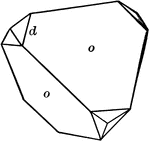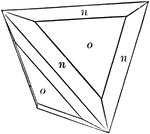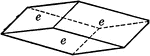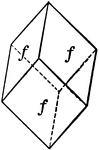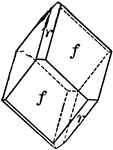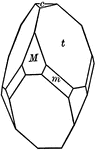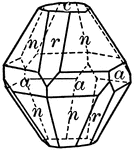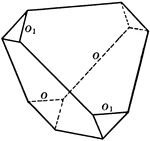
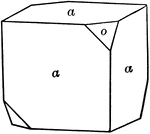
Tristetrahedron
"The faces of the tristetrahedron correspond to one-half the faces of a trapezohedron." — Ford,…
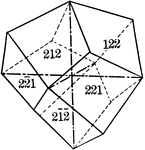
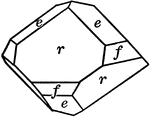
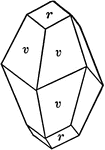
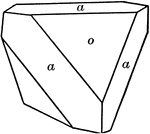
Deltoid dodecahedron
"The faces of the deltoid dodecahedron correspond to one-half those of the trisoctahedron." —…
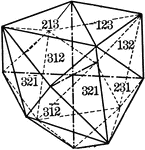
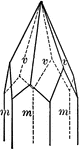
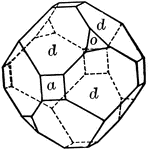
Hexakistetrahedron
"The faces of the hexakistetrahedron correspond to one-half the faces of the hexoctahedron." —…
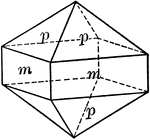
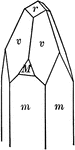
Cube and tetrahedron
"A combination of cube and tetrahedron. It will be noted that the tetrahedron faces truncate the alternate…
Tetrahedron and cube
"A combination of cube and tetrahedron. It will be noted that the tetrahedron faces truncate the alternate…
Cube, dodecahedron and tetrahedron
"A combination of cube, dodecahedron, and tetrahedron." — Ford, 1912
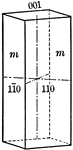
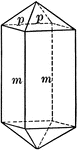
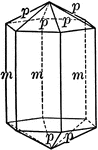
First order prism
"The prism of the first order consists of four rectangular vertical faces, each of which intersects…
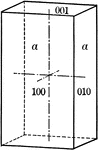
Second order prism
"The prism of the second order consists of four rectangular vertical faces, each of which intersects…
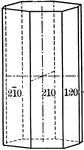
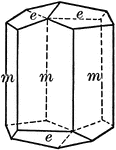
Ditetragonal prism
"The dietetragonal prism is a form consisting of eight rectangular vertical faces, each of which intersects…
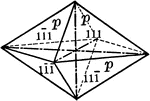
First order pyramid
"The pyramid of the first order is a form consisting of eight isoceles triangular faces, each of which…
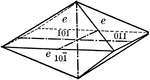
Second order pyramid
"The pyramid of the second order is a form composed of eight isoceles triangular faces, each of which…
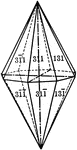
Ditetragonal pyramid
"The ditetragonal pyramid is a form composed of sixteen isoceles trianglular faces, each of which intersects…
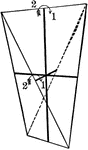
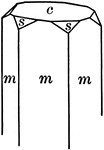
Symmetry of Sphenoidal class
"The Sphenoidal Class corresponds in the Tetragonal system to the Tetrahedral class in the Isometric…
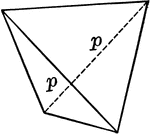
Sphenoid
"It consists of four isoceles triangular faces which intersect all three of the crystallographic axes,…
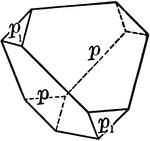
Sphenoid, positive and negative
"It consists of four isoceles triangular faces which intersect all three of the crystallographic axes,…
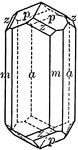
