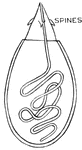Clipart tagged: ‘jellyfish’
Acaleph
"One of the Acalephae; a name given to a large number of marine animals; and redpresenyted chiefly by…

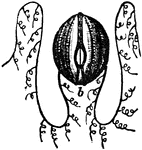
Acalephae
"The under surface, showing the mouth in the center, surrounded by the tentacula, and overial chambers…
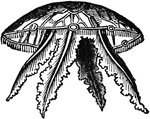
Acalephae
"Side-view, showing the tentacula hanging down in their natural position." — Chambers' Encyclopedia,…
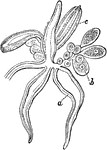
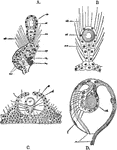
Athorybia Gonoblastidium
"Gonoblastidium of Athorybia rosacea, bearing three hydroclysts, a, a gynophore, b, and two androphores,…
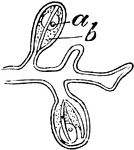
Athorybia Gonophores
"A, female gonophores of Athorybia rosacea on their common stem or gynophore: a, ovum; b, radial canals."…
Athorybia Gonophores
"C, female gonophores: a, genital vesicle; b, vitellus; c, radial canals." -Whitney, 1911
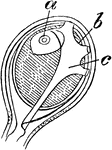
Athorybia Gonophores
"D, female gonophores, enlarged: c, radial canals; d, canal of manubrial cavity." -Whitney, 1911
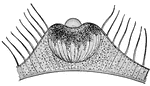
Auditory Organs of the Jellyfish
Auditory and equilibrative organs of jellyfishes. A, of Cunarcha. B, of Pectis. C, of Rhopalonema. D,…
Medusa, aurita
"One of the commonest species, and must have been observed by those who frequent the sea-shore. In the…
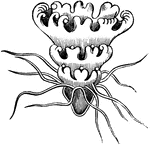
Cuvieria carisochroma
"Which is without a central peduncle, yet has numerous long appendages hanging from its border." —…

Fire Coral
Fire corals are colonial marine organisms that look rather like real coral. However they are technically…

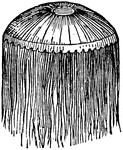
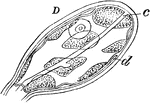
Rhizostoma cuvieri
"The Rhisostoma Cuvieri, a British species, measures two feet, or ever more, in diameter, while…

Hydra
Hydra are in the Jellyfish family, class Hydrozoa. Cross-section of the body showing the two layers…
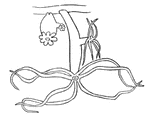
Hydra
If undisturbed, the body and tentacles may occasionally sway gently. If disturbed, a hydra usually shortens…
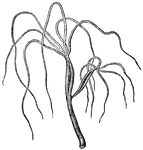
Hydra Viridis
"The Hydra Viridis is another freshwater polyp, common to ponds and still waters Sometimes…
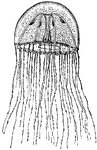
Medusa of a Hydroid
Colonial, plant-like animals closely related to jellyfish, with stinging cells, Any member of the invertebrate…
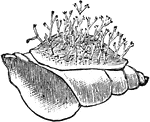
Hydrozoa Encrusting a Small Shell
Hydrozoa (hydrozoans) are a taxonomic class of very small, predatory animals which can be solitary or…
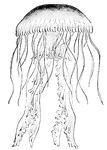
Jellyfish
Jellyfish are saucer-shaped and can be a foot or more in diameter. They are gelatinous and semitransparent.
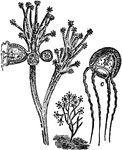
Jellyfish
An illustration of a small jellyfish. Jellyfish are free-swimming members of the phylum Cnidaria. ellyfish…
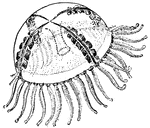
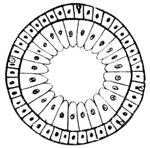
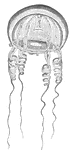
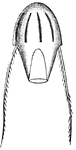
Gonionemus Jellyfish
Gonionemus is a type of hydrozoan related to jellyfish. It uses adhesive discs near the middle of each…
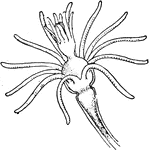
Gonionemus Jellyfish
Gonionemus is a type of hydrozoan related to jellyfish. It uses adhesive discs near the middle of each…
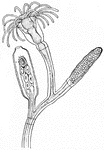
Gonionemus Jellyfish
Gonionemus is a type of hydrozoan related to jellyfish. It uses adhesive discs near the middle of each…

