Clipart tagged: ‘Cells’

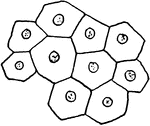
Sphaerozoum Ovodimare
"A genus compound radiolarians, typical of the family Sphaerozoidae, the protoplasm of which contains…
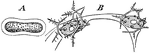
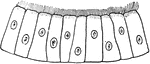
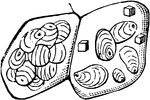
Sphærozoum Punctatum
"A. natural size; B. two of the sacs with colored vesicles and spicules which lie in the investing protoplasm,…
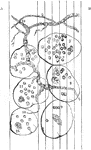
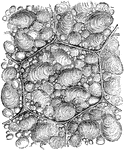
Microscopic view of a fermented apple
"Portions of the rotting pulp were placed on a microscopic slide, divided into hundredths and thousandths…
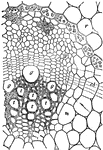
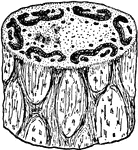
Cambium
"Transverse section of an open fibro-vascular bundle. c, cambium; cb, continuation of cambium between…
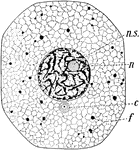
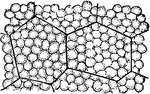
Typical amimal cell
A typical cell consists of two portions, one, te firmer, forming an excessively delicate meshwork enclosing…
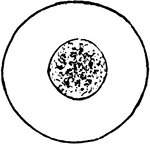
Blood cell
Blood cell function is to transport nutrients and oxygen to the cells; wastes and carbon dioxide to…
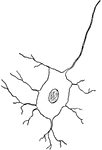
Nerve Cell
Animal nerve cells are specialized cells called neurons. Figure 1C is a nerve cell with parts of its…
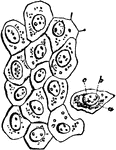
Cells from the Abdominal Lining
Flat cells from the surface of the lining membrane of the abdomen (peritoneum). Labels: a, cell-body;…
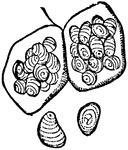
Starch Cells
"a, Starch cells of the Pea, showing grains of starch in the interior. b, Seperate starch grains, with…
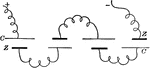
Series Connection
"When several cells are conected so that the positive plate of one is joined to the negative plate of…
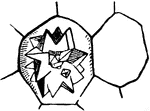
Formation of the Embryos
Figures to illustrate the earlier stages in the formation of an embryo; a single mass of protoplasm…
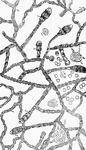
Stages of fungus growth
This illustration "represents its mycelium growth; 2,2 its budding cells, which terminate in fruit cells;…
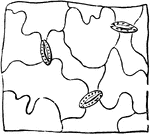
Garden Balsam
Small portion of epidermis of the Garden Balsam, showing very sinuous-walled cells, and three stomata.
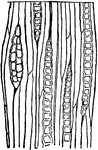
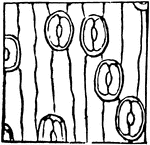
Bit of Young Maple Wood
Magnified view of surface of a bit of young Maple wood from which the bark has been torn away, showing…

Non-Striated Muscle
"Non-striped spindle-shaped cells which branch and join with one another." — Richardson, 1906
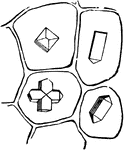
Onion-Peel
Four cells from dried Onion-peel, each holding a crystal of different shape, one of them twinned.
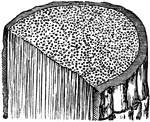
Palm-stem
A Palm-stem in transverse and longitudinal section, the dots on the cross sections represent cut ends…
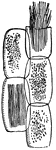
Rhubarb-plant
Some cells from stalk of Rhubarb-plant, three containing chlorophyll; two (one torn across) with rhaphides.
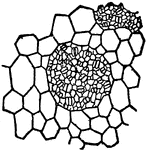
Saxifraga Sarmentosa
"Epidermis of leaf of Saxifraga Sarmentosa, showing clusters of stomata s, surrounded by large epidermal…
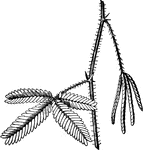
Sensitive Plant
Piece of stem of Sensitive Plant (Mimosa pudica), with two leaves. the lower open, the upper in the…

Shield-Fern
A small piece (pinnule) of a Shield-Fern: a row of fruit-dots on each side of the midrib, each covered…

Snake Plant
Sansevieria Zeylanica is the Latin name, but this plant is also called a Mother-in-law's Tongue. "A…
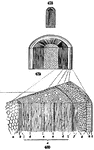
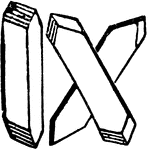
Piece of Stem from a Soft Maple
Piece of a stem of Soft Maple, of a year old, cut crosswise and lengthwise.
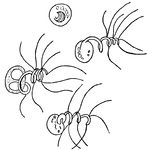
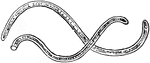
Spermatozooid of the Southern Maidenhair Fern and Venus Hair Fern
Spermatozooid, mature male germ cells, of Adiantum capillus-veneris. Also called spermatozoid.

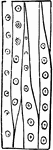
Stem of Flax
Short piece of stem of Flax, magnified, showing the bark, wood, and pith in a cross section.

Telegraph-plant
Portion of stem and leaves of Telegraph-plant (Desmodium gyrans), almost of natural size.

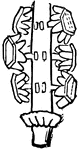
Tetratheca
"Tetratheca hirsuta. 1. the stamens; 2. the pistil, with one of the cells laid open." -Lindley, 1853

Tree-Fern
A Tree-Fern, Dicksonia arborescens, with a young one near its base. In front a common herbaceous Fern…
The Segmentation of the Vitellus
"The first change in the parent-cell is that by which it becomes broken up into a mass of cells, each…
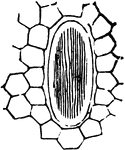
White Lily
Magnified section of a leaf of White Lily, to exhibit the cellular structure, both of upper and lower…