!["View of the remains of the French Works. These remains are in the southeastern suburbs of the city, about half way between the [African American] Cemetary and the residence of Major William Bowen, seen toward the right of the picture. The banks have an average height, from the bottom of the ditch, of about five feet, and are dotted with pines and chincapins or dwarf chestnuts, the former draped with moss. The ground is an open common, and although it was mid-winter when I was there, it was covered with green grass, bespangled with myriads of little flowers of stellar form. This view is from the direction of the town looking southeast."—Lossing, 1851](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/14100/14147/french-works_14147_mth.gif)
French Works
"View of the remains of the French Works. These remains are in the southeastern suburbs of the city,…

Fort Moultrie
"View at Fort Moultrie. This view is from the southwestern angle of Fort Sullivan, looking toward Jame's…

Turtle Bay
"View at Turtle Bay. Turtle Bay is a small rock-bound cove of the East River, at the foot of Forty-seventh…
Broadway
"View at the foot of Broadway. General Charles Lee's troops marched to New York."—Lossing, 1851

Gravesend Bay
"View at Gravesend Bay. This view is from the road on the high shore, a little below Fort Hamilton,…

Brower's Mill
"Brower's Mill. This is a view of the old mill of the Revolution, as it appeared when I made the sketch…

Washington's Head-Quarters
"Washington's head-quarters. The house occupied by Washington while the army was at White Plains is…

Bronx
"Place where the British crossed the Bronx. This view is from the southeastern side of the Bronx, a…

Chatterton's Hill
"Chatterton's Hill, from the rail-way station. This is a view of the southeastern side of Chatterton's…

Fort Washington
"View at Fort Washington. This is a view from the site of the interior works at Fort Washington from…

King's Bridge
"View at King's Bridge. This view is from the southwest side of the stream, from near the tide-mill.…

Lee Medal Back
"Medal awarded to Lee. On the twenty second of September, Congress honored Lee with a vote of thanks,…

Washington's Quarters
"Washington's Quarters. This is a view of the southwest front of the mansion. The room occupied by Washington…
Sowing
"Egyptian Sowing. The people were mainly agricultural, but employed rude methods of cultivation. In…

Pompey
"Pompey was one of the men, who, having distinguished himself in foreign wars, was looked upon as the…

Caesar's Death
"The Death of Caesar. Naturaly such extraordinary success made him enemies, and though the city seemed…

Godfrey de Bouillon Tomb
"Tomb of Godfrey de Bouillon. During the Crusades, the Kingdom of Jerusalem in 1099. The conquered lands…

Canterbury Cathedral
"Canterbury Cathedral, which was a key place during the contest with King John. In the quarrel with…

William the Conqueror
"William the Conqueror (1066-1087), as represented on his seal. Although William really ruled 'as king…

Death of Becket
"Death of Becket. During the early years of the reign Thomas A. Becket, as the king's chancellor, had…

Charles V
"Charles V ruled over wider dominions than any European sovereign since Charlemagne. He belonged to…

Henry VIII
"Henry VIII (1509-1547) came to the throne in 1509, inheriting a vast treasure which he owed to the…

Gustavus Adolphus
"Gustavus Adolphus entered Germany at the head of 16,000 men. Among some of the Protestants there was…

Louis XIV
"The age of Louis XIV. during the reign of Louis XIV, the son and successor of Louis XIII (1643-1715),…

Charles I
"Charles I (1625-1649) was a far abler ruler than his father. He was a man of greater courage and more…

Acanthophis
"A genus of venomous serpents, they are of small size, live on dry land, and feed upon frogs, lizards,…

Frederick the Great
"Frederick II (The Great, 1740-1786). The young Frederick had been brought up in a rough school. His…

George III, King of England
"George III (1760-1815). The first two Hanoverian kings were ignorant of English politics and obliged…

Bastile
"The taking of the Bastile, July 14, 1789. The Parisian mob, not satisfied with the formation of the…

Acorn-moth
"a, larva within acron; b, acorn infested with the larva; c, head and thoracic segments of larva; d,…

Garibaldi
"Garibaldi was a patriot who started up a revolt in Sicily and took possession of the island, then passed…

Stamp Act
"Stamp from the Stamp Act. The first direct issue of importance between the colonies and England came…

Stamp Act
"Stamp from the Stamp Act. The first direct issue of importance between the colonies and England came…

Pheasant Feather
"Feather from Argus Pheasant. (a,d, main stem; d, calamus; a, rachis; c,c,c, vanes cut away on right…

Hale Statue
"Statue of Nathan Hale. It was during his treated that an event occurred which showed how much Americans…

Agnel
"Agnel of John II., King of France. Agnel- A French gold coin bearing a figure of the paschal lamb,…

Western Train
"A western emigrant train. The occupation of the west. With every year the line of settlements was pushed…
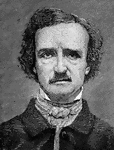
Edgar Allan Poe
"Edgar Allan Poe, the son of a Baltimore gentleman and an actress, Elizabeth Arnold, was born in Boston,…

Perch
"An embiotocoid fish, with small scales, uniserial and jaw teeth, and lip free and deeply cut along…

Atlantic Cable
"Laying the Atlantic Cable. In 1866, a previous attempt in 1858 having failed, a telegraphic cable was…

Tiger Beetle Larve
"The common European species, Cincindela campestris, may be found flying and running around…

Tiger Beetle and Larvae
"The common European species, Cincindela campestris, may be found flying and running around…

Bombadier Beetle
"The bombadier beetle has a large oval abdomen, which secretes a caustic fluid. They live in societies,…

Click Beetle
"The Elater striatus of Caenne, is an inch long, of a black color, and striped upon the back."…

William McKinley
"In the general election of 1896, the principal question at issue was the financial policy of the country.…

Capricorn Beetle
"The insects of this tribe, called Capricorn Beetles and distributed throughout most parts…

Honey Bee
"They are said to have originated in Greece, but have since spread all over the world; they live in…