The Structural Geology ClipArt gallery provides 172 illustrations of the study of the stresses and deformations of rock layers. The study of the various folds and deformations of rock strata is an important part of the search for petroleum and mineral resources.
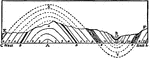
Anticlinal and Synclinal Folds
An illustration of a section of anticlinal and synclinal folds on the like CD.
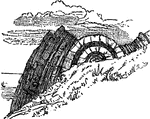
Anticlinal Fold
A symmetrical anticlinal fold, the top of which has been eroded. Near St. Abb's Head, Scotland.

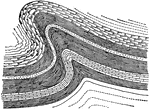
Anticline
This illustration shows a perspective view and a vertical section of an anticline. It shows the half-cigar-shaped…
Anticlinorium
A mountain mass composed of a number of anticlines may have these so arranged that they form a part…
Appalachian Mountains
This illustration shows the Appalachian Mountains, a region of numerous flexures on a grand scale, as…

Archaean Time
This is a diagram showing the rocks of the successive periods of time. They are shown in order from…
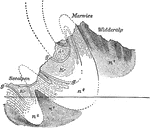
Basin of Middle Tennessee
Different physiografic provinces make up the Basin of Middle Tennessee. Sections from east to west across…
Bassin du Puy
General view, in part schematic, of the "Bassin du Puy" and the "Chaine du Velay" or "Chaine du Deves,"…
Black Hills Dome
Cross-section of the Black Hills dome, showing the present structure and topography and the former continuation…
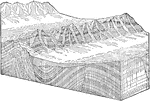
Development of a Block Mountain
Diagram illustrating the development of the block mountain topography of the Basin Ranges.
Breached Asymmetrical Anticline
Eroded fold, breached asymmetrical anticline, the hard stratum forming two opposing uniclines.
Caucasus
Cross-section of the Caucasus along the Grusinian military road. Dark beds are lava streams.
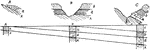
Clastic Deposits in the Sea
Natural and columnar sections at each end and in the center of a line 100 miles long and extending at…
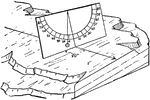
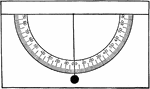
Clinometer Measuring Inclined Strata
Diagram illustrating gently inclined strata, with the clinometer in proper position to measure the dip…
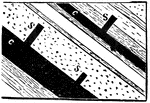
Coal Beds
This illustration shows coal-beds with stumps of trees rising out of the coal. The stumps always stand…
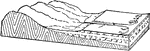
Coastal Plain
The costal plain of an overlapping strata after the development of subsequent streams and the formation…
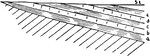
Coastal Plain Strata
Diagrammatic section of coastal plain strata formed in a retreating sea (off-lapping series).
Compound Regressive-Transgressive Series
Diagram showing the relationship of the strata in five successive sections, in a compound regressive-transgressive…
Concentric Ridges in Anticlinal Structures
Development of concentric ridges in anticlinal structures. A) An anticlinal or cigar-shaped mountain…
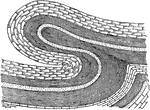
Concentric Ridges in Synclines
Development of concentric ridges in synclines. A) a region with synclinal or canoe-shaped folds. B)…

Contorted Rocks
"Curved and contorted rocks, near Old Head of Kinsale." — Encyclopedia Britannica, 1893

Crag and Tail
Crag and tail, a term used to designate a peculiar hill conformation. a, crag; b, tail (boulder clay,…

Cuestas and Lowlands
Block diagram illustrating the formation of three cuestas and lowlands by normal drainage on the peneplaned…

Shale Deformation
"Deformation of shale by porphyry, Burlington Railroad, east of Whitetail Gulch." -Walcott, 1901
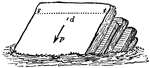
Dip
"Dip, in geology, the name given to the angle of slope of inclined rock strata, as dip in the diagram...The…
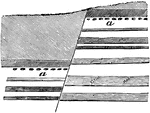
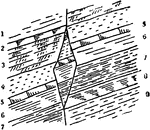
Displacement of Strata
"Section showing displacement of strata by a fault. a and a were once a continuous mass of rock." -Whitney,…
Eozoic Strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum (plural: strata) is a layer of rock or soil with internally…
Eroded Anticlines
Eroded anticlines with horizontal and with pitching axes. In the first case the strata crop out in parallel…

Erosion
This illustration shows a cliff, having its lower layers near the level of low tide, extending out as…

Erosion Development
"Diagram illustrating development of erosion profiles on laccolith domes." -Walcott, 1901
Change in Facies
Diagram illustrating change in facies of marine clastics, from sands and muds near the shore to calcareous…
Flattop Mountain, a Synclinal Mountain
Section across the Livingston and Lewis ranges, with the Flattop Mountain, a synclinal mountain, and…
Flexures
This illustration shows a rock formation with folds or flexures in strata. a x represents the axis or…
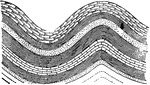
Strata Folds
"A syncline is a downfolding of the strata in the form of a trough, as at a...An anticline is an upfolding…

Freiburg Region
Diagrammatic section through the Freiburg region showing the former and present topography and the extensive…

Granite Section
"Section showing Granite nucleus, with strata lying on its flanks, the overlapping and continuous portions…
Gravel Hill
"Suppose a to be a gravel hill, and b a strata of clay or rock, impervious to water. The fluid percolating…
Groundwater Source
The diagram shows the source of groundwater: water falls into porous ground (a), flows underground to…

Hesperus Mountain
Hesperus Mountain, showing wedges and sheets of trachyte intruded into the shales, from the laccolith…
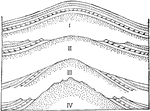
Development of Hog-backs
Diagrammatic sections representing the development of hog-backs. I, a simple anticlinal ridge consisting…

Hog-back Diagram
Hog-backs (RR) changing into cuestas (CC) and these into steps (HH) by progressive flattening of strata;…
Horizontal Rock
This illustration shows exceptions to horizontal rock formations. When a river empties ino a lake or…
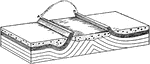
Inclined Strata
Diagram to illustrate the underground extension of inclined strata which crop out on the surface, and…

Inclined Strata Dip and Strike
Diagram illustrating the relationships of dip and strike of the inclined strata of an outcropping series…
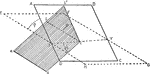
Deflection of Outcrop of an Inclined Stratum
Diagram illustrating the deflection of outcrop of an inclined stratum, from the true strike on a horizontal…