
Burnside Expedition
"Burnside Expedition- the fleet and transports off Hatteras during the storm- the general giving orders.…

Battle of Cedar Mountain
"Gordon's and Crawford's Brigades driving the Confederate forces from the woods at the Battle of Cedar…

Siege of Island
"Siege of Island No. 10, on the Mississippi River- night bombardment by the Federal mortar boats, ten…

Battle of Cedar Mountain
"The Confederate batteries shelling the Federal position on the night of the Battle of Cedar Mountain,…

Battle of Winchester
"Battle of Winchester, VA., March 23rd, 1862- decisive bayonet charge of the Federal troops, led by…

Ulric Dahlgren
"Colonel Ulric Dahlgren, born in Bucks County, Pa., in 1842, died near King and Queen's Courthouse,…

Attack at Harrisonburg
"Gallant attack by 150 of the Pennsylvania Bucktails, led by Colonel Kane, upon a portion of General…

Second Naval Battle
"Second naval battle in Hampton Roads- fight between the Federal ironclad Monitor, of two guns,…

Fort Hatteras
"General view of Forts Hatters and Clark, N. C., captured on the 29th of August, 1861, by the Federal…

Battle at Potomac
"Engagement between the Federal troops and the Confederates on the Virginia side of the Potomac, opposite…

Battle of Pea Ridge
"Battle of Pea Ridge, Ark., fought March 6th, 7th and 8th, 1862, between the Federal forces, 13,000…

First Minnesota Regiment
"Fort built around the officer's quarters of the First Minnesota Regiment, Colonel Sully, near Fair…

Red Lemur
"This lemur is noted for its brillant colorings, the greater part of the body being covered with a vivid…
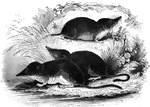
Shrews
"Is about the size of a rat.. Their legs are of equal length, and terminate into five toes, which are…

Pougonie
"P. typus, is of a yellowish brown, marked with three ranges of obscure spots on the back.;…

Cryptoprocta Ferox
"The only species, C. ferox, is but fifteen inches long, but its strength is great. Its disposition…

Battle of Charles City
"Battle of Charles City Road- charge of the Jersey Brigade- the first New Jersey brigade, General Tayler,…

Zouaves
"Encampment of Colonel Ellsworth's New York Fire Zuoaves, on the heights opposite the Navy Yard, Washington,…

View of Grafton
"View of Grafton, West Virginia, occupied by the Federal Troops, under the command of General McClellan,…

Battle of Gaines's Mill
"Battle of Gaines's Mill, Friday, June 27th, 1862. At eleven o'clock each division, brigade, regiment…
Occupation of Norfolk
"Occupation of Norfolk, VA., by the Federal troops- view of the city- Federal vessels at anchor." —Leslie,…
Federal Fleet
"Panoramic view of the Federal fleet passing the forts of the Mississippi, on its way to New Orleans,…

Strasburg Woods
"In the Shenandoah Valley- General Fremont's division marching through the woods to attack the Confederates.…

Mortar Practice - Rear View
"Mortar practice- rear view of 13-inch mortar, with its usual complement of seven gunners. The mortar…

Blue Ridge Pass
"The victory at Blue Ridge Pass, Sunday, September 14th, 1862- infantry charge, and rout of the Confederates.…

Fort Thompson
"View of New Berne, N. C., from the interior of Fort Thompson after its capture by the Federal forces-…

Battle of Secessionville
"Battle of Secessionville, James Island, S. C.- bayonet charge of Federal troops, commanded by General…

Police Headquarters
"Interior of the outbuilding attached to Marshal Kane's Police Headquarters, Holliday Street, Baltimore-…

Battle of Savages Station
"Battle of Savages Station. Brigadier General Smith's division hotly engaged with the enemy, at noon,…

Battle of Cedar Mountain
"Battle of Cedar Mountain, fought Saturday, August 9th, 1862, between the Federal troops commanded by…

Commencement of Bull Run
"The Confederate forces under General Jackson advancing upon the Rapphannock Station at the river. Federal…

Landing at Parkersburg
"Landing of Federal troops at Parkersburg, Western Virginia. Parkersburg, Va., in 1861 was a thriving…

Frederick City
"General McClellan and the Federal troops passing through Frederick City, Md., in pursuit of the Confederate…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Fort Runyon
"Section of Fort Runyon, Va., guarding the road to Alexandria, occupied by the Twenty-first Regiment,…

Bombardment of Fort Henry
"Bombardment of Fort Henry, Tennessee River, Tenn., by the Mississippi Flotilla, Flag Officer Foote,…

Monitor
"Loss of the Monitor- gallant attempt of the officers and crew of the United States steamer…

View of Strasburg
"View of the town of Strasburg, valley of the Shenandoah, occupied by the Federal forces under General…

Battle of Munfordville
"Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the Confederates charging through the abatis…

Conrad's Ferry
"Conrad's Ferry, Md., above Harrison's Island, on the Potomac River, the place of passage of Colonel…
Kingfish
"King mackeral is also called kingfish. It is distinguished from other mackeral by weught, by its bluer…

Mullet
"Mullet, known as Florida's "money fish" are caught in large quantities in Florida, particularly along…

Bird's Point
"View of the fortifications erected by the Federal troops at Bird's Point, MO., opposite Cairo, Ill."—…

Army of the Potomac
"Advance of the Army of the Potomac. Occupation of Winchester, VA., and the abandoned Confederate Fortifications,…

Fort Thompson
"Bombardment and capture of Fort Thompson, thirteen guns, near New Berne, on the Neuse River, by the…

Columbus, Kentucky
"General view of Columbus, Ky., and its fortications, looking down the river, showing the 'Iron Bluffs'…

Paducah, Kentucky
"View of the town of Paducah, Ky., at the confluence of the rivers Ohio and Tennessee, the Northern…

The Forlorn Hope
"'The Forlorn Hope.' Volunteers storming party, consisting of portions of the Seventh Michigan and Nineteenth…

Confederate Schooner
"Bird's-eye view of the burning of a Confederate schooner in Quantico or Dumfries Creek, Potomac River,…









