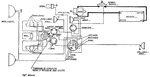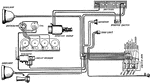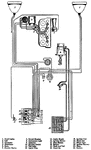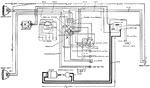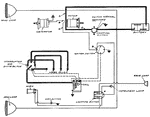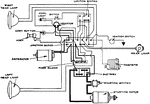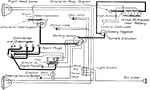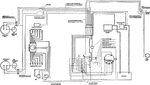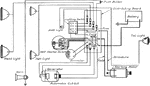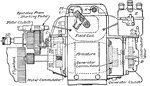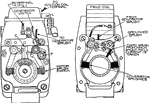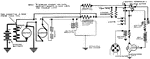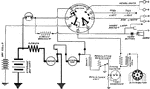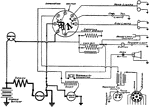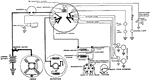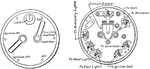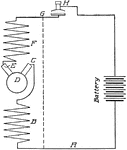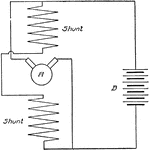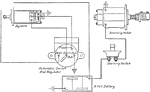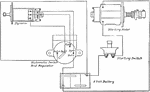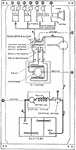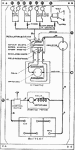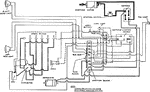
Apperson
Wiring diagram showing Remy ignition and Bijur starting and lighting systems on 6-16, 8-16, 6-17 and…
Nervous System
"Scheme showing the essential relations of the parts of a nervous system: 1, the sensory end organ (epithelial);…

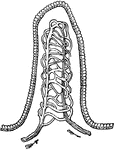
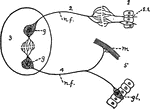
Aplysia Nervous System
"Nervous System of the Aplysia, a Gasteropodous Mollusc: c, cerebral ganglia; g, thoracle or sub-aesophageal…
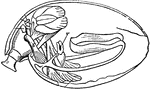
Muscular System
"Diagram showing the muscular system. M, ventral, N, dorsal valve; l, loop; V, mouth; Z, extremity of…
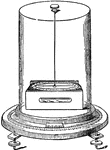
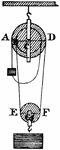
Astatic Multiplier
"The coil is of flat, rectangular shape, with a narrow central opening just large enough to allow one…
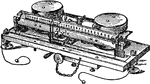
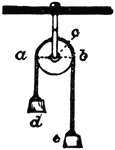
Lord Kelvin's Ampere Balance
"When a current is passed through the instrument it causes one end of the movable system to tilt downwards,…
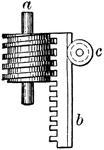
Rack and Worm Gears
A gear system with a rack gear and worm gear. Used to conovert circular motion to rectilinear motion.
Rack and Pinion Gears
A gear system with a rack gear and small pinion gear. Used to conovert circular motion to rectilinear…
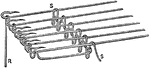
Hosiery
"In the year 1589 the stocking-frame, the machine which mechanically produces the looped stitch in hosiery,…
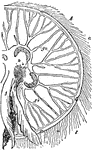
Aurelia Aurita
"Half of the lower surface of Aurelia aurita. The transparent tissues allow the enteric cavities and…
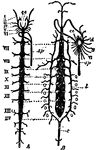
Aurelia Aurita
"Tentaculocyst and marginal lappets of Aurelia aurita. In the lefthand figure-ML, marginal lappets;…
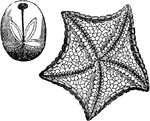
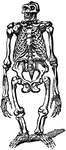
Echinodermata
"A class of radiate animals, the highest in organisation of the great division of the animal kingdom.…
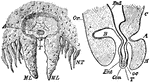
Limulus
"Ventral surface of the entosternum of Limulus polyphemus, Latr. NF, neural fossa protecting the aggregated…
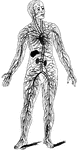
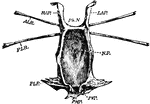
Arterial System
"Diagram of the arterial system of A, Scorpio, and B, Limulus. The Roman numerals indicate the body…

Galeodes
"Galeodes sp., one of the Solifugae. Ventral view with the appendages cut off at the base. I to VI,…

Bee Ovaries
"Ovaries of Queen and Workers (Apis). A, Abdomen of queen, under side. P, Petiole. o, o, Ovaries. hs,…
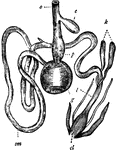
Fowl Digestive System
"Digestive system of the common Fowl. o, Gullet; c, Crop; p, Proventriculus; g, Gizzard; sm, Small intestine;…
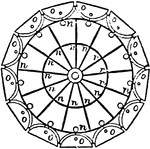
Revolving Light
"In order to produce, on the catoptric system, a fixed light showing all round the circle, a number…
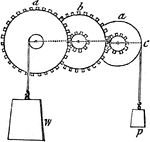
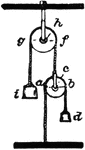
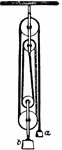
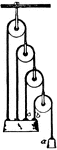
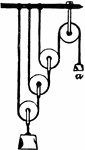
System of Wheels
"System of Wheels.—As the wheel and axle is only a modification of the simple lever, so a system…
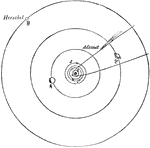
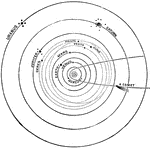
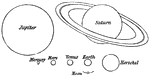
Planet Distance
"Relative distance of the Planets. Having now given a short account of each planet composing the solar…
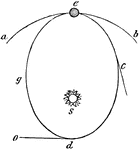
Planet Motion
"Elliptical Orbits.—It has been supposed that the Sun's attraction, which constitutes the Earth's…
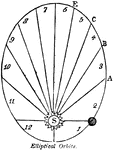
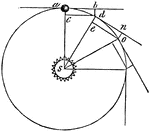
Elliptical Orbit
"The elliptical circle being supposed to be the Earth's orbit, with the Sun, S, in one of the foci.…