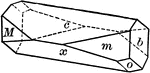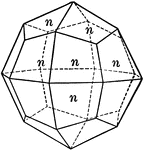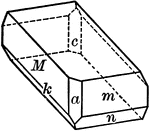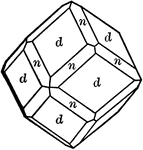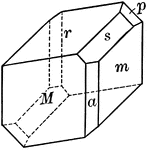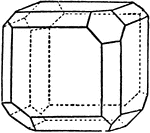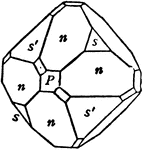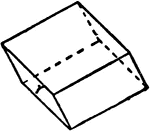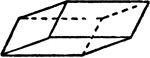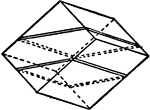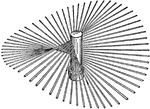
Albite
"Triclinic. Twinning very common, according to the albite law and evidenced by fine striation lines…
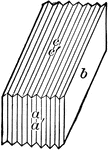
Amphibole
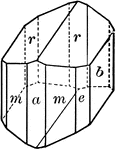
"Monoclinic. Crystals prismatic in habit; the prism faces make angles of 55 and 125 degrees with each…
Amphibole
"Monoclinic. Crystals prismatic in habit; the prism faces make angles of 55 and 125 degrees with each…
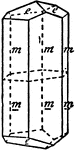
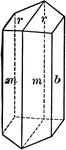
Beryl
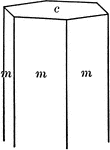
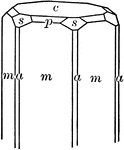
"Hexagonal. Strong prismatic habit. Frequently vertically striated and grooved. Forms usually present…
Beryl
"Hexagonal. Strong prismatic habit. Frequently vertically striated and grooved. Forms usually present…
Wernerite
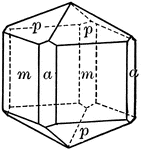
"Tetragonal; tripyramidal. Crystals usually prismatic. Prominent forms are prisms of the first and second…
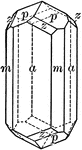
Wernerite
"Tetragonal; tripyramidal. Crystals usually prismatic. Prominent forms are prisms of the first and second…
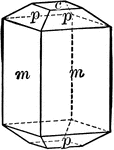
Vesuvianite
"Tetragonal. Prismatic in habit. Often vertically striated. Common forms are prisms of first and second…
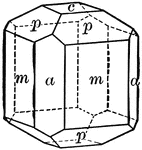
Vesuvianite
"Tetragonal. Prismatic in habit. Often vertically striated. Common forms are prisms of first and second…
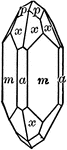
Zircon
"Tetragonal. Crystals usually show a simple combination of prism and pyramid of the first order. The…
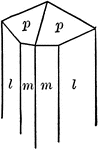
Topaz
"Orthohombic. In prismatic crystals terminated by pyramids, domes, and basal plane." — Ford, 1912
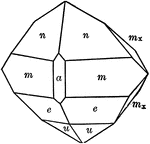
Datolite
"Monoclinic. Habit varied. Crystals usually nearly equidimensional in the three axial directions and…
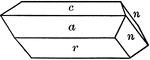
Epidote
"Monoclinic. Crystals are often much elongated parallel to the ortho-axis with a prominent development…
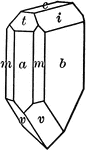
Calamine
"Orthohombic, hemimorphic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to the brachypinacoid. They show prism…
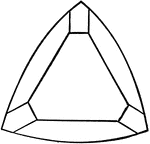
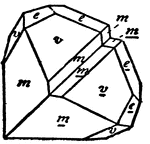
Tourmaline
"Hexagonal-rhombohedral; hemimorphic. Crystals usually prismatic, vertically striated. A triangular…
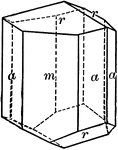
Tourmaline
"Hexagonal-rhombohedral; hemimorphic. Crystals usually prismatic, vertically striated. A triangular…
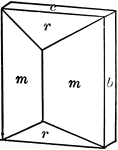
Staurolite
"Orthohombic. Habit prismatic, showing usually a combination of prism with large angle, brachypinacoid,…
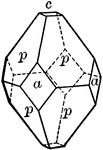
Apophyllite
"Tetragonal. Usually shows a combination of prism of second order, pyramid of first and basal plane."…
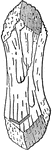
Stilbite
"Monoclinic. Uniform in cruciform twins. Commonly tabular parallel to clinopinacoid. Crystals usually…
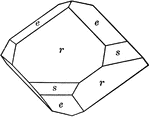
Chabazite
"Hexagonal-rhombohedral. Common form is the simple rhombohedron, r, having nearly cubic angles. May…
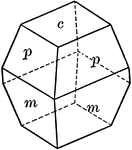
Titanite
"Monoclinic. Crystals varied in habit. Often with prominent basal plane which is steeply inclined and…
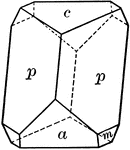
Titanite
"Monoclinic. Crystals varied in habit. Often with prominent basal plane which is steeply inclined and…
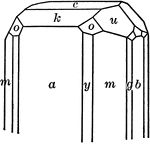
Columbite
"Orthohombic. Habit of crystals is short prismatic; often in square prisms because of prominent development…
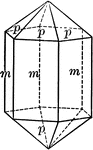
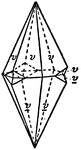
Apatite
"Hexagonal; tri-pyramidal. Crystals usually long prismatic in habit; sometimes short prismatic or tabular.…
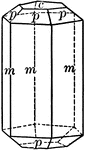
Apatite
"Hexagonal; tri-pyramidal. Crystals usually long prismatic in habit; sometimes short prismatic or tabular.…
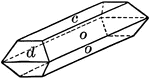
Barite
"Orthohombic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to base; often diamond shaped because of the presence…
Barite
"Orthohombic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to base; often diamond shaped because of the presence…
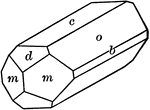
Celestite
"Orthorhombic. Crystals resemble closely those of barite. Commonly tabular parallel to the base or prismatic…
Gypsum
"Monoclinic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to clinopinacoid; in diamond-shaped crystals with edges…
Gypsum
"Monoclinic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to clinopinacoid; in diamond-shaped crystals with edges…
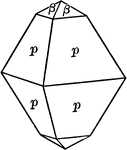
Scheelite
"Tetragonal; tri-pyramidal. Crystals usually simple pyramids of first order. Closely resemble isometric…
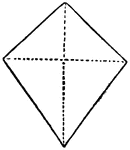
Deltoid
"A four-sided figure, formed of 2 unequal isosceles triangles on different sides of a common base."…
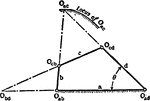
Centrodes
Aronhold stated if any three bodies have plane motion their three virtual centers are three points on…