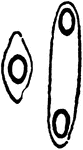
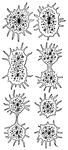Sphaerozoum Ovodimare
"A genus compound radiolarians, typical of the family Sphaerozoidae, the protoplasm of which contains…
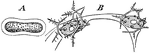
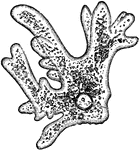
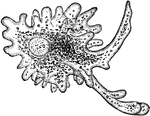
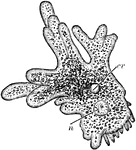
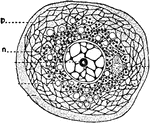
Sphærozoum Punctatum
"A. natural size; B. two of the sacs with colored vesicles and spicules which lie in the investing protoplasm,…
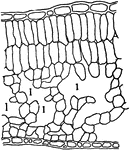
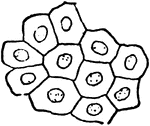
Apple Leaf
A magnified portion of an apple leaf. It shows many small sacks grown together. Each of these sacks…
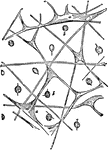
Aurelia
"Gelatinous substance of the disc of Aurelia, showing-a, fibrous trabeculae, and b, wandering endoderm…

Bamboo
"Section of Bamboo, showing an angular network of cells, and the round apertures of pitted vessels."…

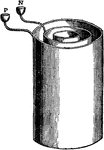
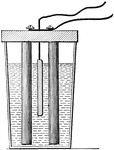
Battery
"The term battery is applied either to a single jar, or cell, containing the generating materials, or…
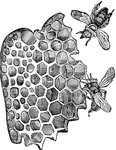
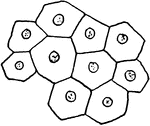
Cells of Honey Bees
"The hexagonal cells for the honey are build upon precisely that mathematical angle which affords the…
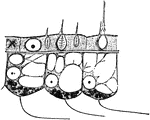
Body-wall
"Portion of the body-wall of Hydra, showing ectoderm cells above, separated by "structureless lamelia"…
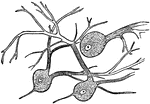
Nerve Cells of the Brain
"Wherever nerve cells are abundant, the nerve tissue has a gray color; in other places, it looks white.…
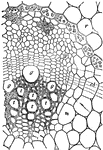
Cambium
"Transverse section of an open fibro-vascular bundle. c, cambium; cb, continuation of cambium between…
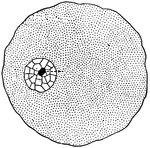
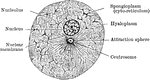
Cell
"In a general what we may describe a cell as a tiny mass of jelly in which floats another still smaller…
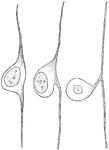
Development of Cell from Spinal Ganglion
Three stages in the development of a cell from a spinal ganglion.
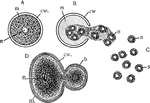
Cell Reproduction
Modes of cell reproduction. A, B, and C, stages in the reproduction of the Infusorian, Colpoda, by the…
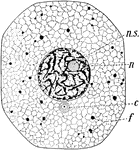
Typical amimal cell
A typical cell consists of two portions, one, te firmer, forming an excessively delicate meshwork enclosing…
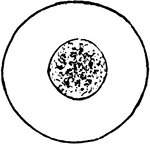
Blood cell
Blood cell function is to transport nutrients and oxygen to the cells; wastes and carbon dioxide to…
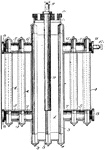
Electrolytic Cell
A cell containing an electrolyte in which an applied voltage causes a reaction to occur that would not…

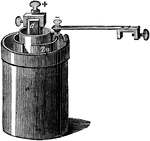
Grove Cell
An illustration of Bussen's cell.The Grove cell was an early electric primary cell named after its inventor,…
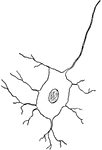
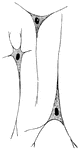
Nerve Cell
Animal nerve cells are specialized cells called neurons. Figure 1C is a nerve cell with parts of its…

Voltaic cell
"Just as a head of water supplies a hydraulic pressure that causes the liquid to flow through a pipe…
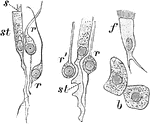
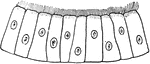
Cells from the Olfactory Region of a Rabbit
Cells from the olfactory region of the rabbit. Labels: st, supporting cells; r, r', varieties of rod-cells;…

Reproduction of Cells
Successive stages of mitosis or karyokinesis. A, B, C, D, and E illustrate the phenomena of the prophase;…
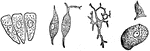
Various forms of cells
"A, columnar cells found lining various parts of the intestines (called columnar epthelium);…
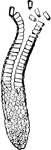
Columnar Epithelium
"In the stomach, intestines and elsewhere the epithelial cell is obling in profile and is called columnar…

Cytolysis, Stage 4
"Ehrlich's diagrams illustrating the mechanism of immunity and cytolysis. The figures in black…

Daniel Cell
"Daniel gravity cell, 'crowfoot' pattern. this is a two fluid cell in which gravity instead of a prous…

Daniel Cell
The first two-fluid cell was incented by Daniell, and English electrician in 1836..." -Atkinson 1903

Diblastula
"Diagram of a Diblastula. a, orifice of invagination (blastopore); b, archenteric cavity; c, endoderm;…
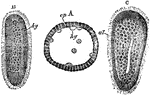
Diblastula
"Formation of the Diblastula of Eucope (one of the Calyptoblastic Hydromedusae) by delamination. A,…

Edison Cell
"Edison cell, type RR. The electrolyte used is caustic soda, the positive element zinc, and the negative…

Edison-Lalande Cell
"...is constructed with a plate of black oxide of copper suspended between two plates of zinc, and the…

Endoderm Cell
"Vacnolated endoderm cells of eartilaginous consistence from the axis of the tentacle of a Medusa (Cunina)."…

Epiderm Cels
"Epidermo-muscular cells of Hydra m, muscular-fiber processes." — Encyclopedia Britannica, 1893

Epidermis
"Vertical section of epidermis, from the lower surface of the leaf of Madder, showing the intimate union…

Various kinds of epithelial cells
"A, columnar cells of intestine; B, polyhedral cells of the conjuctiva; C, ciliated conical cells of…