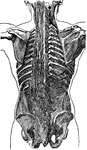
Spinal Column
Lateral view of the spinal column. Labels: 1, atlas; 2, dentata 3, seventh cervical vertebra; 4, twelfth…
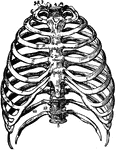
The Bones of the Thorax
Front view of the bones of the thorax, including the ribs, sternum and vertebrae. Labels: 1, first bone…
Humerus
Anterior view of humerus (bone of the leg) of the right side. Labels: 1, shaft or diaphysis; 2, the…
Radius
Anterior view of radius (bone of the arm) of the right side. Labels: 1, cylindrical head; 2, surface…
Ulna
Anterior view of the ulna (bone of the arm) of the left side. Labels: 1, olecranon process; 2, greater…
Femur
Posterior view of the femur (bone of the leg). Labels: 1, depression for round ligament; 2, the head;…
Tibia
Anterior view of the tibia (bone of the leg). Labels: 1, spinous process; 2, surface for condyles of…

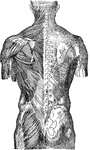
Back View of the Muscles of the Body
Muscle of the body, back view: The fascia is left upon the left limbs, removed from the right.

Front View of the Muscles of the Body
Muscle of the body, front view: On the right half, the superficial muscles; left half, deep-seated muscles.
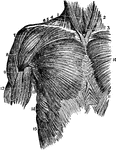
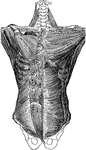
Muscles of the Upper Trunk
Superior muscles of the upper front of the trunk. Labels: 1, sterno-hyoid; 2, sterno-cleido-mastoid;…
Muscles of the Forearm
Outer layer of muscles on the front of the forearm. Labels: 1, biceps flexor cubiti; 2, brachialis internus;…
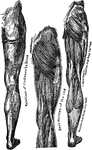
Muscles of the Front of the Leg
Muscles of the front of the leg. Labels: 1, tendon of quadriceps; 2, spine of tibia; 3, tibialis anticus;…
Forearm and Hand
Deep dissection of the front of the forearm and hand, showing the muscles, nerves, blood vessels, etc.…
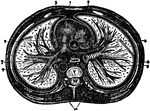
The Thorax
Diagram of a transverse section of the thorax. Labels: 1, anterior mediastinum; 2, internal mammary…
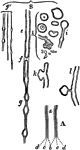
Nerve Tubules
A diagram of nerve tubules A nerve tube consists of a white portion which is fatty, and which protects…
Brain and Spinal Cord
Anterior view of the brain and spinal marrow. Labels: 1, 1, hemispheres of the cerebrum; 2, great middle…
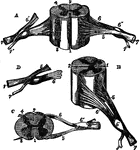
Different View of the Spinal Cord
Different views of a portion of the spinal cord from the cervical region, with roots of the nerves slightly…
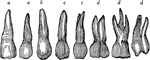
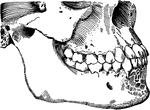
Teeth of the Upper Jaw
Half of the teeth of the upper jaw. a,a, are the two front cutting teeth. d,d,d are…
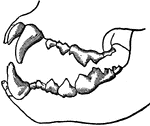
Teeth of a Carnivorous Animal
Teeth of a carnivorous animal that lives on flesh alone. The front teeth are designed for tearing, while…

Teeth of an Herbivore
Teeth of an herbivore, showing the rough surface of some of these teeth. Herbivores have no tearing…
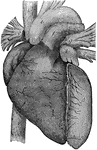
Heart, Front View of
A representation of the heart as it really appears showing the front view. At a is the right…
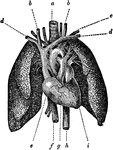
Heart and Lungs
The heart, showing its relative position to the lungs. The heart is almost wholly covered up by the…
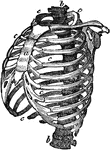
Structure of the Chest
Structure of the chest, showing the framework of the bones which are connected together chiefly by muscles.…
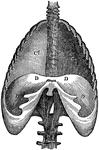
The Diaphragm
The diaphragm, which is the principal muscle that act sin breathing. Here you have the cavity of the…
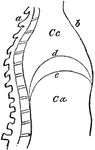
The Diaphragm
Diaphragm of the diaphragm and it's placement in the chest. Let a represent the spinal column,…
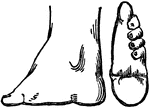
Foot of Chinese Woman
On the left is a side view of a Chinese lady's foot that has been bound while it was growing to stunt…
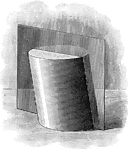
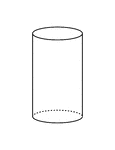
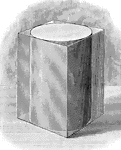
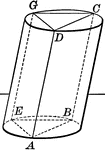
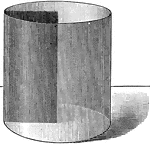
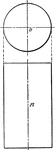
Plane Passing Through A Cylinder
Illustration of a plane passing through a cylinder. Every section of a cylinder made by a plane passing…
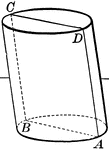
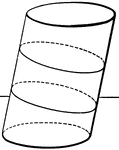
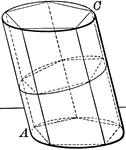
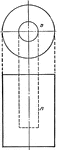
Plane Passing Through A Cylinder
Illustration of a plane passing through a cylinder. Every section of a cylinder made by a plane passing…
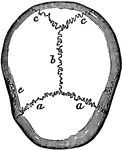
Cranial Sutures
The bones of the top of the head are fastened together by what are called sutures which are locked together…
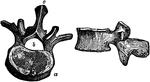
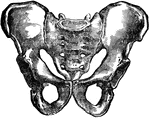
Two Views of a Vertebra
Two views of vertebra. 24 vertebrae make up the spinal column. On the left figure, a is the…
The Spinal Column
View of the entire spinal column. The bodies of the vertebrae are in the front with the spinous processes…
Vertebra of a Fish
The vertebra of a fish, which is very different from that of a human. It has but two processes, …
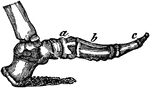
Side View of the Bone of the Foot
Bones of the foot, side view. In this figure the bones of the tarsus extend from the heel to a;…
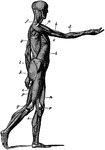
Side View of the Muscles of the Body
Side view of the muscles of the body, showing those that lie directly under the skin. Other deeper muscles…
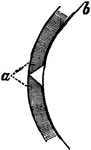
Eye Lid
The lids of the eye close in such a way as to leave a three-cornered canal between them and the surface…
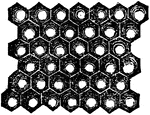
Eye of an Insect
A magnified view of a small portion of the surface of an insect's compound eye which is composed of…
Copper Hard Times Token, ND
Hard Times Token (unknown) US coin. Obverse has an image of the front of the Merchants Exchange surrounded…