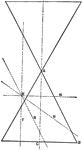
Conic Sections 2D
Two dimensional view of the cuts required to create the conic sections hyperbola, parabola, ellipse,…
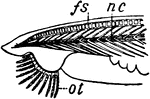
Side view of lancelet
"Side view of Amphioxus: fs, fin supports; nc, notochord; ot, oral tentacles."—Finley,…
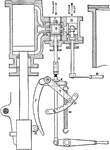
Valve gear of a steam hammer
"The valve gear for operating the steam hammer is shown separately, the cylinder and valve chest being…
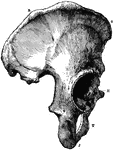
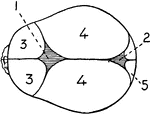
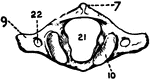
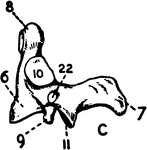
Part of the Human Pelvic Bone
The Os Innominatum, or nameless bone, so called from bearing no resemblance to any known object, is…
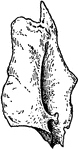
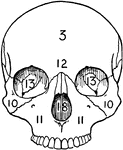
Human Lachrymal Facial Bone
Lachrymal Bone. The lachrymal are the smallest and most fragile bones fo the face. They are situated…
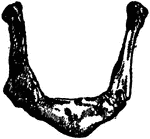
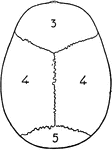
Human Hyoid Bone
The hyoid, os hyoides, or tongue bone, is an isolated, U-shaped bone lying in front of the throat, just…
Human Spinal Column
Side view of spinal column, without sacrum and coccyx. Labels: 1 to 7, cervical vertebrae; 8 to 19,…
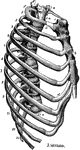
Human Thorax (Chest)
Thorax. The thorax, or chest, is an elongated conical-shaped cage, formed by the sternum and costal…
Human Sternum Bone
Sternum, front and side view. The sternum, or breast bone, is a flat narrow bone, situated in the median…
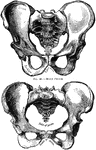
Human Pelvis, Male and Female
Male pelvis (top) and female pelvis (bottom). The pelvis is stronger and more massively constructed…
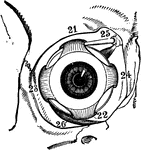
Muscles of the Human Eyeball
Muscles of right eyeball within the orbit, seen from the front. Labels: 21, superior rectus; 22, inferior…
Muscles of the Forearm
Muscles in front of forearm. Labels: 62, pronator teres; 63, 65, 66, 67, flexors; 70, supinator longus;…
Muscles of the Leg
Muscles of the leg, superficial view of the calf. Labels: 22, tendo Achillis (Achilles heel); 21, gastrocnemius;…
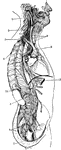
General View of the Sympathetic Nervous System
General view of the sympathetic nervous. Labels: 1,2,3, cervical ganglia; 4, 1st thoracic ganglion;…
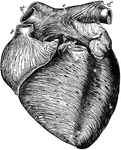
Anterior View of the Heart
Anterior view of the heart, dissected, after long boiling to show the superficial muscular fibers. The…
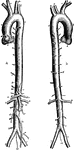
The Aorta
The aorta. A, from in front; B, from behind, with the origin of its principal branches. Labels: 1,2,…
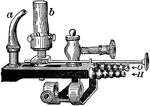
Lime-Light Burner
a is the burner tip for an oxy-hydrogen flame, and b is the cylinder of quicklime.
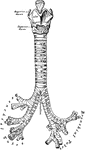
Front View of the Cartilages of the Larynx, Trachea and Bronchi.
Front view of cartilages of larynx, trachea and Bronchi.
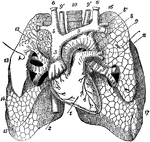
Anterior View of the Lungs and Heart
Anterior view of the lungs and heart. Labels: 1, heart; 2, inferior vena cava; 3, superior vena cava;…
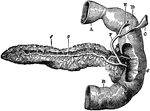
Posterior View of Pancreas
Posterior view of pancreas. Labels: 1, pancreas; 2, pancreatic duct; 6, opening of common duct, formed…
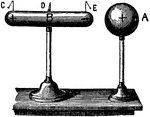
Induced Charge
"Experiment illustrating the nature of an induced charge. The apparatus consists of a metal ball and…
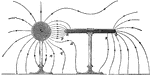
Lines of Force under Induction
"Lines of force of a charged sphere and a conductor under induction. The negative electrification on…

Lenz's Law
"Experiment illustrating Lenz's Law. If a copper ring be held in front of an ordinary elecromagnet,…
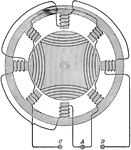
Altenating Current Motor
"...consists of a circular, multipolar field magnet, inclusing a cylinder armature with coils wound…

