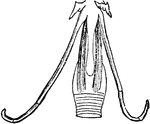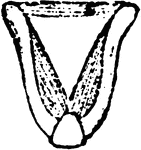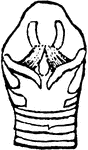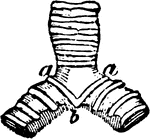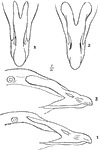
The Bill of an Eider
"Somateri mollissima. Somateri dresseri. Common Eider. Bill gibbous at base of upper mandible; outline…
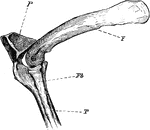
The Knee-joint of a Cormorant
"Phalacrocorax bicristatus. Cormorant. The knee-joint of a Cormorants. F, femur; P, patella; T, tibia;…
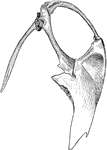
Cormorant Sternum and Shoulder
"Phalacrocorax bicristatus. Red-Faced Cormorant. Sternum and the shoulder from the skeleton of a Cormorant."…
Cormorant Skull
"Phalacrocorax bicristatus. Red-Faced Cormorant. Skull showing sto, occipital style or nuchal bone;…
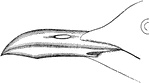
Laughing Gull Bill
"Chroicocephalus atricilla. Laughing Gull. Black-headed Gull. Bill longer than middle toe and claw,…

Tail of Forster's Tern
"Sterna forsteri. Forster's Tern. Tail 5.00 - 8.00, forked 2.50-5.00." Elliot Coues, 1884
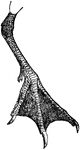
Sooty Tern Foot
"Sterna fuliginosa. Sooty Tern. feet stout; toes short; with much incised webs; tibia bare .70; tarsus…

The Foot of a Bridled Foot
"Sterna anaisthetikos. Bridled Tern. The foot of a Bridled Tern; Tarsus .85; middle toe the same, with…

The Bill of a Skimmer
'Rhynchops. Skimmer. Bill hypognathous Among the singular bills of birds that frequently excite our…
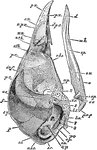
Ripe Chick's Skull
"Ripe chick's skull, longitudinal section, vied inside, x 3 diameters; after parker. In the mandible…
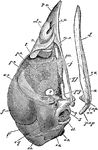
Ripe Chick's Skull Profile
"Ripe chick's skull, longitudinal section, vied inside, x 3 diameters; after Parker. px, premaxillary;…

The Skull of a Woodpecker
"Side view of a woodpecker's skull, showing the long slender basihyal (bh), bearing slight elements…

Top View of a Woodpecker Skull
"Top view of skull of Cloaptes, (flickers) showing thyrohyals running along the skull and into right…
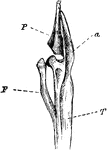
Leg Bones of a Grebe
"F. Fibula; T, tibia, with a, its cnemial process, and P, large patella, of a grebe." Elliot Coues,…
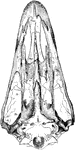
The Skull Structure of an Ostrich
"Dromaeognathous skull of ostrich, nat. size specimen no. 16,629, U.S. Nat Museum, by Dr. R. W. Shufeldt,…
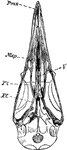
The Skull of a Tinamou
"Dromaeognathous skull of a tinamou (Tinamus robustus); copies by Shufeldt from Huxley. Letters as before;…
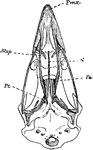
Common Fowl Skull
"Schizognathous skull of common fowl, nat. size, from nature, by Dr. R.W. Shufeldt, U.S.A. Letters as…

Mallard Duck Skull
"Desmognathous skull of mallard duck, Anas boscas, nat. size, from nature, by Dr. R.W. Shufeldt, U.S.A.…
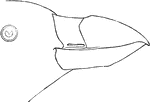
Tufted Puffin Bill
"Lunda cirrata. Tufted Puffin. Crests about 4 inches long, straw-yellow, some of the posterior feathers…
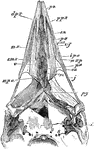
Woodpecker Skull
"Saurognathous skull of a nesting Picus minor. x4 diameters, after Parker. Px premaxillary: dpx, its…
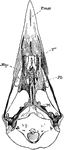
The Skull of a Raven
"Aegithognathous skull of raven, Corvus corax, nat. size, from nature, by Dr. R. W. Shufeldt, U.S.A.…
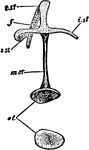
The Ear Bone of Fowl
"Mature stapes of fowl, about x4; after Parker. st, its foot, fitting fenestra ovalis; mst, main shaft,…
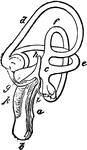
The Inner Ear of an Eagle
"Membranous labyrinth of Haliaetus albicilla (White-tailed Eagle), X2. a,b, cochlea; b, its saccular…
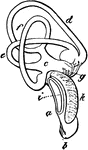
The Inner Ear of a White-tailed Eagle
"Membranous labyrinth of Haliaetus albicilla (White-tailed Eagle), X2. a,b, cochlea; b, its saccular…
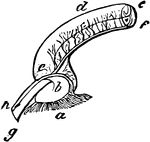
Eagle's Ampulal
"Part of the superior vertical semicircular canal, showing its ampulla (which is the dilatation of the…
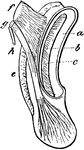
Eagle Cochlea
"Cochlea, X3. a, external, b, internal, cartilaginous prism; c, membranous zone; d, saccular extremity…
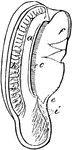
A Section of an Eagle's Cochlea
"Section of the cochlea, X3. a, vestibular surface of external cartilaginous prism, extending into d,…

