The Textile Manufacturing ClipArt gallery offers 103 illustrations of ginning, scutching, carding, spinning, weaving, knitting, and finishing of cotton, wool, and other fibers. This gallery illustrates commercial scale processes. For illustrations of hand weaving, please see the Fabric Arts gallery in the Crafts section.
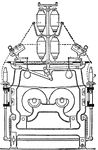
Lace Machine
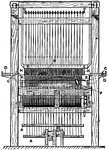
"A section of part of a lace machine. E is the cylinder or beam upon which the lace is rolled as made,…
Loom
The first completely automated loom was made by Jacques Vaucanson in 1745. A different power loom was…
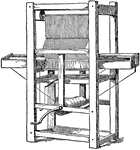
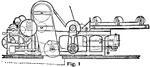
Cartwright's First Power Loom
A mechanized loom powered by a drive shaft. It eased the process of constructing fabric.
Shuttle Loom
Any loom that uses a shuttle. Most looms use a shuttle of some sort, however there are some shuttle-less…
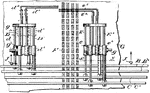
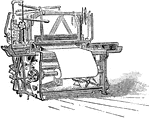
Weaving Loom
This machine is used to weave cloth, the purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension.
Machine For Inserting Diagonal Strips in Woven Cane Work
All woven seats need a protective finish. Caned surfaces may be left natural and waxed, or they may…
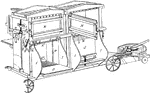
Baling Press Machine
A machine for compressing bolts of cloth or waste into compact bales for shipment.

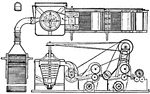
Mill
This mill was manufactured in Birmingham, England. It was possibly used as a textile mill for processing…
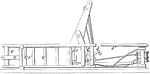
Cotton Press
This cotton press design allowed for cotton to filter through a windlass, later received by the hoop.

Calico Printing
Calico printing was the first "operation connected with the printing of cloth."- Lupton
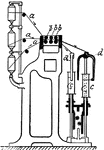
Roving Machine
Cotton manufacturing. Fig. 5B, Roving machine with rack and pinion adjustment for raising and lowering…
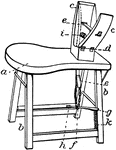
Sewing Horse
"Sewing-horse. In saddlery, a sewing-clamp with its supports. a, seat; b, legs; c, c', clamping-jaws,…
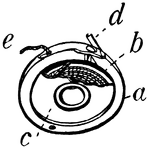
Bobbin Detail of Wheeler and Wilson Sewing Machine
"a is the bobbin case; c, bobbin; b, thread wound on bobbin; d, projection from bobbin-case which keeps…
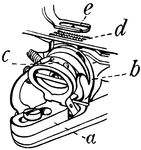
Bobbin Detail of Wheeler and Wilson Sewing Machine
"a is the bobbin holder, partly opened to show hook b, and bobbin-case c; d, feed-points; e, presser-foot."…
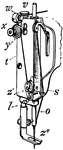
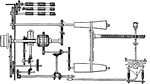
Detail of Wheeler and Wilson Sewing Machine
A detail of the Wheeler and Wilson Sewing Machine. "s, thread-leader; t, face-plate covering...; v,…
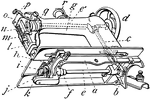
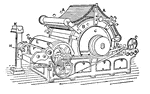
Wheeler and Wilson Sewing Machine
"a, is the frame; b, shaft-crank which rocks the hook-shaft; e, receiving its motion from the double…
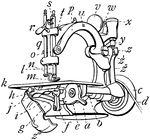
Willcox and Gibbs Sewing Machine
A detailed illustration of one of the most collected sewing machines of all time. Today, many of these…
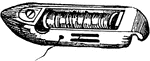
Shuttle
An instrument used by weavers for passing the thread of the woof from one side of the cloth to the other,…
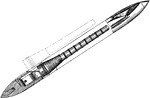
Shuttle for Looms
The term shuttle loom refers to any loom that uses a shuttle. Most looms use a shuttle of some sort,…
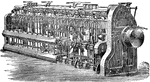
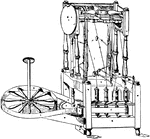
Slubbing Frame
"The operation which succeeds that of the drawing frame is slubbing, where the sliver has a certain…
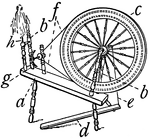
Spinning Wheel for Flax
"A machine for spinning flax into threads by hand. It consists of a wheel, band, and spindle, and is…
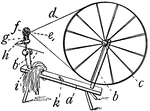
Spinning Wheel for Wool
"A machine for spinning flax into threads by hand. It consists of a wheel, band, and spindle, and is…
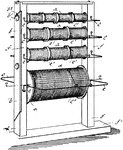
Rack Spool
A cylinder of wood, plastic, cardboard, or other material on which wire, thread, or string is wound.
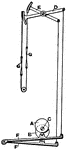
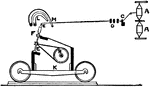
Tappet Motion
Cotton manufacturing. Fig. 2D, tappet motion: A, B, cams on shaft C, operate the tappet levers D, E…
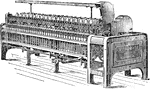
Throstle
"The spinning frame, or throstle, is made with two sets of drawing rollers, one on each side. Between…
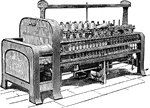
Throstle
"The spinning frame, or throstle, is made with two sets of drawing rollers, one on each side. Between…
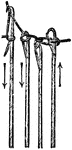
Tumbler Needle
"An improvement of great importance in the hosiery trade was effected through the invention of the tumbler…
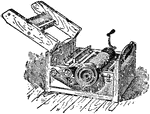
Whitney's Cotton Gin
A machine which separated the seeds from raw cotton more rapidly than could be done by hand.

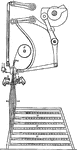
Winding a Skein of Yarn
A man seated on a stool holds a skein of yarn as a standing woman winds it. In the background is a large…
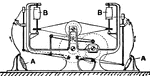
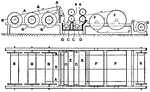
Winding Machine
Cotton manufacturing. Fig. 4C, Warder's bobbin winding machine, with cam motion for raising and lowering…