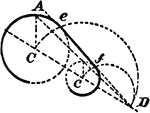
Construction Of Tangent To 2 Circles
An illustration showing how to construct a tangent to 2 given circles of different diameters. "Join…
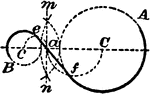
Construction Of Tangent Between 2 Circles
An illustration showing how to construct a tangent between 2 given circles. "Join the centers C and…
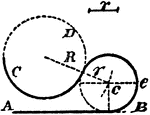
Construction Of A Circle Tangent To A Line And A Circle
An illustration showing how to construct a circle tangent to a given line and given circle. "Add the…
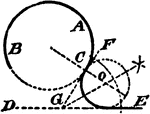
Construction Of A Center And Radius Of A Circle That Will Tangent A Given Circle
An illustration showing how to construct the center and radius of a circle that will tangent a given…
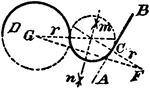
Construction Of A Center And Radius Of A Circle That Will Tangent A Given Circle And Line
An illustration showing how to construct the center and radius of a circle that will tangent a given…
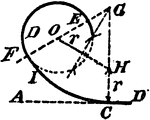
Construction Of A Center And Radius Of A Circle That Will Tangent A Given Circle And Line
An illustration showing how to construct the center and radius of a circle that will tangent a given…
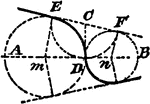
Construction Of Two Circles That Tangent Themselves and 2 Given Lines
An illustration showing how to construct two circles that tangent themselves and two given lines. "Draw…
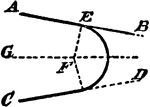
Construction Of A Circle That Tangents 2 Given Lines
An illustration showing how to construct a circle that tangents two given lines inclined to one another…
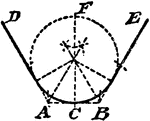
Construction Of A Circle That Tangents 2 Given Lines And Goes Through A Given Point
An illustration showing how to construct a circle that tangents two given lines and goes through a given…
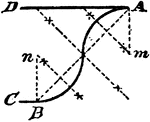
Construction Of A Cyma
An illustration showing how to construct a cyma, or two circle arcs that will tangent themselves, and…
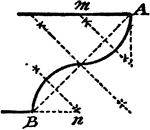
Construction Of A Talon
An illustration showing how to construct a talon, or two circle arcs that will tangent themselves, and…
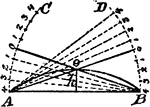
Construction Of A Circle Arc
An illustration showing how to construct a circle arc without recourse to its center, but its chord…
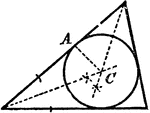
Construction Of The Center And Radius Of A Circle Tangent To Triangle Sides
An illustration showing how to construct a center and radius of a circle that will tangent the three…
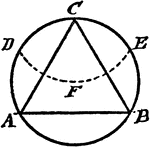
Construction Of An Equilateral Triangle Inscribed In A Circle
An illustration showing how to construct an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle. "With the radius…
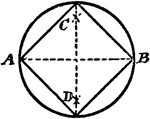
Construction Of A Square Inscribed In A Circle
An illustration showing how to construct a square inscribed in a circle. "Draw the diameter AB, and…
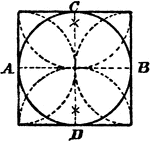
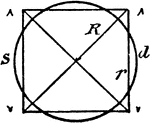
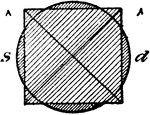
Construction Of A Square Circumscribed About A Circle
An illustration showing how to construct a square circumscribed about a circle. "Draw the diameters…
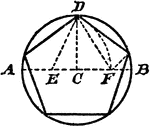
Construction Of A Pentagon Inscribed In A Circle
An illustration showing how to construct a pentagon inscribed in a circle. "Draw the diameter AB, and…
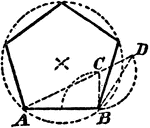
Construction Of A Pentagon On A Line
An illustration showing how to construct a pentagon on a given line. "From B erect BC perpendicular…
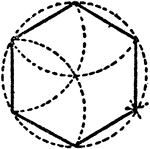
Construction Of A Hexagon In A Circle
An illustration showing how to construct a hexagon in a given circle. "The radius of the circle is equal…
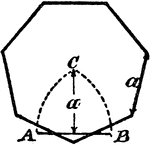
Construction Of A Heptagon
An illustration showing how to construct a heptagon, or septagon. "The appotem a in a hexagon is the…
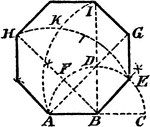
Construction Of An Octagon
An illustration showing how to construct an octagon on a given line. "Prolong AB to C. With B as center…
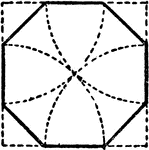
Construction Of An Octagon From a Square
An illustration showing how to construct a regular octagon from a square by cutting off the corners…
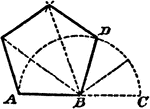
Construction Of A Regular Polygon On A Line
An illustration showing how to construct a regular polygon on a given line without resort to its center.…
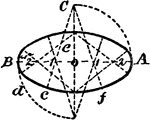
Construction Of An Isometric Ellipse
An illustration showing how to construct an isometric ellipse by compass and six circle arcs. "Divide…
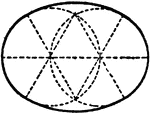
Construction Of An Ellipse
An illustration showing how to construct an ellipse using circle arcs. "Divide the long axis into three…
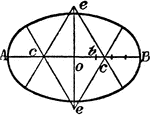
Construction Of An Ellipse
An illustration showing how to construct an ellipse using circle arcs. "Given the two axes, set off…
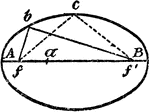
Construction Of An Ellipse
An illustration showing how to construct an ellipse. Given the two axes, set off half the long axis…
Construction Of An Ellipse Tangent To Two Parallel Lines
An illustration showing how to construct an ellipse parallel to two parallel lines A and B. "Draw a…
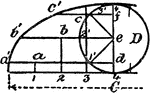
Construction Of A Cycloid
An illustration showing how to construct a cycloid. "The circumference C=3.14D. Divide the rolling circle…
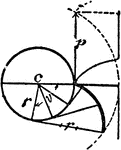
Construction Of An Evolute Of A Circle
An illustration showing how to construct an evolute of a circle. "Given the pitch p, the angle v, and…
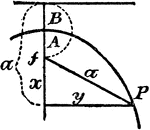
Construction Of A Parabola
An illustration showing how to construct a parabola. "Given the axis of ordinate B, and vertex A. Take…
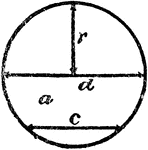
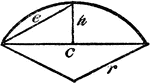
Radius, Diameter, and Chord In A Circle
An illustration showing a circle with radius r, diameter d, and chord c.
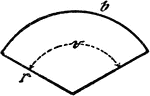
Circle Sector
An illustration showing a circle sector with radius r, center/central angle v, and length of circle…
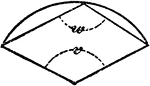
Circle Sector
An illustration showing a circle sector with center/central angle v and polygon angle w.
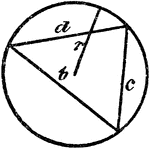
Triangle Inscribed In A Circle
An illustration showing a triangle with sides b, c, and d inscribed in a circle with radius r.
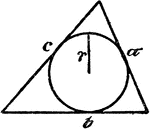
Circle Inscribed In A Triangle
An illustration showing a circle with radius r inscribed in a triangle with sides a, b, and c.
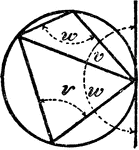
Quadrilateral Inscribed In A Circle
An illustration showing a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle that is tangent to a line.
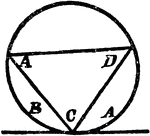
Triangle Inscribed In A Circle
An illustration showing a triangle with angles A, C, and D inscribed in a circle which is tangent to…
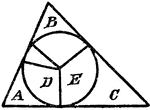
Circle Inscribed In A Triangle
An illustration showing a circle with sectors D and E inscribed in a triangle with angles, A, B, and…
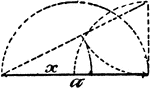
Model Of Geometric Proportions
An illustration showing a model that illustrates the following relationships: a:x = x:a - x, x = √(a²…
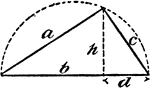
Right Triangle Inscribed In A Semicircle
An illustration of a right triangle inscribed in a semicircle.
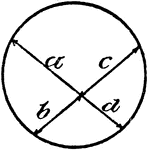
Model Of Geometric Proportions In A Circle
An illustration showing a model of a circle with intersecting chords that illustrates the following…

