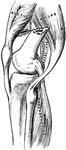Human Appendicular Skeleton
The Human Appendicular Skeleton ClipArt gallery offers 36 illustrations of arms, hands, pelvis, legsa and feet. These are the bones that are appended to the axial or central skeleton.
Bones of Arm
Arm of humans; h Humerus or bone of upper arm; r and u Radius and Ulna, or bones of the forearm; c Carpus,…
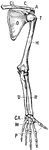
Bones of the Shoulder and Upper Extremity - Front View
"A, acromion; C, coracoid; CA, carpus; CL, clavicle; H, humerus; M, metacarpals; O, ventral surface…
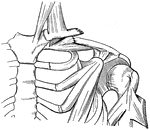
Broken Clavicle
"When a bone is broken, blood trickles out between the incjured parts, and afterwards gives place to…
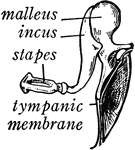
Bones of the Ear
"Across the middle ear a chain of three small bones stretches from the tympanic membrane to the inner…

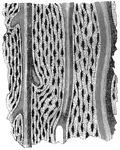
Softened fibula
"The Fibula tied into a Knot after the Mineral Matter has been dissolved by Acid." — Blaisedell,…

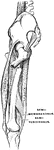
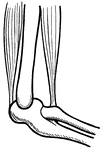
Ligaments of the Foot and Ankle
"The bones are fastened together, kept in place, and their movements limited, by tough and strong bands,…
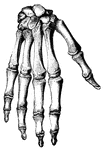
Bones of the Foot
"The foot is built in the form of a half-dome or half-arch. This is to afford a broad, strong support…
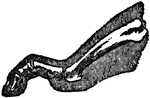
Side View of Bones in Foot
"The Foot is that part of the lower extremity below the leg on which we stand and walk. It is composed…
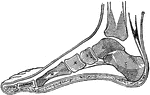
Side View of Bones in Foot
"The Foot is that part of the lower extremity below the leg on which we stand and walk. It is composed…
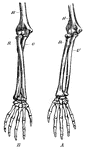
Forearm Bones
This diagram shows the bones of the right fore-arm. H, the humerus; R, the radius; and U, the ulna.

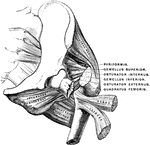
Powerful Ligament at the Hip Joint
"The bones are fastened together, kept in place, and their movements limited, by tough and strong bands,…
Human Leg (Front View)
This illustration shows a front view of a human leg. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA.…
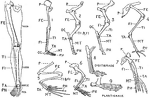
Human Leg (Front View), and Comparative Diagrams showing Modifications of the Leg
This illustration shows a human leg (front view), and comparative diagrams showing modifications of…

Human Leg (Side View)
This illustration shows a side view of a human leg. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA.…
Humerus
"The humerus, a long, hollow bone, rests against a shallow socket on the shoulder blade. It…
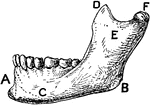
Lower Jawbone of Man
"A, symphysis menti; B, angle of jaw; C, body or horizontal ramus; D, coronoid process; E, ascending…
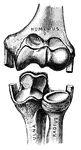
Elbow Joint
"Showing how the Ends of the Bones are shaped to form the Elbow Joint. The cut ends of a few ligaments…
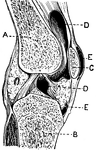
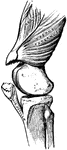
Section of the Knee
This illustration shows a section on the knee (A, Femur; B, Tibia; C, Patella; D, Synovial sac; E, bursæ).…
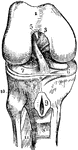
Knee-Joint
The right knee-joint, laid open from the front. 1: Articular surface of the femur. 2 and 3: Ligaments.…
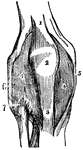
Knee-Joint
Front view of the right knee-joint. 1: Tendon of the extensor muscle. 2: Patella. 3: Ligament of the…
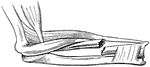
Broken Radius
"When a bone is broken, blood trickles out between the injured parts, and afterwards gives place to…
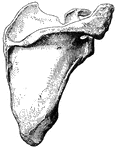
Scapula
"The shoulder-blade is a large, flat, three-sided bone, which is placed on the upper and back…
Tibia and Fibula
"The leg consists, like the forearm, of two bones. The larger, a strong, three-sided bone with…
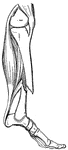
Broken Tibia
"When a bone is broken, blood trickles out between the injured parts, and afterwards gives place to…
Ulna and Radius
"The ulna, or elbow bone, is the larger of these two bones. It is joined to the humerus by…