Clipart tagged: ‘lighthouse’
Beacon
"Beacons in exposed situations are constructed sometimes of stone, and cement-concrete or cement-rubble,…
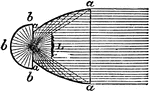
Catadioptric Holophote
"Catadioptric Holophote.—Part of the anterior hemisphere of rays is intercepted and at once parallelized…
Catadioptric Holophote
"Catadioptric Holophote.—Part of the anterior hemisphere of rays is intercepted and at once parallelized…
Coal-gas
"Coal-gas was first used as a lighthouse illuminant at Salvore, near Trieste, in 1817. For many years…
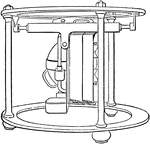
Condensing Apparatus
"Condensing Apparatus for Steamer's Side Lights.—By means of this application of the condensing…
Condensing Apparatus
"Condensing Apparatus for Steamer's Side Lights.—By means of this application of the condensing principle…
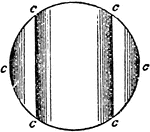
Differential Lens
"Differential Lens.—Horizontal divergence may be obtained to any required amount by varying the radius…
Differential Lens
"Differential Lens.—Horizontal divergence may be obtained to any required amount by varying the radius…
Differential Lens
"Differential Lens.—Horizontal divergence may be obtained to any required amount by varying the radius…
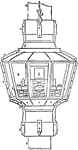
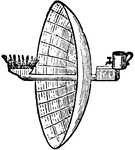
Floating Lights
"aa is the mast, b tackle hook, c, c brass flanges for fixing parts of lantern together, e and g weather…

Fort Jefferson
An illustration of Fort Jefferson which is located today in what is Dry Tortugas National Park. Dry…
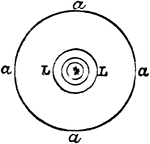
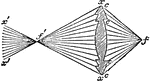
Holophotal Catadioptric
"Holophotal Catadioptric Apparatus Revolving round a Central Flame." —The Encyclopedia Britannica,…
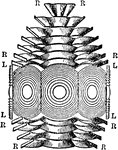
Holophotal Catadioptric
"Holophotal Catadioptric Apparatus Revolving round a Central Flame.—If in place of Fresnel's compound…
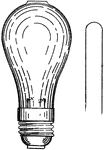
Incandescent Lamp
Incandescent bulbs are made in a wide range of sizes and voltages, from 1.5 volts to about 300 volts.…

Ida Lewis
A woman who resided in a lighthouse in Newport. She was an expert rower, and saved the lives of many…

Lighthouse
An elevated structure or tower placed near a seaport or some headland for the purpose of protecting…
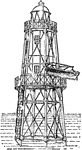
Lighthouse
"An iron pile light erected at Haneda, in the Bay of Yedo, Japan." —The Encyclopedia Britannica,…

Lighthouse
"A tower or other elevated structure bearing a light at the top and erected at the entrance of a harbor…
Lighthouse
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Lighthouse
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Lighthouse
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…

Lighthouse
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…

Lighthouse on Horse Island
The Sackett's Harbor lighthouse was erected on Horse Island during the War of 1812.

Eddystone Lighthouse
"Eddystone is a group of gneiss rocks, daily submerged by the tide, in the English Channel, 9 miles…
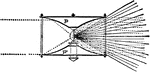
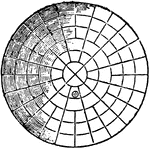
Parabolic Profile
"In order strictly to equalize a fixed light over the whole horizon, which could not possibly be done…
Parabolic Reflector
"In 1763, or at latest before 1777, parabolic reflectors were first used for lighthouse illumination…
Parabolic Reflector
"In 1763, or at latest before 1777, parabolic reflectors were first used for lighthouse illumination…
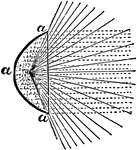
Paraboloid
"It will be seen that the parabolic mirror a is at best but a very imperfect instrument, for even if…
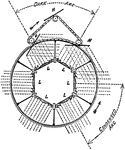
Repeating Light
"Plane mirrors M revolve on an endless chain placed outside of the apparatus and alter the direction…
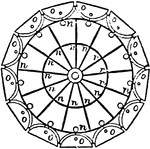
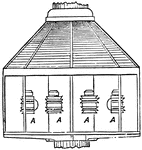
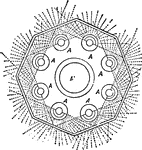
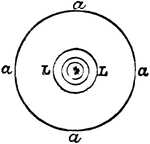
Revolving Light
"In order to produce, on the catoptric system, a fixed light showing all round the circle, a number…
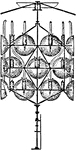
Revolving Light
"If again the light was to revolve, then a revolving chandelier was employed having a certain number…

Seahorse Key
An illustration of Seahorse Key lighthouse which is located in Cedar Keys, a cluster of islands close…
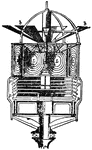
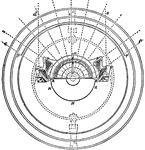
Stevensons Revolving Light
"In 1835 Mr. Stevenson, in a report to the Northern Lighthouse Board, proposed to add fixed reflecting…
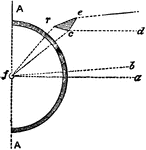
Straight Prisms
"Condensing Straight Prisms.—These, either by reflexion or refraction or both, cause a ray fr…
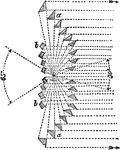
Swans Designs
"Professor Swan's Designs.—Among several ingenious arrangements and new forms of agents proposed by…
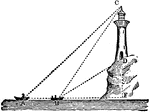
Triangle with Lighthouse
An illustration of a three triangles created with boats and a lighthouse. This is an example illustration…