Geometry
Two students drawing geometrical shapes on the chalkboard. A student is also using a scale while students…
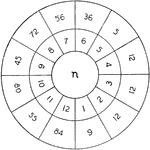
Multiples
The circle of multiples can be used as a practice game in class. The outside ring are multiples and…
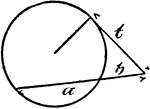
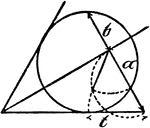
Model Of Geometric Relationships In A Circle
An illustration showing a model of a circle with an exterior angle formed between a tangent and a secant…
Model Of Geometric Relationships In A Circle
An illustration showing a model of a circle with angles formed between tangents and secants that illustrates…
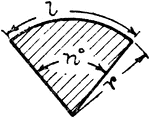
Sector Of Circle
Illustration of a sector of a circle. A sector is the space between an arc and two radii drawn to the…
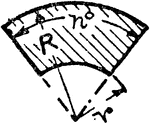
Sector Of A Hollow Circle
Illustration of a sector of a hollow circle. A sector is the space between an arc and two radii drawn…
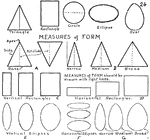
Shapes
Four different types of forms or shapes: right triangle, isosceles triangle, rectangle, and circle.
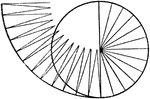
Triangles Making Up A Circle
Illustration showing that a circle may be considered as made up of triangles whose bases form the circumference.

Math Game
Three students playing a math game in the classroom, throwing beanbags into a circle and doing multiplication…
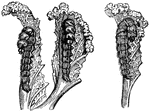
Caterpillars of the Cabbage-Butterfly
"Shows how the head advances over half the circumference of the circle which it has to describe, and…

Wreath of roses
"Use the entire blossom mingled with buds and green leaves, all short stemmed, not longer than three…

Pentacrinus Caput Medusae (Muller)
"The Crinoidea, which belong to the family of starfishes, are mostly attached to marine rocks…

Cristatella Mucedo (Cuvier)
"The whole internal cavity in these animals is occupied by little, white tubes. The mouth opens at the…
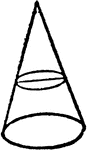
Circle
Illustration showing a circle formed by the intersection of a plane perpendicular to the axis of the…