Clipart tagged: ‘cerebellum’
Brain
"Diagram illustrating the general relationships of the parts of the brain. A, fore-brain; b, midbrain;…
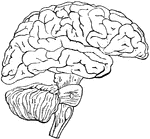
Brain
"The brain from the left side. Cb, the cerebral hemispheres forming the main bulkl of the fore-brain;…
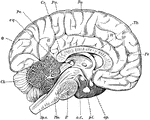
Brain
"Diagram of the left half of a vertical median section of the brain. H, H, convoluted inner surface…
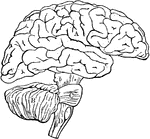
Brain
Diagram illustrating the general relationships of the parts of the brain. Labels: A, fore-brain; b,…
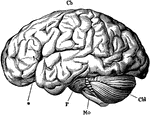
Brain
The brain from the left side. Labels: Cb, the cerebral hemispheres forming the main bulk of the fore-brain;…
Brain and Spinal Cord
Anterior view of the brain and spinal marrow. Labels: 1, 1, hemispheres of the cerebrum; 2, great middle…
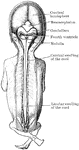
Brain and Spinal Cord of Fetus
Human fetus in the third month of development, with the brain and spinal cord exposed from behind.
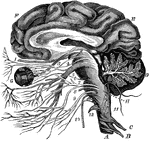
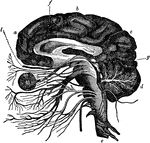
The Brain and the Cranial Nerves
The brain and the origin of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves. Labels: F, E, the cerebrum; D, the cerebellum,…
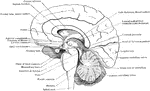
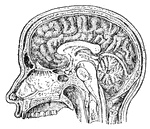
Brain in Mesial Section
Simplified drawing of brain as seen in mesial section, showing relation of brain stem, cerebrum and…
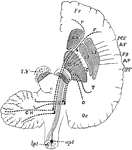
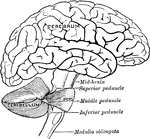
Brain Showing Connection of Frontal Occipital Lobe with Cerebellum
Diagram to show the connecting of the Frontal Occipital Lobes with the Cerebellum. The dotted lines…
Relation of Brain Stem to Spinal Cord
Simplified drawing of brain as seen from below, showing relations of brain stem to spinal cord and cerebrum.
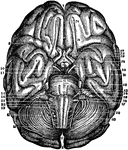
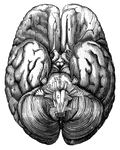
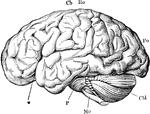
Base of Brain
The base of the brain. Labels: 1, longitudinal fissure; 2, 2, anterior lobes of cerebrum; 3, olfactory…
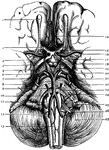
Base of the Brain
The base of brain. Labels: 1. Olfactory Bulb; 2. Second, or Optic Nerves; 3. Anterior Perforated Space;…
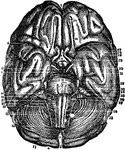
Base of the Brain
Base of the Brain. Labels: 1,2, longitudinal fissure; 3, anterior lobes cerebrum; 4, middle lobe; 5,…

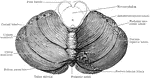
Cerebellum of Dog's Brain
Vertical section of dog's cerebellum. Labels: p m, pia mater; p, corpuscles of Purkinje, which are branched…
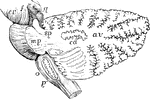
The Cerebellum of the Brain
Outline sketch of a section of the cerebellum, showing the corpus dentatum. The section has been carried…
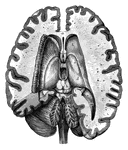
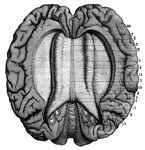
Human Brain
A top view of a dissection of the human brain showing the lateral fourth and fifth ventricles.
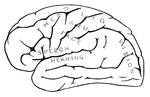
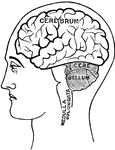
Human Brain
Side diagram of the human brain showing which parts of the brain control hearing, speech, vision, legs,…
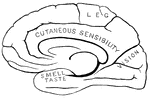
Human Brain
Side diagram of the human brain showing which areas perform the sense of taste, smell, and vision.
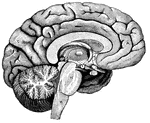
Left Half of the Brain
"A,frontal love of the cerebrum; B, parietal lobe; C, parieto-occipital lobe;…
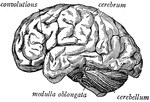
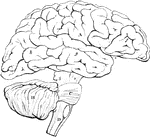
Side view of the brain
"The brain seen from the side, showing the three principal divisions." — Ritchie, 1918
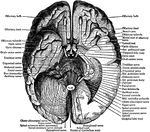
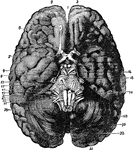
Under Surface of the Brain
View of the under surface of the brain, with the lower portion of the temporal and occipital lobes,…
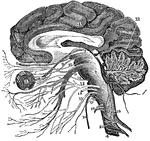
Vertical Section of the Brain
A vertical section of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata, showing the relation of the…
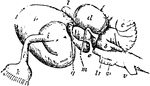
Carcharias Brain
"Brain of Carcharias. ae, nervus acousticus; b, corpus restiforme; c, cerebellum; d, lobus opticus;…
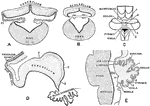
Development of Cerebellum
Showing the development of the cerebellum. A, Transverse section through the forepart of the cerebellum…
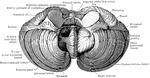
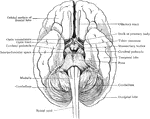
Lower Surface of Cerebellum
The lower surface of the cerebellum. The tonsil on the right side has been removed so at to display…
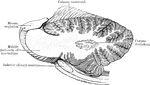
Sagittal Section Through Cerebellum
Sagittal section through the left lateral hemisphere of the cerebellum. Showing the "arbor vitae" and…
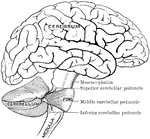
Outline of the Encephalon
Plan in outline of the encephalon, as seen from the right side. The parts are represented as separated…
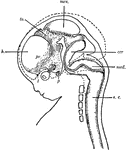
Human Fetus
"Diagram of head and brain of human foetus six weeks old (heavy boundaries). The dotted line indicates…
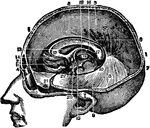
Head, Section of
Section of the head showing the greater scythe, the horizontal apophysis of the dura mater between the…
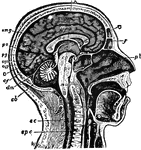
Human Brain
"The Brain is the encephalon, or center of the nervous system and the seat of consciousness and volition…
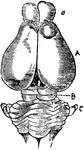
Opossum Brain
"The size of the hemispheres of the brain (A) is so small that they leave exposed the olfactory ganglion…
Polypterus Brain
"Brain of Polypterus. Upper aspect. a, medulia; b, corpora restiformia; c, cerebellum; d, lobi optici;…
Polypterus Brain
"Brain of Polypterus. Lateral aspect. a, medulia; b, corpora restiformia; c, cerebellum; d, lobi optici;…
Polypterus Brain
"Brain of Polypterus. Lower aspect. a, medulia; b, corpora restiformia; c, cerebellum; d, lobi optici;…
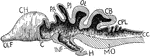
Vertebrate Brain
"Partial section of a Vertebrate brain (diagrammatic). OLF., Olfactory lobe; CH., cerebral hemispheres;…