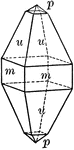
Scapolite
"A crystal of scapolite, upon which the faces of the third-order pyramid are shown." — Ford, 1912
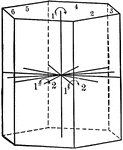
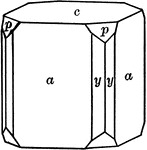
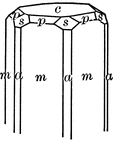
Symmetry of normal class
"The symmetry of the Normal Class of the Hexagonal System is as follows: The vertical crystallographic…
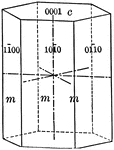
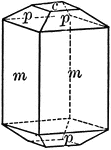
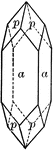
Prism of the first order
"This is a form consisting of six rectangular vertical faces each of which intersects two of the horizontal…
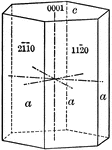
Prism of the second order
"This is a form consisting of six rectangular vertical faces, each of which intersects two of the horizontal…
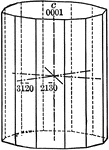
Dihexagonal prism
"The dihexagonal prism has twelve rectangular vertical faces, each of which intersects all three of…
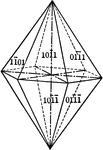
Pyramid of the first order
"This form consists of twelve isoceles triangular faces, each of which intersects two of the horizontal…
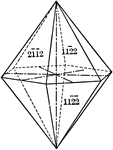
Pyramid of the second order
"This is a form composed of twelve isoceles triangular faces, each of which intersects two of the horizontal…
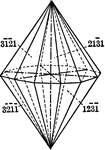
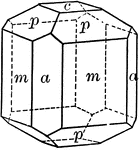
Dihexagonal pyramid
"The dihexagonal pyramid is a form of twenty-four isoceles triangular faces, each of which intersects…
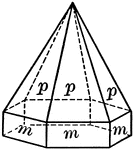
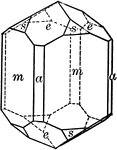
Zincite
"A crystal of zincite with a prism terminated by a pyramid above a basal pinacoid below." — Ford,…
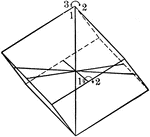
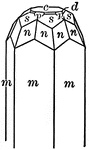
Symmetry of Rhombohedral Class
"The vertical crystallographic axis is one of trigonal symmetry, and the three horizontal crystallographic…
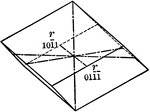
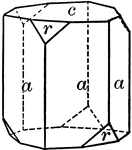
Positive rhombohedron
"The rhombohedron is a form consists of six rhombic-shaped faces, which correspond in their position…
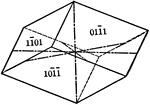
Negative rhombohedron
"The rhombohedron is a form consists of six rhombic-shaped faces, which correspond in their position…
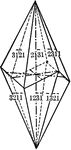
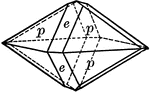
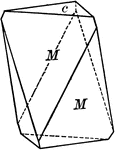
Scalenohedron
"This form consists of twelve scalene triangular faces. These faces correspond in their position to…
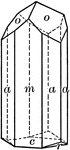
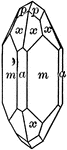
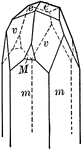
Tourmaline
"Tourmaline crystals show the forms of the Rhombohedral Class but with hemispherical development. They…
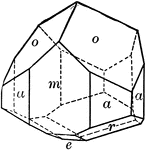
Tourmaline
"Tourmaline crystals show the forms of the Rhombohedral Class but with hemispherical development. They…
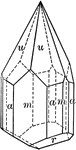
Tourmaline
"Tourmaline crystals show the forms of the Rhombohedral Class but with hemispherical development. They…