81 illustrations from Greek mythology including: Achilles, Admetus, Adonis, Aegis, Aeneas, Aeolos, Aesculapius, Aethra, Amazon, Amphion, Amphitrite, Aphrodite, Apollo, Argus, Ariadne, Artemis, Astrae, Atlanta, Athena, and Atlas

The Acropolis of Athens - Restoration of the Propylaea
Illustration of the Acropolis restored to what it may have looked like when originally completed. The…

Adonis and Venus
Adonis was loved by Venus. When he was killed by a wild boar while hunting, Venus changed his blood…

Aegis
"signifies, literally, a goat skin. According to ancient mythology, the aegis worn by Jupiter was the…

Dido parting with Aeneas
"Aeneas parted from Dido, though she tried every allurement and persuasion to detain him." —Bulfinch,…

Amphion and Zethus
"Amphion was the son of Jupiter and Antiope, queen of Thebes. With his twin brother, Zethus he was exposed…

Aphrodite
"The Greek goddess of love and beauty, identified by the Romans with their Venus, who was originally…

Phoebus Apollo
Apollo was the son of Zeus and Leto, twin brother of Diana, one of the principal gods of the Greeks,…
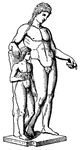
Apollo and Hyacinthus
"Apollo was passionately fond of a youth named Hyacinthus. He accompanied him in his sports, carried…

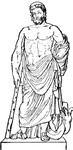
Apollo of the Belvedere - Front View of Statue
Illustration of the famous statue Apollo Belvedere. Created circa AD120-140, the statue depicts Apollo…
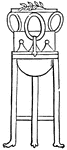
Tripod of Apollo
"It was the universal practice of the Greeks to undertake no matter of importance without first asking…

Apotheosis
"The enrollment of a mortal among the gods. The mythology of Greece contains numerous instances of the…

Building the Argo
"At that time the only species of navigation known to the Greeks consisted of small boats or canoes…
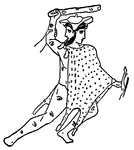
Argus
"Now Argus had a hundred eyes in his head, and never went to sleep with more than two at a time, so…

Ariadne abandoned
"Ariadne on wakening and finding herself deserted abandoned herself to grief." —Bulfinch, 1897