Mold
The Mold ClipArt gallery offers 33 images of microscopic fungi that grow as multicellular hyphae.
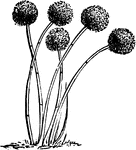
Aspergillus Glaucus
A genus of Mucedines (Hyphomycetous fungi) forming common molds, such as the blue of cheese. Aspergillus…
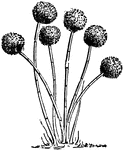
Aspergillus Glaucus
A genus of Mucedines (Hyphomycetous fungi) forming common molds, such as the blue of cheese. Aspergillus…
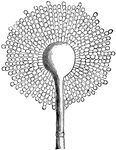
Aspergillus Glaucus
A genus of Mucedines (Hyphomycetous fungi) forming common molds, such as the blue of cheese. Aspergillus…
Aspergillus Glaucus
A genus of Mucedines (Hyphomycetous fungi) forming common molds, such as the blue of cheese. Aspergillus…
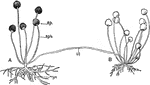
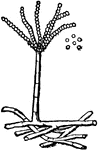
Bread Mold
"Bread mold (Rhizopus nigricans). A, older plant; myc, mycelia; sph, sporangiophore; sp, sporangium;…
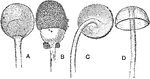
Bread Mold Stages
"Rhizopus nigricans. A, Young sporangium, showing columella within; B, older sporangium, with the wall…
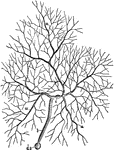
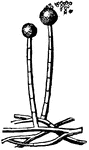
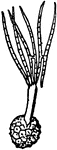
Brown Mold
An example of brown mold (mucor mucedo). s, spore; m, mycelium; t, gonidiophore; sp, sporangium.
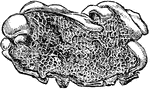
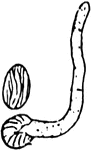
Dry Rot Fungus
Dry-rot fungus (Merulius lacrymans). A decay affecting timber, occasioned by various species of fungi,…
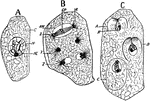
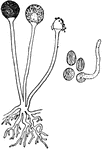
E. Communis Cell
"Free cell formation of spores in the ascus of Erysiphe communis. A, ascus with single nucleus; C, cytoplasm;…

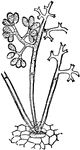
Ergot
"1. Cross-section of the ovary (sphacelia), in the early stage of the fungus, showing the mycelium (a…
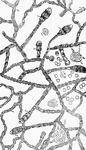
Stages of fungus growth
This illustration "represents its mycelium growth; 2,2 its budding cells, which terminate in fruit cells;…
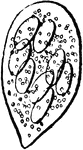
Powdery Mildew Ascus Containing Eight Ascospores
An illustration of powdery mildew showing the ascus containig eight ascospores.
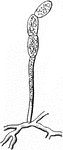
Powdery Mildew Conidia Bearing Hypha
An illustration of powdery mildew showing conidia bearing hypha.
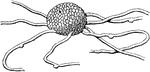
Powdery Mildew Sporocarp & Mycelium
An illustration of the sporocarp and mycelium of powdery mildew.
Powdery Mildew
An illustration of erysiphe communis, powdery mildew, that is on the epidermis of the leaf of the flower,…
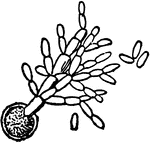
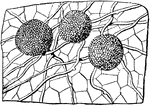
Mold
The green mold, Penicillium, one of the most common of the Sac Fungi. The hyphae of the branching mycelium…
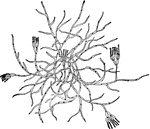
Common Mold
"Showing One of the More Common Molds found on Fruits and Bread. The tiny stalks grow verticallyinto…
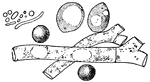
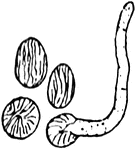
Molds, yeast, and bacteria
"Showing the Comparative Size of Molds (a), Yeast (b and c), and Bacteria (d)." — Blaisedell,…
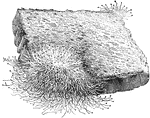
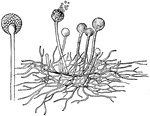
Mucor, a Common Mold
"A Piece of Bread upon which One of the Common Molds, known as Mucor, is growing." — Blaisedell,…
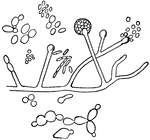
Fermentation of wine
"Organisms found upon the Skin o a Grape and concerned in the Fermentation of Wine." — Blaisedell,…
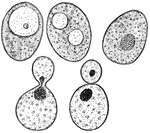
Yeast cake
"Showing a Bit of Common Yeast Cake when mixed with Water and examined under the Microscope. There are…
Yeast cells
"Yeast Cells, found in the Juice of Apples, which cause the fermentation of Cider." — Blaisedell,…
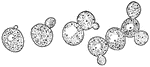
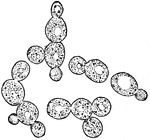
Growing yeast cells
Growing Yeast Cells, showing Method of budding and forming Groups of Cells. Each bud appears as a little…