Brain of Embryo
Profile view of brain of a human embryo of ten weeks. The various cranial nerves are indicated by numerals.…
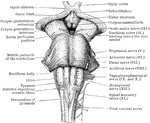
Front view of Medulla, Pons, and Mesencephalon
Front view of the medulla, pons, and mesencephalon of a full term human fetus.
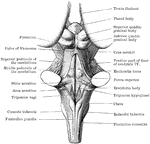
Back View of Medulla, Pons, and Mesencephalon
Back view of the medulla, pons, and mesencephalon of a full term human fetus.
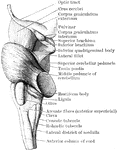
Lateral View of Medulla, Pons, and Mesencephalon
Lateral view of the medulla, pons, and mesencephalon of a full term human fetus.
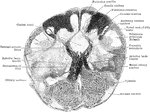
Transverse Section Through Closed Part of Medulla
Transverse section through the closed part of the human medulla immediately above the decussation of…
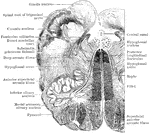
Section Through Medulla in Olivary Region
Transverse section through the human medulla in the lower olivary region.
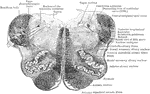
Section Through Medulla in Olivary Region
Transverse section through the the middle of the olivary region of the human medulla or bulb.
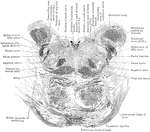
Section Through Pons Varolii
Section through the lower part of the human pons varolii immediately above the medulla.
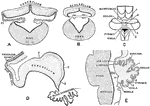
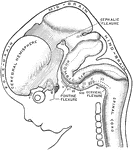
Development of Cerebellum
Showing the development of the cerebellum. A, Transverse section through the forepart of the cerebellum…
Biscayne Bay
An illustration of Biscayne Bay, is a lagoon that is approximately 35 miles (56 km) long and up to 8…

Shedu
The Shedu is a celestial being from Mesopotamian mythology. He is a human above the waist and a bull…

Norse Galley
An illustration of a Norse Galley. Norse is an adjective relating things to Norway, Denmark, Faroe Islands,…
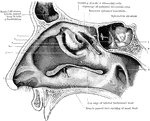
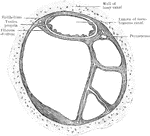
Outer Wall of Nose
View of the outer wall of the nose. The turbinated bones having been removed. Labels: 1, vestibule,…
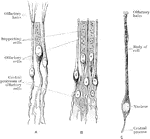
Olfactory and Supporting Cells
Olfactory and supporting cells in a frog and a human. A. Frog. B. Human. C. Human.

Cones and Rods of Retina
A. A cone and two rods from the human retina (modified from Max Schultze); B. Outer part of rod separated…
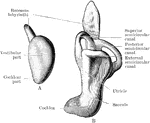
Development of Labyrinth
A, Left labyrinth of a human embryo of about four weeks; B, left labyrinth of a human embryo of about…

Tongue of Human and Rabbit
A, Section through papilla vallata of a human tongue. B, Section through part of the papilla foliata…
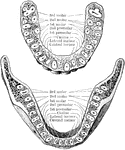
Jaw Showing Roots of Teeth
Horizontal section through both the upper and lower jaws to show the roots of the teeth. The sections…

Cockroach
An illustration of a male (right) and female (left) cockroach. Cockroaches (or simply "roaches") are…
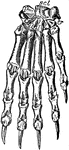
Bear Foot
"Palmar aspect of left fore foot of a black bear (Ursus americanus). scl, scapholunar; c, cuneiform;…
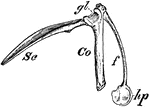
Bird Scapula
"Right shoulder-girdle or scapular arch of fowl, showing hp, the hypoclidium; f, furculum; Co, coracoid;…

Watercress
Watercresses are fast-growing, aquatic or semi-aquatic, perennial plants native from Europe to central…

American Harpy Eagle
The American Harpy Eagle (Harpia harpyja) is a neotropical eagle, often simply called the Harpy Eagle.…

