the Atlantic coasts. The body is more or less star shaped, and consists of a central portion, or disk, surrounded by five or more lobes, or arms, radiating from the body and containing prolongations of the viscera. The mouth is situated in the center of the lower surface of the body, and the anus is either absent or on the upper surface. Locomotion is effected by means of peculiar tube-like processes, which are protruded from the under surface of the arms. They possess in a high degree the power of reproducing lost members and abound in all seas. [Pictured]Common Starfish (Asterias rubens)"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16200/16278/starfish3_16278_mth.gif)
Common Starfish
"Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the…
!["Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the Atlantic coasts. The body is more or less star shaped, and consists of a central portion, or disk, surrounded by five or more lobes, or arms, radiating from the body and containing prolongations of the viscera. The mouth is situated in the center of the lower surface of the body, and the anus is either absent or on the upper surface. Locomotion is effected by means of peculiar tube-like processes, which are protruded from the under surface of the arms. They possess in a high degree the power of reproducing lost members and abound in all seas. [Pictured]Eyed Cribella (Cribella oculata)"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16200/16280/starfish4_16280_mth.gif)
Eyed Cribella Starfish
"Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the…
!["Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the Atlantic coasts. The body is more or less star shaped, and consists of a central portion, or disk, surrounded by five or more lobes, or arms, radiating from the body and containing prolongations of the viscera. The mouth is situated in the center of the lower surface of the body, and the anus is either absent or on the upper surface. Locomotion is effected by means of peculiar tube-like processes, which are protruded from the under surface of the arms. They possess in a high degree the power of reproducing lost members and abound in all seas. [Pictured]Gibbous Starlet (Asterina gibbosa)"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16200/16282/starfish5_16282_mth.gif)
Lesser Sand-star Starfish
"Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the…
Revolving Ring
"This game is played something like lawn billiards, except that there are six revolving rings instead…
Whizzer
"Get a circular piece of tin, three inches or more in diameter, and cut it round the edges in the form…

Spine Tailed Chimney Swift
A well known black chimney swift of the United States. So called because the shafts of the tail feathers…

Stilus
"Stilus or Stylus conveys the general idea of an object tapering like an architectural column. It signifies:…
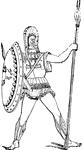
Greek soldier
"The early Greeks used a very short sword, as may be seen from the preceding cut. The ancient Homeric…

Thyrsus
"Thyrsus, a pole carried by Bacchus, and by Satyrs, Maenades, and others who engaged in Bacchic festivities…
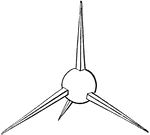
Tribulus
"Tribulus, a caltrop, also called murex. When a place was beset with troops, the one party endeavoured…

Head of a thyrsus
"Shows the head of a thyrsus composed of the leaves and berries of the ivy, and surrounded by acanthus…

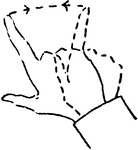
Hand signal
"To change elevation, indicate the amount of increase or decrease by fingers; point upward to indicate…
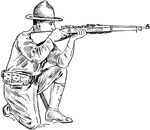
Aim kneeling
"In aiming kneeling, the left elbow rests on the left knee, point of elbow i nfront of kneecap." —…

Bayonet Guard
"At the second command sake the position of guard; at the same time throw the rifle smartly to the front,…

Butt Strike
"Straighten right arm and right leg vigorously and swing butt of rifle against point of attack, pivoting…