Gonionemus Jellyfish
Gonionemus is a type of hydrozoan related to jellyfish. It uses adhesive discs near the middle of each…
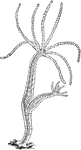
Hydra Jellyfish
Fresh water Hydra, a jellyfish, is a many celled animal. Shown enlarged 25 times, is the entire animal.
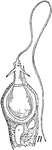
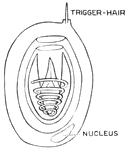
Hydra Jellyfish
Fresh water Hydra, a jellyfish, is a many celled animal. Shown is a Hydra nettle cells.

Hydra Jellyfish
Fresh water Hydra, a jellyfish, is a many celled animal. The organs of defence, nettle cells or lasso…
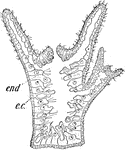
Hydra Jellyfish
Fresh water Hydra, a jellyfish, is a many celled animal. The organs of defence, nettle cells or lasso…
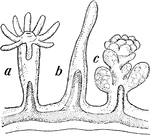
Hydroid Jellyfish
Hydroids, related to the jellyfish, have three basic life-cycle stages: a tiny free-swimming planula…
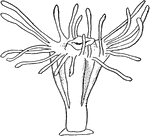
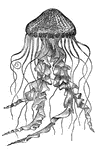
Scyphozoan Jellyfish
Jellyfish have several different morphologies that represent several different cnidarian classes including…
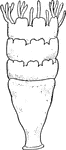
Scyphozoan Jellyfish
Jellyfish have several different morphologies that represent several different cnidarian classes including…
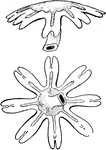
Scyphozoan Jellyfish
Jellyfish have several different morphologies that represent several different cnidarian classes including…

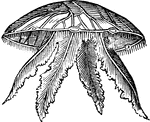
Pelagia labiche
"With four foliaceous arms, and long filaments depending from the rim of th umbrella, also found in…
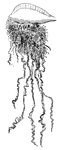
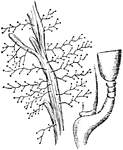
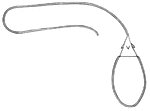
Portuguese Man-of-War
The Portugures man-of-war has a bladderlike float, and locomotion depends upon the wind and current.…

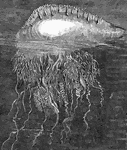
Fleet of Medusa
"They usually inhabit the deep seas. They are rarely solitary, but seem to wander about in considerable…
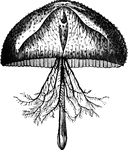
Favonia octonema
"With a nearly hemispherical body, showing a long proboscis, at the root of which are eight branchiferous…
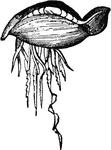
Physalia
"Physalia has no proper mouth, but the food is conveyed to the digestive cavity through a number of…
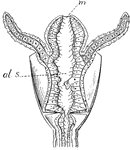
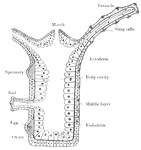
Polyp
Obelia, a simple polyp, vertical section, highly magnified, m = mouth opening, as.s = alimentary sac
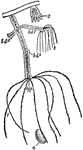
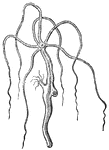
Freshwater Polyp
"Fresh-water polype (hydra), two specimens, the one expanded the other contracted, showing multiplication…

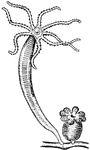
Porpita Pacifica
"The Porpitae consist of colonies of floating animals furnished with a cartilaginous, horizontal…

Rhyzostoma Cuvierii
"These fragile creatures are able to make long voyages on the surface of the sea. Their nature is such…

Portuguese Man of War
There is a large oblong crested float which buoys the fish up, from which hang many tenticles, which…