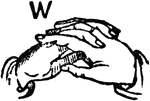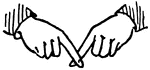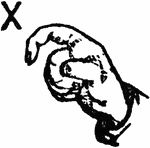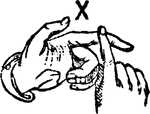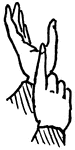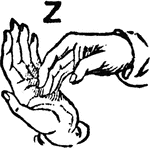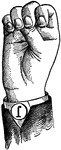
Normal Aperture Front Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
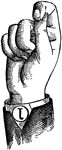
Normal Aperture Front Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Front Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Front Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Front Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Front Primary Wide Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Mixed Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Mixed Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Mixed Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Mixed Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Mixed Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Mixed Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Back Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Back Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
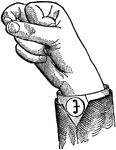
Round Back Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
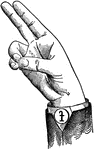
Round Back Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Back Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
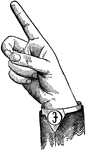
Round Back Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
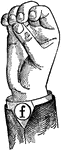
Round Front Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
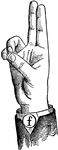
Round Front Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Mixed Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Mixed Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
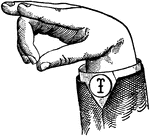
Round Mixed Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
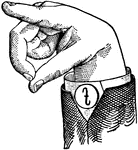
Round Mixed Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…