Optics of the Eye
The Optics of the Eye ClipArt gallery includes 56 illustrations of the human eye. Additional views of the human eye are available in the Human Sensory Systems Clipart gallery under Human Anatomy.
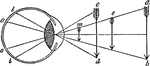
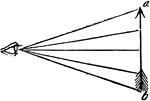
Angle of Vision
"The angle under which the rays of light, coming from the extremities of an object, cross each other…
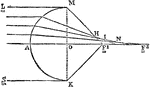
Diagram Illustrating Astigmatism
An illustration depicting an astigmatism. An optical system with astigmatism is one where rays that…
Convergence of Rays in the Aqueous Humor of the Eyeball
The convergence of light rays in the eyeball begins in the aqueous humor is perfected in the crystalline.…
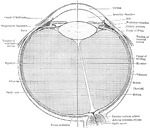
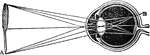
Eye
"Next in order is the aqueous humor, b, e, in the middle of which is the iris, d, c. Behind the pupil…
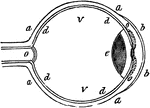
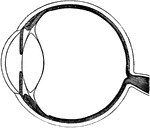
Eye
"a, sclerotic membrane; b, cornea; d, retina; o, optic nerve; v, vitreous humor." -Comstock 1850
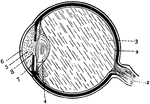
Eye
Section of the eye. 1: Optic nerve; 2: Retina; 3: Vitreous humor; 4: Crystalline lens; 5: Aqueous humor;…
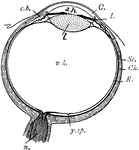
Eye
"Diagram of the eye. C., Cornea; a.h., aqueous humour; c.b., ciliary body; l., lens; I., iris; Sc.,…
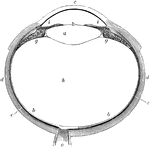
Eye
The human eye. Labels: a, crystalline lens; b, retina; c, cornea; d, sclerotic; e, choroid; g, ciliary…
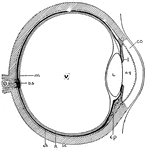
Eye Cross-Section
"Cross-section of the eye. Parts: co, cornea; I, iris; aq, anterior chamber of aqueous humor; L, lens;…
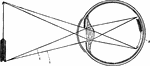
Eye Diagram
Diagram of the eye. 1: Lines of light from end of arrow; 2: Small, inverted image in the eye.
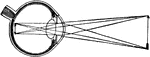
Optical Position and Size of Image Through Lens in Front of Eye
The illustration of putting lenses in front of the eye. The focal point of the image is reflected into…
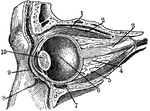
Eye Section
"Section through the left eye, closed. 1, lifting muscle; 2, upper straight muscle; 3, optic nerve;…
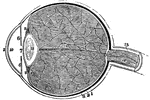
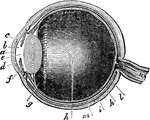
A Section of the Eye
A section of the eye. Labels: 1, The sclerotic coat. 2, The cornea. 3, The choroid coat. 6, The iris.…
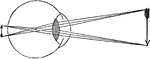
Cornea too Concave on Eye
"...and the cornea will become too flat, or not suffciently convex, to make the rays of light meet at…
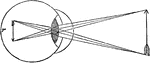
Cornea too Convex on Eye
"If the cornea is too convex, or prominent, the image will be formed before it reaches the retina, for…
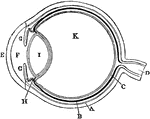
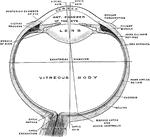
Diagram of the Eye
Plan of the eye seen in section. Labels: A, The Sclerotic Coat; B, The Choroid Coat; C, The Retina;…
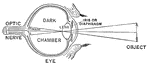
Diagram of the Eye
"Diagram illustrating the Manner in which the Image of an Object is inverted on the Retina." — Blaisedell,…
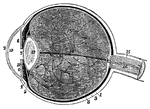
Human Eye
1, the sclerotic thicker behind than in front; 2, the cornea; 3, the choriod; 6, the iris; 7, the pupil;…
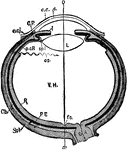
Human Eye
"Diagrammatic horizontal section of the eye of man. c, cornea; ch. choroid (dotted); C. P, ciliary processes;…
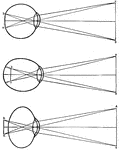
Human Eye
Diagrams of how an image is displayed with a normal eye (top image), myopic or nearsighted eye (middle…

Lens of the Eye
Lens of the eye. The rays of light are brought nearer together by the lenses of the eye, just as they…
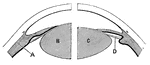
Lens of the eye
"Diagram showing the Change in the Lens during Accomadation. On the right the lens is arranged for distant…
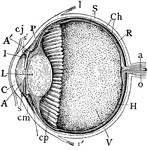
Median Vertical Anteroposterior Section of Eye
"Human Eye, in Median Vertical Anteroposterior Section. (Ciliary processes shown, through not all lying…

