Clipart tagged: ‘forces’
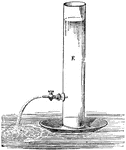
Backward Movement of Discharging Vessel
This experiment illustrates the law of action and reaction, which asserts that momentum cannot be imparted…
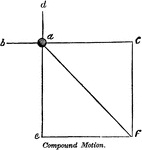
Compound Motion
"Compound motion is that which is produced by two or more forces, acting in different directions, on…
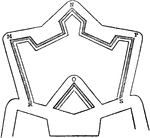
Crown-Work
"Crown-work, in Fortification, is formed to strengthen a weak front, or to occupy ground which might…
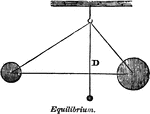
Equilibrium
"When two forces counteract, or balance each other out, they are said to be in equilibrium." -Comstock…
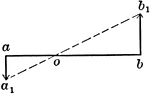
Motions Of 2 Points In Same Plane And Parallel
Illustration showing two points a and b to be in the same plane and parallel.
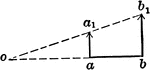
Motions Of 2 Points In Same Plane And Parallel
Illustration showing two points a and b to be in the same plane and parallel.
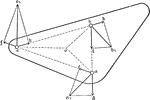
Motions Of 3 Points
Illustration showing three points a, b, and c in motion. The magnitude and direction of a and b are…
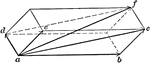
Parallelopiped of Motions
Illustration used "If three component motions ab, ac, and ad are combined, their resultant af will be…
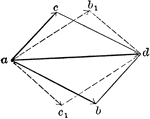
Vector Addition Given Resultant
Illustration "where ad is the given resultant, if the two components have the magnitudes represented…
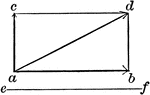
Vector Motion Into Two Components - Resultant
Illustration used to resolve a motion into two components, one of which is perpendicular, and the other…
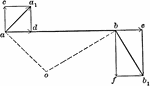
Velocities Of Rigidly-connected Points
Illustration for rigidly-connected points. "If two points are so connected that their distance apart…
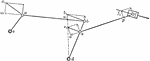
Velocities Of Rigidly-connected Points
Illustration for rigidly-connected points. In the series of links shown, c and d are fixed axes and…
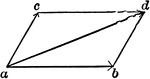
Vector Addition
Illustration showing two component forces ab and ac acting upon point a. The result is the vector ad…
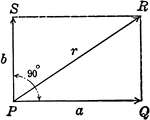
Resultant Vector With Vectors at 90 degrees
Illustration of the resultant vector when two vectors are acting upon a body at point P at 90 degrees.
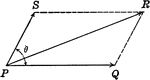
Resultant Vectors
Illustration of the resultant vector when two vectors are acting upon a body at point P.
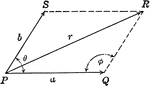
Resultant Vector With Vectors at Angle Ǝ
Illustration of the resultant vector when two vectors are acting upon a body at point P at Ǝ degrees.
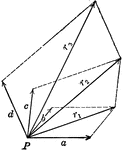
Resultant Vector From 4 Forces
Illustration of the resultant vector when four vectors are acting upon a body at point P.