Clipart tagged: ‘Ectoderm’
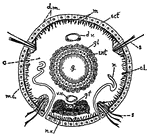
Annelid
This diagram shows a transverse section of dero. c., caelom; c.l., cells of the so-called "lateral line";…
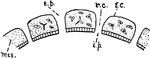
Ascon Sponge
Diagram showing the Ascon type of sponge. ec., ectoderm; r.c., radiating canals; i.p., internal pores;…
Astroides Calicularis
"Tangential section of a larva of Astroides calicularis which has fixed itself on a piece of cork. ec,…
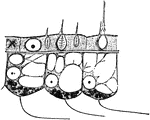
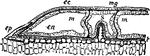
Body-wall
"Portion of the body-wall of Hydra, showing ectoderm cells above, separated by "structureless lamelia"…

Diblastula
"Diagram of a Diblastula. a, orifice of invagination (blastopore); b, archenteric cavity; c, endoderm;…
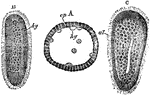
Diblastula
"Formation of the Diblastula of Eucope (one of the Calyptoblastic Hydromedusae) by delamination. A,…
Longitudinal Section of an Embryo
Diagram of a longitudinal section of an embryo, showing the different areas of the blastodermic vesicle.…

Heliopora Corerulea
"A, Portion of the surface of a colony of Heliopora coerulea magnified, showing two calices and the…
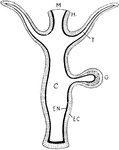
Hydrazoan Polyp
"Diagram of a typical Hydrozoan polyp. EC., Ectoderm; EN., endoderm; C., the cavity of the gut (coelenteron);…
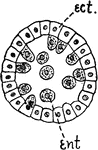
Hydroid Blastula
"A, blastula in which the entoderm (ent.) is produced by proliferation from ectoderm (ect.)." -Galloway,…
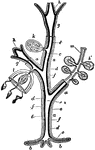
Hydromedusa
"Diagram showing possible modifications of persons of a gymnoblastic Hydromedusa. a, hydrocaulus (stem);…
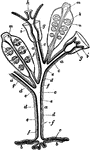
Hydromedusa
"Diagram showing possible modifications of the persons of a Calyptoblastic Hydromedusa. a, hydrocaulus…
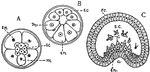
Mesoderm
"Modes of forming mesoderm. A and B, special mesoblasts distinguishable early in egmentation (annelid):…
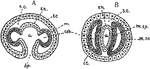
Mesoderm Forming
"Mesoderm formed by pouches from entoderm after gastrulation. A and B, early and later stages in formation…
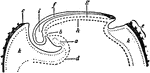
Developing Ovum
Diagram of a developing ovum, seen in longitudinal section. Labels: a, pericardium; b, bucco-pharyngeal;…
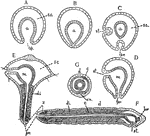
Polygordius
"Diagrams of stages in the metamorphosis of Polygordius, a primitive annelid. Ectoderm throughout is…
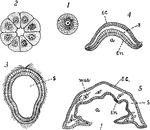
Simple Sponge Development
"Diagrams to illustrate the development of one of the simpler types of sponge: I, the egg; 2, section…
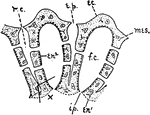
Sycon Sponge
Diagram showing the Sycon type of sponge. ec., ectoderm; r.c., radiating canals; i.p., internal pores;…
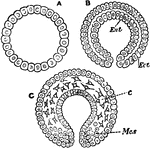
Unilaminar
"Sections through the unilaminar (A), bilaminar (B), and trilaminar (C) conditions of the typical biastoder.…
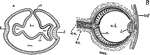
Vertebrate Eye
"Diagrams illustrating two stages in the development of the vertebrate eye. A, showing the relation…
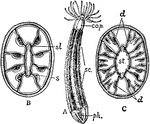
Zooid
"Single zooid with the adjacent soft tissues as seen after removal of the exoskeleton by decalcification.…