Sphinx
A Sphinx is a zoomorphic mythological figure which is depicted as a recumbent lion with a human head.
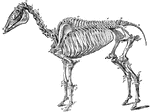
Skeleton of a Horse
The skeleton of a horse. Axial Skeleton. The Skull. Cranial Bones: a, occipital, 1; b, wormian, 1; c,…
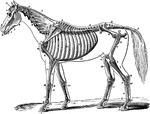
Skeleton of a Horse
The skeleton of a horse. Showing its relation to the contour of the animal, viewed laterally. Labels:…
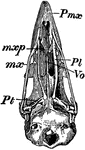
Bird Skull
"Schizognathous skull of common fowl. pmx, premaxilla; mxp, maxillopalatine; mx, maxilla; pl, palatine;…
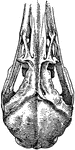
Curlew Skull
"Schizorhinal skull of curlew (top view), showing the long cleft, a, between upper and lower forks of…
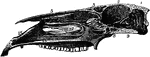
Longitudinal Section of Horse Skull
Longitudinal section of a horse's skull. Labels: 1, supraoccipital bone and crest; 2, parietal bone;…
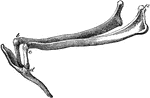
Hyoid Series of Bones in a Horse
The hyoid series is composed of five distinct pieces- a body, or hyoid bone proper, two cornua or horns…
Horse Leg
External view of bones of right carpus, metacarpus, and digit of a horse. 1, distal end of radius; 2,…
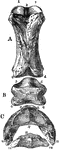
Phalanges of a Horse
Posterior view of phalanges of a horse disarticulated. Labels: a, os suffraginis; b, os coronae; C,…
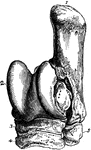
Tarsus of a Horse
Bones of left tarsus of a horse, seen from in front and outside. Labels: 1, calcaneum; 2, astragalus;…
Horse Leg
External view of bones of left tarsus, metatarsus, and digit of a horse. Labels: 1, distal end of tibia;…
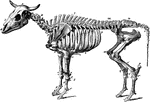
Ox Skeleton
The skeleton of an ox. Axial Skeleton. The skull. Cranial Bones- occipital, 1: b, parietal, 2; a, frontal,…
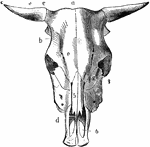
Ox Skull
Skull of an ox, superior aspect. Labels: a, frontal crest; b, lateral crest; c, horn core; d, nasal…
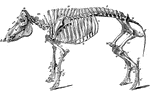
Skeleton of a Hog
Skeleton of the hog. Axial skeleton. The skull. Cranial bones- a, occipital, 1; b, parietal, 2; d, frontal,…
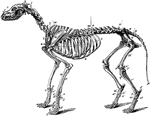
Skeleton of a Dog
The skeleton of the dog. Axial skeleton. The skull. Cranial bones- a, occipital, 1; b, parietal, 2;…

The Wyoming Monument
The Monument marks the grave site of the bones of victims of the Wyoming Massacre, which took place…

Osborn Hall, Yale University
Many buildings stood on the Old Campus which were removed to make way for the current configuration…

Chirotherium Tracks
An illustration of a fossil containing Chirotherium tracks. Chirotherium (also known as Cheirotherium)…

Sedan
The sedan or litter is a wheelless, human-powered vehicle used to carry one person sitting inside.
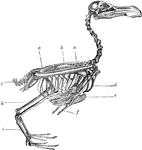
Skeleton of a Bird
The skeleton of a bird. Labels: a, radius and ulna; b, dorsal vertebrae; c, sacrum and pelvis; g, ploughshare…
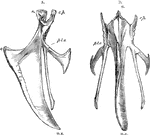
Sternum of a Bird
The sternum of a bird. Label: a, lateral aspect; b, inferior aspect; r, rostrum; c.p, costal process;…
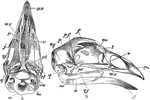
Skull of a Bird
The skull of a bird. Labels: a, inferior aspect, the mandible being removed; b, lateral aspect; px,…
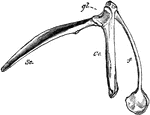
Pectoral Arch of a Bird
The pectoral arch of a bird. Labels: sc, scapula; co, coracoid bone; f, clavicle, terminating below…
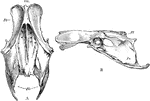
Pelvis of a Bird
The pelvis of a bird. Labels: a, superior; b, lateral aspect; sm, sacrum; Il, ilium; Is, ischium; Am,…

Pixy and a Man
A pixy named Thomas alarmed that a human has just invaded his lawn by jumping over Thomas' wall.
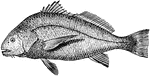
Saltwater Drum
Pogonias chromis, a name of several fish so called from the drumming noise they make, said to be due,…

Foxglove
An illustration of: 1, Coralla cut open showing the four stamens; 2, Unripe fruit (lengthwise); 3, ripe…

Masked Crab
Corystes cassivelaunus, the masked crab, helmet crab or sand crab, is a burrowing crab of the North…

Entrance to the Great Temple at Abu Simbel
In 1959 an international donations campaign to save the monuments of Nubia began: the southernmost relics…

Winged Bull from Nimrud
The Sumerian word lama, which is rendered in Akkadian as lamassu, refers to a beneficient protective…