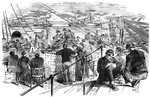
Banks Expedition
"The Banks Expedition- scene on the hurricane deck of the United States transport North Star-…
!["A detachment of the First South Carolina [African American] Federal Volunteers, under command of Colonel Beard, in the United States transport steamer <em>Darlington</em>, picking off Confederate sharpshooters concealed in the trees on the banks of the Sapelo River, Ga."— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/11600/11647/aa-volunteer_11647_mth.gif)
African American Volunteers
"A detachment of the First South Carolina [African American] Federal Volunteers, under command of Colonel…

Pontoon Bridge
"The Pontoon bridge 'On The March'- the pontoon wagons on their way from Aquia Creek to the Rappahannock.…

Confederate Batteries
"Fredericksburg, Va., and the Confederate batteries and pickets, as seen from Falmouth Heights, headquarters…

Confederate Invasion
"The Confederate invasion of Maryland and Pennsylvania. The Confederate cavalry crossing the Potomac,…

Rear Admiral James Alden
"Rear Admiral Alden, born in Portland, Me., March 31st, 1810, died in San Francisco, Cal., February…

Banks Expedition
"The Banks Expedition- scene on the levee, Baton Rouge, La. Contrabands unloading military stores from…

Fort Walker
"View from the interior of Fort Walker, Hilton Head, S. C. looking inland, showing the defenses from…

Northern Armies
"The enthusiasm of the Northern armies- re-enlistment of the Seventeenth Army Corps. Financial tests…

Battle of Spottsylvania
"The war in Virginia. Battle of Spottsylvania Courthouse- opening of the fight at Alsop's Farm, May…

Hooker's Battle
"The war in Tennessee. Hooker's Battle above the clouds, and capture of the Confederate position on…

Fort Stevens
"The operations near Washington, scene of the fight in front of Fort Stevens, July 12th-13th, 1864.…

General Benjamin Harrison
"General Harrison, twenty-third President of the United States, was born at North Bend, Ohio, August…

Bummers
"Sherman's 'Bummers' foraging in South Carolina. Our artist sent us with this sketch of 'Bummers Foraging'…
!["The war in Virginia. The Twenty-second [African American] Regiment, Duncan's Brigade, carrying the first line of Confederate works before Petersburg. On the morning of the 15th of June, 1864, General Hinks formed his command in line of battle, and advanced upon the Confederates, with Duncan commanding his right and Holman his left. The result of this charge was waited for with great anxiety. The majority of the whites expected that the [African American] troops would run, but the sable forces astonished everybody by their achievements. With a wild yell that must have struck terror into the hearts of their foes, the Twenty-second and Fifth United States [African American] regiments, commanded by Colonels Kidder and Connor, charged, under a hot fire of musketry and artillery, over the Confederate ditch and parapet, and drove the enemy before them, capturing a large field-piece, and taking entire possession of their works, its defenders, Ferrybee's Fourth North Carolina Cavalry, and Graham's Petersburg Battery, seeking safety in rapid flight, leaving their dead and wounded in the works."— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/11700/11799/duncan-brig_11799_mth.gif)
Duncan's Brigade
"The war in Virginia. The Twenty-second [African American] Regiment, Duncan's Brigade, carrying the…

Campaign in Georgia
"The campaign in Georgia. A baggage train crossing the mountains in a storm. General Sherman, after…

Daughters of Maryland
"How the Daughters of Maryland received the Sons of the North as they marched against the Confederate…
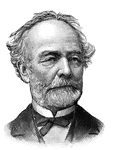
General Joseph E. Johnston
"General Johnston, born in Cherry Grove, near Farmville, Va., February 3rd, 1807; died at Washington,…
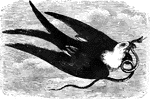
Fork-Tailed Kite
"The fork-tailed kite, (N. furcatus) is twenty-five inches long; the wings and tail black;…

Red-Shouldered Hawk
Also known as the winter falcon, is found in California, Wisconsin, and South Carolina.

