
Egyptian Free-Tailed Bat
The Egyptian Free-Tailed Bat (Tadarida aegyptiaca) is a species of bat in the Molossidae family of free-tailed…
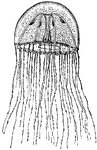
Medusa of a Hydroid
Colonial, plant-like animals closely related to jellyfish, with stinging cells, Any member of the invertebrate…
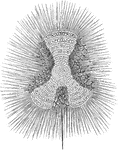
Euchitonia
"A pelagic family of radioflagellate infusorians, typified by the genus Euchitonia. The animalcules…
!["A pipe of this nature fitted with a piece of glass so as to exhibit the reed (which is a "free reed") is shown in [the illustration]. Q is the wind-chest of the bellows, into which P is fitted. In the right-hand figure the upper part of the pope is removed, so as to show the reed more clearly. A plate of metal c c, has a slit but in it, in which the tongue I may just past. By means of a curved wire, r, projecting above the top of the pipe, and the play of the tongue may be controlled and the pipe tuned. The conical pipe, H, placed at the top, serves to increase the power of the sound". -Benson, 1891](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/62100/62146/62146_reed_mth.gif)
Reed
"A pipe of this nature fitted with a piece of glass so as to exhibit the reed (which is a "free reed")…
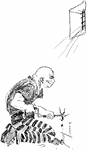
Prisoner Drilling Hole
An illustration of a prisoner drilling a hole in the wall of his prison cell.

Ancient Houses in Strasburg
Strasburg, originally known as Strateburguen in the sixth century, on the first partition of the Frankish…

Simonswald
Archaeological artifacts show that Simonswald was home to farmers as early as 6000 to 3000 BC. Roman…

The Prater
The Wiener Prater is a large public park in Vienna's 2nd district Leopoldstadt. Prater is derived from…

Peter Delivered from Prison by an Angel
"And, behold, the angel of the Lord came upon him, and a light shined in the prison: and he smote Peter…

Normal Aperture Back Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Back Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Back Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Back Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Back Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Back Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Mixed Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Mixed Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Mixed Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Mixed Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Mixed Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Front Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Front Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Front Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Front Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Front Primary Wide Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Front Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Back Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Back Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Back Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Back Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Back Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Back Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Mixed Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Mixed Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Mixed Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Mixed Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Mixed Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Mixed Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Front Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Front Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Front Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
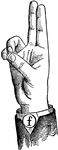
Round Front Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Front Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Front Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
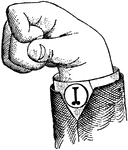
Normal Aperture Mixed Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

John Brown
John Brown (1800 – 1859) was an American abolitionist who advocated and practiced armed insurrection…

Robinson's House in Battle of Bull Run
The Robinson House belonged to a free African American during the First Battle of Bull Run. The house…
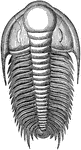
Paradoxides Harlani
Paradoxides was a genus of relatively large trilobites, extinct marine arthropods, that form the class…
Vorticella
The Bell Animalcule (Vorticella) (fig 10) in certain respects resembles the Slipper Animalcule. It is…
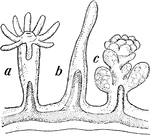
Hydroid Jellyfish
Hydroids, related to the jellyfish, have three basic life-cycle stages: a tiny free-swimming planula…
Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…
Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…

Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…
Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…
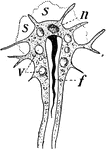
Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…

Bust of Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius, known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and General. He was an important…

Bust of Commodus
Lucius Aurelius Commodus Antoninus (31 August 161 – 31 December 192) was a Roman Emperor who ruled…
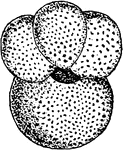
Globigerina
"Globigerina bulloides. GLOBIGERINIDAE. A family of chiefly pelagic foraminiferous rhizopods, with the…
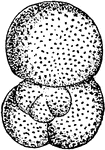
Globigerina
"Globigerina bulloides. GLOBIGERINIDAE. A family of chiefly pelagic foraminiferous rhizopods, with the…
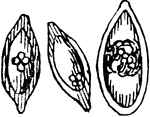
Gregarina
"Gregarina, free pseudo-navicellae. GREGARINIDAE. A family or other major group of endoplastic protozoans,…