This ClipArt gallery offers 209 illustrations of ancient Greek architecture.
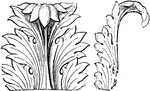
Acanthus Leaf, Front and Side Views
The acanthus is one of the most common ornaments used to depict foliage.

Acropolis
"The citadel of a Grecian city, usually the site of the original settlement, and situated on an eminence…

Acropolis
"Acropolis, 'the highest point of the city.' Many of the important cities of Greece and Asia Minor were…

The Acropolis of Athens - Restoration of the Propylaea
Illustration of the Acropolis restored to what it may have looked like when originally completed. The…

The Acropolis
An image of the Acropolis, as it was, seated in Athens, Greece. The Acropolis is an ancient, famed citadel…
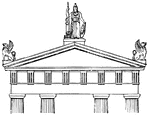
Acroteria
"Small pedestals placed on the apex or angle of a pediment for the support of a statue or other ornament."-Whitney,…

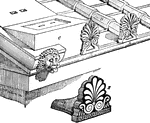
Acroteria from the Temple of Minerva at Ægina
On the apex and two lower angles of the pediment were introduced acroteria, sometimes ornaments of flowers…
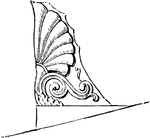
Acroteria, or Roof-Pedestal, from the Temple of Theseus at Athens
On the apex and two lower angles of the pediment were introduced acroteria, sometimes ornaments of flowers…
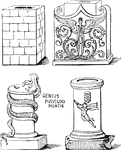
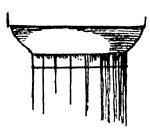
Altars
"Altars were either square or round. Specimens of both kinds are here given from ancient sculptures."…
Amphitheatrum
"An amphitheatre was a place for the exhibitions of public shows of combatants and wild beasts, entirely…
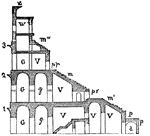
Amphitheatrum
"An amphitheatre was a place for the exhibitions of public shows of combatants and wild beasts, entirely…

Antae
"Square pillars, which were commonly joined to the sidewalls of a building, being placed on each side…
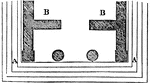
Antae
"Square pillars, which were commonly joined to the sidewalls of a building, being placed on each side…

Ante-fixae
Ante-fixae (from Latin antefigere, to fasten before), the vertical blocks which terminate the covering…

Ante-fixae
Ante-fixae, the vertical blocks which terminate the covering tiles of the roof of a Roman, Etruscan,…

Anthemion-Molding
"A molding or frieze ornamented with a series of anthemia, usually in graceful alternation of two forms."-Whitney,…

Double Twist on an Astragal
An astragal is molding profile composed of a half round surface surrounded by two flat planes (fillets).…

Ancient Athens
"The mosted noted of the orations of Isocrates is the Panathenaicus or Panegyric of Athens, a work on…
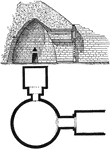
Treasury of Atreus
The Treasury of Atreus or Tomb of Agamemnon is an impressive "tholos" tomb at Mycenae, Greece (on the…

Treasury of Atreus Doorway
The Treasury of Atreus or Tomb of Agamemnon is an impressive "tholos" tomb at Mycenae, Greece (on the…

Tomb of Atreus
The Tomb of Atreus also known as the Treasury of Atreus is a tomb located in Mycenae, Greece built between…
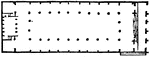
Basilica
"A building which served as a court of law and an exchange, or place of meeting for merchants and men…
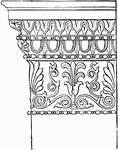
Ionic Antæ Capital from the Temple of Minerva Polias at Athens
The capital of the antæ and pilasters is without volutes, as is seen here. The shaft has no flutings;…
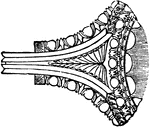
Plan of Ionic Antæ Capital from the Temple of Minerva Polias at Athens
The capital of the antæ and pilasters is without volutes, as is seen here. The shaft has no flutings;…

Corinthian Capital
The structural tendency which prevails in the capitals of all orders to change from the circular form…
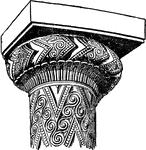
Early Greek Capital
An illustration of an early Greek capital. In several traditions of architecture including Classical…
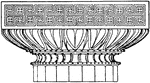
Graeco-Doric Capital
The Graeco-Doric capital is an antique design. It is found on the upper termination of a column.

Graeco-Ionic Capital
The Graeco-ionic capital is a design of a scroll rolled on both sides with spiral curves. It has an…

Grecian Doric Capital
"The Doric Order is, in architecture, the second of the five orders, being that between the Tuscan and…
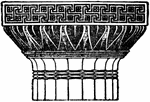
Grecian Doric Capital
"The Doric Order is, in architecture, the second of the five orders, being that between the Tuscan and…
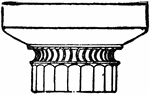
Grecian Doric Capital
"The Doric Order is, in architecture, the second of the five orders, being that between the Tuscan and…

Greek Corinthian Capital
The Greek Corinthian capital is found in a monument in Lysikrates, Athens. It is a design of spiral…

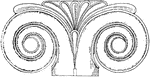
Volute of the Corinthian Capital
"A kind of spiral scroll used in Ionic, Corinthian, and Composite capitals, of which it is a principal…
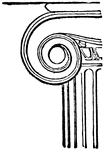
Volute of the Ionic Capital
"A kind of spiral scroll used in Ionic, Corinthian, and Composite capitals, of which it is a principal…

Caryatic Order
An order of architecture wherein the entablature is supported by female figures clothed in long garments,…
Greek Caryatid
The Greek Caryatid is a female figure used as a support in place of a column. It is found in the temple…

Caryatides
"Caryae was a city in Arcadia, near the Laconian border, the inhabitants of which joined the Persians…
Caryatis from the Erechtheum at Athens
Caryatides are a blending of architecture and sculpture, but they are not of frequent occurrence. These…
Profile of the Caryatis with Pedestal and Entablature
Caryatides are a blending of architecture and sculpture, but they are not of frequent occurrence. These…