Eye Focusing on Object
"Showing how the image of an object which is seen is formed on the retina of the eye." —Croft 1917
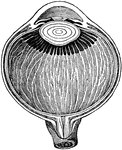
Section of the Eye
Section of the eye magnified, showing the crystalline lens in its proper situation, between the aqueous…
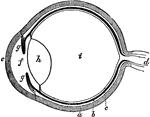
The Eye
The eye. Labels: a, sclerotica; e, cornea; b, choroid; d, optic nerve; f, aqueous humor; g g , iris;…
Eyeball
"The most essential parts of human vision are contained in the eyeball, a nearly spherical body, about…
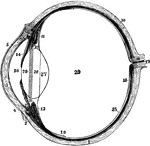
Left Eyeball in Horizontal Section
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
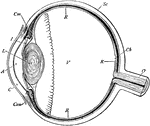
Section of the Eyeball
Section of the eyeball. Labels: Con, conjunctiva; C, cornea; A, aqueous humor; I, iris; L, crystalline…
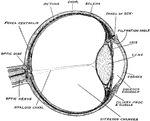
Eyeball
Horizontal section of the eyeball, showing the suspensory ligament of the lens, the aqueous and vitreous…
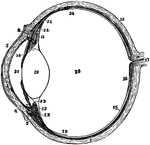
The Eyeball in Horizontal Section
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
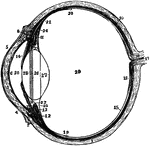
Section of Left Eyeball
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
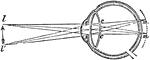
Flattened Eye
"A representation of the manner in which the image is formed in the eye, when the cornea or crystalline…
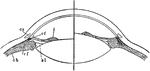
Focusing of the Eye
Diagram to illustrate the mechanism of accommodation (focusing); on the right half of the figure for…
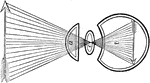
Formation of an Image on the Eyeball
In passing through the crystalline, the rays cross each other, so that those rays which pass from the…
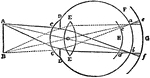
Formation of Circles of Diffusion
An illustration depicting the formation of circles of diffusion. "From point A luminous rays enter the…
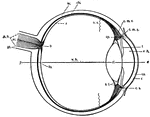
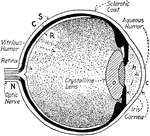
Human Eye
This diagram shows a side view of the right eye of man. a.c., central artery; a.h., aqueous humor; b.,…
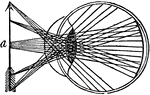
Indistinct Vision
"...where we suppose that the object a, is brought within an inch or two of the eye, and that the rays…
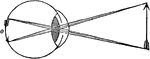
Inversion of Objects by the Eye
"The actual position of the vertical object a, as painted on the retina, is therefore such as is represented…
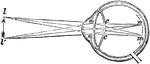
Near-sighted
"A representation of the manner in which the image is formed in the eye of a near-sighted person. The…

Nearsighted Vision
The lenses and humors of the eye must be very exactly arranged, in order that the sight may be perfect.…
Position and Size of Image for Eye Optics
An illustration of the position and the size of the image viewed by the eye. The eye approximates the…
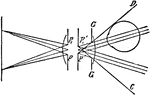
Optical Position of Diaphragms using Lens
"The intersection of the principal rays in this case lies in the middle of the entrance pupil or of…
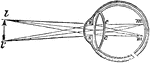
Perfect Eye
"A representation of the manner in which the image is formed upon the retina in the perfect eye. The…
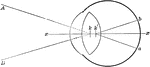
Retina
"Diagram illustrating the points at which incident rays meet the retina. xx, optic axis; k, first nodal…
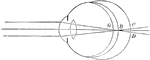
The Position of the Retina in Near and Far Sight
A flattened shape of the globe of the eye causes farsightedness and an elongated shape of the globe…
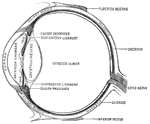
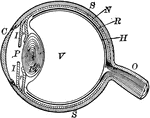
![An illustration of a transverse section of an ideal eye. "A, summit of cornea; SC, sclerotic; S, Schlemm's canal; CH, choroid; I, iris; M, ciliary muscle; R, retina; N, optic nerve; HA, aqueous humour; L, crystalline lens, the anterior of the double lines on its face showing its form during accommodation; HV, vitreous humour; DN, internal rectus muscle YY', principle optical axis; C, [center] of the ocular globe..." (Britannica, 132).](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/58100/58122/58122_ideal-eye_mth.gif)
Transverse Section of an Ideal Eye
An illustration of a transverse section of an ideal eye. "A, summit of cornea; SC, sclerotic; S, Schlemm's…