![It has been observed that the pentagonal dodecahedron, [∞o2/2], π {201}, on pyrite may have but six of its twelve planes developed in such a manner a to produce an apparent rhombohedron.](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/86800/86856/86856_pyrite_mth.gif)
Pyrite
It has been observed that the pentagonal dodecahedron, [∞o2/2], π {201}, on pyrite may have but six…
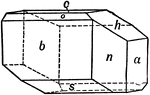
Rhodonite
This figure shows a crystal of Rhodonite (manganese meta-silicate), whose forms are: (c), (b), (a),…
Rhodonite
An alternate combination of manganese meta-silicate (Rhodonite), showing forms: (c), (b), (a), (n),…
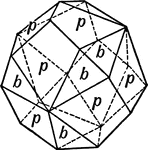
Rhombic Dodecahedron Combined With the Trigonal Tristetrahedron
This form shows a rhombic dodecahedron (d) combined with the trigonal tristetrahedron (q). It sometimes…
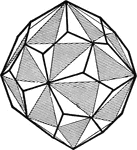
Right-Handed Pentagonal Icositetrahedron
Crystal; If the alternate planes of the hexoctahedron extend until the intersect, a new for will result.…
Rutile Growing Upon Titanic Iron
The tetragonal rutile grows upon the rhombohedral titanic iron, so that its prism of the second order,…
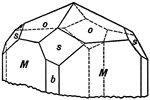
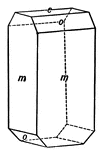
Scapolite
This figure shows a combination of forms sometimes observed on the silicate Scapolite, with the unit…
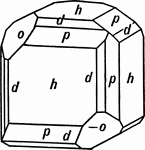
Sodium Chlorate
This is a crystal of Sodium Chlorate, exhibiting the tetrahedron (-o) and the pentagonal dodecahedron…
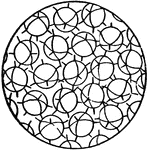
Solid State Showing No Regularity of Molecular Orientation
This figure represents a solid state where there is no regularity of molecular orientation, as in the…
Sphenoidal Crystallization
An example of sphenoidal crystallization is Iron-Copper-Sulfide (FeS_2_Cu), also known as chalcopyrite.
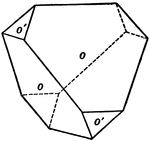
Spinel Contact Twin
This figure shows a contact twin of Spinel, one of the three simplest isometric holohedrons according…
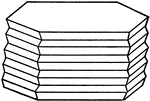
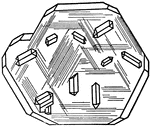
Striation of Crystal Planes
Striation of crystal planes may be produced by repeated polysynthetic twinning. This is well illustrated…
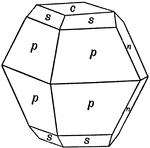
Sulphur
This figure shows an orthorhombic crystal of sulphur, showing the forms: (p), (s), (c), and (n).
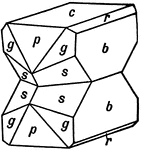
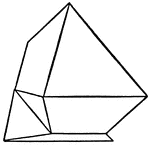
Supplementary Twin
This figure shows a case of a supplementary twin, formed from two hemimorphic crystals, placed symmetrically…
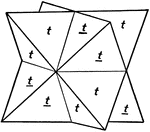
Tetrahedrite
This figure shows two tetrahedrons with parallel axes, and symmetrically placed with reference to the…
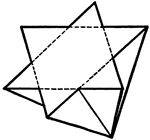
Tetrahedrite Penetration Twin
This figure shows a penetration twin of two tetrahedrons, symmetrical to the octohedral face (tetrahedrite).
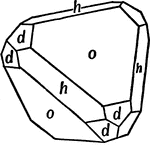
Tetrahedron, Cube, and Dodecahedron in Combination
This form shows a tetrahedron (o), cube (h), and dodecahedron (d) in combination.
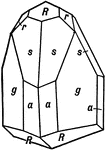
Tourmaline
This crystal of Tourmaline exhibits hemimorphism in the direction of the vertical axis. Its forms are…
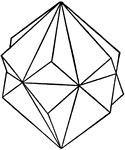
Twin Rhombohedrons
This figure shows two twin rhombohedrons, symmetrical with reference to a prism of the first order,…
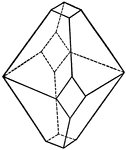
Union of a Pyramid and a Prism of Different Orders
This illustration shows the union of a pyramid and a prism of different orders.
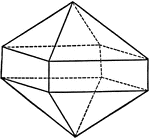
Union of a Pyramid and a Prism of the Same Order
This illustration shows the union of a pyramid and a prism of the same order.
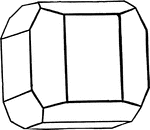
Unsymmetrically Truncated Cube
This form is a cube with its edges unsymmetrically truncated by the faces of the pentagonal dodecahedron.
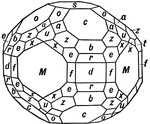
Vesuvianite
This form shows a very complex combination of thirteen tetragonal forms occuring on the mineral Vesuvianite:…
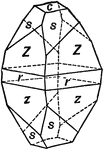
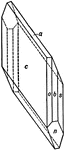
Yttrium Niobate
Also known as Fergusonite, this crystal shows the basal pinacoid, (c); the unit pyramid, (s); and the…
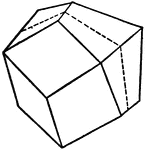
Zinc blende Contact Twin
This figure shows a contact twin of Zinc blende, one of the three simplest isometric holohedrons according…
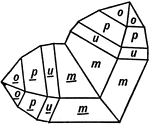
Zircon (Twinning)
In the tetragonal system, the unit pyramid of the second order is the most common twinning plane. This…