Two Men Talking
Two men in renaissance clothing having a conversation on the side of the road. The man to the left is…
Swinging Sign
A swinging sign of the 18th century placed on buildings of business, especially taverns.

Road Machine
"Road-machine. a, telescopic axle for rear wheels; b, scraper delivering spoil between rear wheels;…

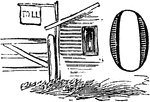
Wrought-Iron Bracket
The wrought-iron bracket is a German Renaissance style sign. It is richly decorated with chasing and…

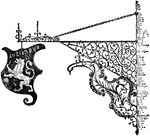
Wrought-Iron Bracket
This wrought-iron bracket is a modern style sign. It is designed with scrolling and curls.
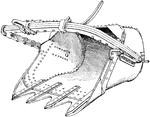
Shovel Bucket
"In railroad construction and canal- or road-work, a large scooping bucket armed with teeth and used…

Street of Tombs at Pompeii
"For tombs of smaller dimensions various forms and abnormal decorations were employed. An ornamented…

Sir Thomas More
Sir Thomas More (7 February 1478 – 6 July 1535) was an English lawyer, author, and statesman who…
Caucasus
Cross-section of the Caucasus along the Grusinian military road. Dark beds are lava streams.
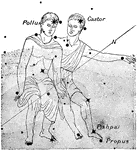
Gemini
"A zodiacal constellation, giving its name to a sign of the zodiac, lying east of Taurus, on the other…

Simeon Taking the Child in His Arms
"Then took he him up in his arms, and blessed God, and said, Lord, now lettest thou thy servant depart…

Saul Struck to the Earth on His Way to Damascus
"And as he journeyed, he came near Damascus: and suddenly there shined round about him a light from…

Skating on Thin Ice
"Presumption often ventures quite too near, where danger should awaken wholesome fear" —Northdrop,…
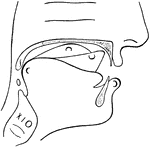
Physiological Bases of the Visible Speech Symbols for Consonants
Physiological Bases of the Visible Speech Symbols - Consonants. In representing the consonant a peculiar…
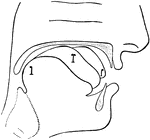
Physiological Bases of the Visible Speech Symbols for Vowels
Physiological Bases of the Visible Speech Symbols - Vowels. In representing the vowel classification…

Code of English Sounds
Chart illustrating 45 hand positions representing sounds in the English language as described in the…

Non-Vocal Primary Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Primary Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Primary Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
Non-Vocal Primary Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
Non-Vocal Mixed Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
Non-Vocal Mixed Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Divided Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Divided Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Divided Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
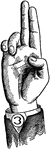
Non-Vocal Divided Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed-Divided Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed-Divided Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed-Divided Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed-Divided Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Shut Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Shut Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Shut Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Shut Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Nasal Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Nasal Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Nasal Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
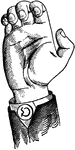
Non-Vocal Nasal Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Primary Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Primary Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Primary Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
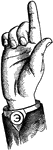
Vocalized Primary Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
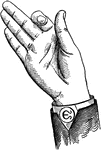
Vocalized Mixed Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
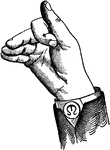
Vocalized Mixed Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Mixed Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Mixed Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
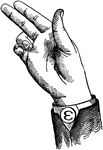
Vocalized Divided Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Divided Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…