Archimedes' Water Screw
"It consists of a tube, made of lead, or strong leather, coiled round a cylinder of wood or iron, as…
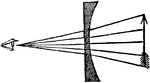
View of an Arrow Through a Plano Convex Lens
"View of an arrow through a plano convex lens will have the arrow appear smaller than it actually is."…
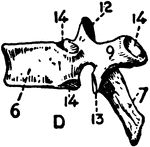
Spinal Column
Side view of the spinal column, with the vertebrae numbered: C1-7, cervical vertebrae; D1-12, dorsal…
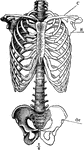
Skeleton of Trunk
The skeleton of the trunk and the limb arches seen from the front. Labels: c, clavicle; S, scapula;…
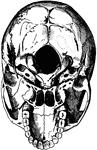
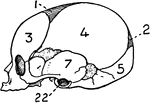
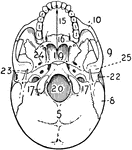
Base of the Skull
The base of the skull. "The lower jaw has been removed. At the lower part of the figure is the hard…
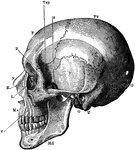
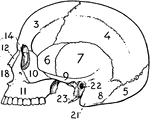
The Skull
A side view of the skull. Labels: O, occipital bone; T, temporal bone; Pr, parietal bone; F, frontal…
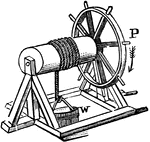
Wheel and Axle with Rope and Bucket
"The wheel and axle consists of a wheel united to a cylinder in such a way that they may turn together…
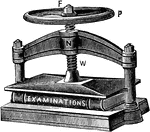
Screw press
"A screw is a cylinder, generally made of wood or metal, with a spiral ridge (the thread) winding about…

Archimedies Principle
"From one end of a scale-beam, suspend a cylindrical metal bucket, b, with a solid cylinder, a, that…
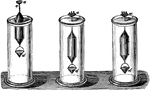
Nicholson Hydrometer
"The Nicholson hydrometer of constant volume is a hollow cylinder carrying at its lower end a basket,…
!["The graphic method of studying sounds, which fairly meets even the exacting demands of physicists, and is largely used by them may be briefly explained thus: Suppose the smoked plate [shown] to be a sheet of smoked paper fastened around a cylinder that is mounted that, when it is turned by a crank, the screw cut upon the axis moves the cylinder endwise as shown. Such and instrument is called a vibroscope." -Avery 1895](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/35900/35992/vibroscope_35992_mth.gif)
Graphic Method of Studying Sounds Using a Vibroscope
"The graphic method of studying sounds, which fairly meets even the exacting demands of physicists,…
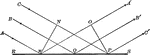
Explanation of Reflection
"Consider a beam of light as made up of a number of ehter waves moving forward in air and side by side,…
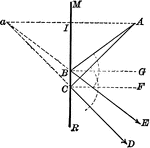
Plane Mirror
"If an object is placed before a plane mirror, a virtual image appears behind the mirror. Each point…
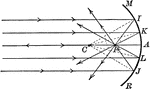
Foci of Concave Mirror
"The foci of concave mirrors may be in front of the mirror, in which case they are real; or they may…
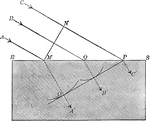
Explanation of Refraction
"Thus, when erher waves that constitute light are transmitted through glass, they are hindered by the…
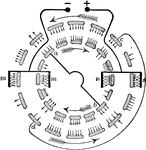
Design of the Wimhurst Machine
"The tin-foil strips or carriers on the rear plate of a Wimhurst machine are represented by the outer…
!["One of the best-known instruments of this [electrometer] class is Coulomb's torsion-balance, which consists essentially of gilt ball, i, carried at the end of a horizontal shellac needle that is suspended by a fine silver wire from the top of a tube that rises from the cover of the enclosing glass cylinder. A vertical insulating rod passing through the cover carries a handle, a, and a gilt ball, e, at its ends." -Avery 1895](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/36000/36071/torsion_bal_36071_mth.gif)
Coulomb's Torsion-Balance
"One of the best-known instruments of this [electrometer] class is Coulomb's torsion-balance, which…
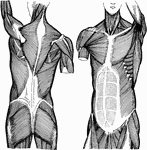
Trunk Muscles
Left - back view of the muscles of the trunk. Right - front view of the muscles of the trunk.
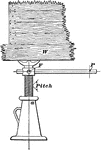
Using a Screw to Raise Weight
"A screw is a cylinder with a helical proection winding around its circumference. This helix is called…
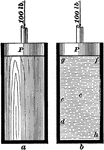
Water versus Wood Pressure
"The vessel a is fitted with a wooden bock of the same size as, and free to move in, the cylinder; the…