Goshawk
"The American goshawk &mdash the black-cap haw of Wilson &mdash A. atricapillus which has been…

King Vulture
Genus sarcoramphus, a large vulture found in the tropical regions of the Americas, sometimes…

Turkey Buzzards
Genus Cathartes, found in the Americas, sometimes as far north as New England. These buzzards…

Great Carolina Wren
The great Carolina wren, known for its ability to imitate various other songbirds.

Fort Walker
"Landing of United States troops at Fort Walker, after the bombardment, November 7th, 1861. In order…

Red-Wing Thrush
The red-wing thrush migrates from the north to the south of Europe in the winter, feeding on worms and…

Common Snowbird
Found as far north as Greenland, the common-snow bird migrates as far south as Virginia in the winter.

Shore Lark
Found in the north of Europe and Asia, specimens of the shore-lark have been ound as far south as France…

Great spotted cuckoo
The great spotted cuckoo divides its time between North Africa and Southern Europe, laying its eggs…

South Carolina flag
"Rattlesnake Flag of South Carolina, during independence of the states."—E. Benjamin Andrews,…

Civil War Banner in South Carolina
"Street banner in Charleston, before the Civil War began."—E. Benjamin Andrews 1895

Battleground near Fort Anne
Battleground near Fort Anne. This sketch was taken from the rail-road, looking north. The forest upon…

Sholes's Landing
View from Shole's Landing. This is a view from Chipman's Point, or Sholes's Landing, looking north.…

Carolina Parrot
The Carolina parrot is native to Guiana, but can be found as far north as Virginia. They often travel…

Point Levi
View of Point Levi from Durham Terrace, Quebec. This sketch is taken from Durham Terrace, near the north…

Cape Diamond
Cape Diamond, this is a view of the spot where Montgomery was killed. The cliff is Cape Diamond, crowned…

Arnold Wounded
Place where Arnold was wounded. This view is in a narrow alley near the north end of Sault au Matelot…

Canada Grouse
Also known as the spotted or spruce grouse, the Canada grouse is found in the northerly latitudes of…
Andelusian Quail
Also known as the hemipode, the Andelusian quail is found in Spain, North Africa, and Sicily.

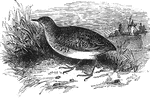
Common American Carolina Rail
Also known as the Carolina rail, soree rail, and the English rail, the common American rail is found…

European Snipe
Ranging as far north as Scandanavia, Iceland, and Greenland in the summer, the European snipe migrates…

Curlew Sandpipers
Averaging about eight inches in length, the curlew sandpiper can be found in Northern Europe, Asia,…
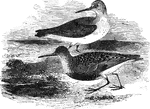
Dunlin
Also known as the purre, stint, ox-bird, and the sea-snipe, the dunlin is found throughout Europe and…

American Bittern
Measuring approximately twenty-six inches in length, the American bittern is a nocturnal hunter. It…

Mallard Ducks
The mallard, also known as the common wild duck averages about twenty-four inches in length. It inhabits…

American Widgeon
The American widgeon (or baldpate) averages about nineteen inches in length. It is common in North America,…

Eider Ducks
The eider duck is found throughout the northern regions of Europe and North America. The female lines…

King Duck
Found in the Arctic regions of Europe, Asia, and North America, the king duck strongly resembles the…

Velvet Scoter
Common in Europe and North America, the velvet scoter is also known as the white-winged coot.

American Scaup Duck
The American scaup duck is common in North America, accidental in Europe. It is also known as the creek…

Harlequin Duck
"The harlequin duck is a very beautiful but small species, fourteen inches lng; fond of the eddying…

Hooded Merganser
Measuring about nineteen inches long, the hooded merganser is common in North America, its head adorned…

Goosander
Found in both Europe and North America, the goosander is also known as the buff-breasted sheldrake,…

Sclavonian Grebe
Also known as the horned grebe, dipper, water-witch, and hell-diver, the sclavonian grebe is common…

Black cormorant
The black cormorant averages about three feet in length, and is found in Greenland, as well as a long…

Wind-Mill Point
Wind-mill Point. This view was sketched from the steam-boat, when a little below the wind-mill, looking…