Search for "archimedes"
Archimedes' Screw
A machine used for lifting water, thought to have been invented by Archimedes in egypt for draining…
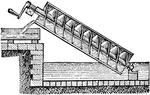
Archimedean Screw
"A device for raising water, said to have been invented by Archimedes."-Whitney, 1902
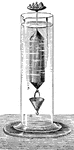
Hydrometer
Nicholson's Hydrometer, consists of a hollow cylinder of metal with conical ends, terminated above by…
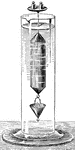
Hydrometer
Nicholson's Hydrometer, consists of a hollow cylinder of metal with conical ends, terminated above by…
Archimedes Principle
"States that: A body when immersed in a fluid loses exactly as much of its weight as is equal to the…
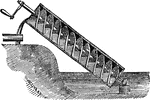
Archimedes Screw
"A machine for raising water, said to have been invented by Archimedes, during his stay in Egypt for…

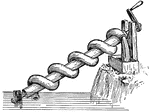
Archimedes' Water Screw
"It consists of a tube, made of lead, or strong leather, coiled round a cylinder of wood or iron, as…
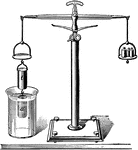
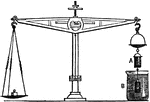
Archimedes Principle
"From on pan suspend a hollow cylinder of metal t, and below that a solid cylinder a of the same size…
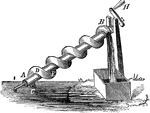
Archimedes' Screw
"Invented to raise water. A hollow tube wound spirally around a solid cylinder. As the cylinder is turned,…
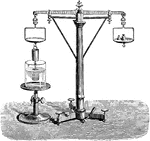
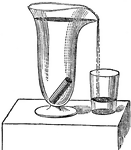
Experimental Verification of Principle of Archimedes
An experimental verification of the Principle of Archimedes.

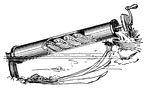
Auger
An auger is a device for moving material or liquid (see Archimedes' screw) by means of a rotating helical…
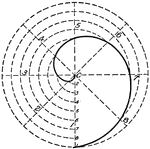
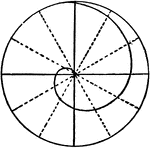
Draw Spiral of Archimedes
"Divide the circumference into a number of equal parts, drawing the radii and numbering the points.…
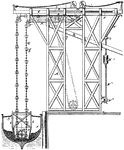
Elevating Apparatus
The first reference to an elevator is in the works of the Roman architect Vitruvius, who reported that…
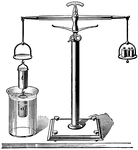
Archimedes Principle
An illustration of Archimedes Principle. "If a body is immersed in a fluid, it will lose in weight an…
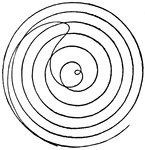
Fermat's Spiral
Also called a parabolic spiral, it is a type of Archimedean Spiral. A spiral is defined as "a plane…
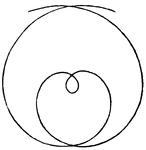
Archimedean Spiral
Illustration of a spiral named after the 3rd century BC Greek mathematician Archimedes.
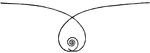
Hyperbolic Spiral
Illustration of a hyperbolic spiral, also called a reciprocal spiral, it is a transcendental plane curve.…