Eurasian Sparrowhawk Muscles
"Muscles of a bird (accipiter nisus), after Carus, Tab. Anat. Comp., 1828, pl. 4. a, pharynx; b, trachea;…
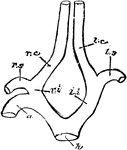
Carotid Arteries of Birds
"h, root of aorta; 1, arch of aorta, to the right side; li, left innominate; ri, innominate; ls, left…

Bird Trachea
"a, an inch of trachea, contracted to the utmost, the rings looking like alternating half-rings; b,…
The Tracheal Rings of a Bird
"1, 2, left, two tracheal rings, separate. b; 1, 2, right hand, the same put together." Elliot Coues,…
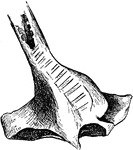
The Bony Labyrinth of a Sea Duck
"Bony labyrinth at the bottom of the trachea of the male Clangula islandica, seen from behind." Elliot…
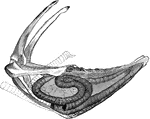
Whooping Crane Windpipe
"Very generally, in cranes and swans, the trachea enters the keel of the sternum, which is excavated…
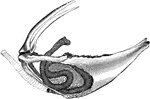
Sandhill Crane Windpipe
"Coiling of the windpipe in the sternum of Grus canadensis. Sandhill Crane." Elliot Coues, 1884
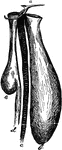
Bustard Gular Pouch
"Gular pouch of bustard; a, tongue; b, the pouch, opening under a, hanging in front of c, the trachea,…
The Respiratory and Vocal Organs of a Rook
"Resipratory and vocal organs of the Rook, Corvus frugilegusm an Oscine Passerine bird; 1 a, tongue;…
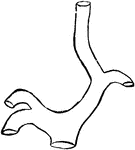
Carotid Arteries of Birds
"h, root of aorta; 1, arch of aorta, to the right side; li, left innominate; ri, innominate; ls, left…
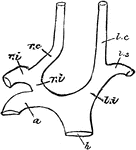
Carotid Arteries of Birds
"h, root of aorta; 1, arch of aorta, to the right side; li, left innominate; ri, innominate; ls, left…
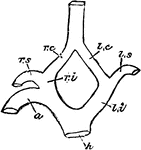
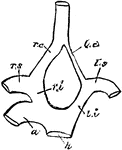
Carotid Arteries of Birds
"h, root of aorta; 1, arch of aorta, to the right side; li, left innominate; ri, innominate; ls, left…
Carotid Arteries of Birds
"h, root of aorta; 1, arch of aorta, to the right side; li, left innominate; ri, innominate; ls, left…
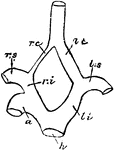
Carotid Arteries of Birds
"h, root of aorta; 1, arch of aorta, to the right side; li, left innominate; ri, innominate; ls, left…
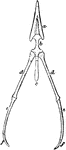
The Hyoid-bone of a Rook
"Hyoid bone; a, glosso-hyal, tipped with cartilage, its posterior horn being certo-hyals proper; b,…
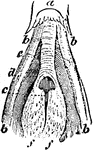
The Glottis of a Rook
"Glottis, or opening of trachea in the mouth; a, base of tongue; b, b, horns of hyoid bone; c, rima…

The Larynx of a Rook
"Larynx viewed from before (below); a, thyroid bone or cartilage." Elliot Coues, 1884
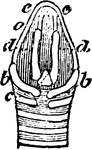
The Larynx of a Rook
"Larynx viewed from behind (above); a, thyroid bone; b, b, its appendages; c, cricoid; d, d, arytenoids;…
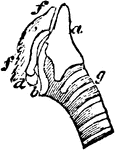
The Larynx of a Rook
"Larynx viewed from the right side; a, thyroid; b, appendage; c, cricoid; d, arytenoid; f, f, cartilage…
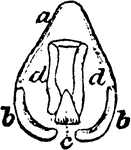
The Larynx of a Rook
"Larynx viewed from behind; a, thyroid; b, b, its appendages; c, cricoid; d, d, arytenoid." Elliot Coues,…
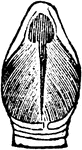
The Larynx Muscles of a Rook
"Muscles of the larynx. thyro-arytenoids, or openers of the glottis" Elliot Coues, 1884
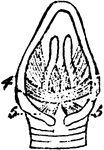
The Larynx Muscles of a Rook
"Muscles of the larynx. Thyro-cricoids, posterior thyro-cricoids." Elliot Coues, 1884

The Trachea of a Rook
"Last entire tracheal ring, viewed from below, crossed by the pessulus." Elliot Coues, 1884
The Trachea of a Rook
"Bifurcation of trachea, and bronchi, viewed from below; a, pessulus, the bolt-bar, or "bone of divarication";…
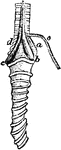
The Laryngeal Muscles of a Rook
"a, b, c, d, inferior laryngeal or syringeal muscles, not well made out in this figure; But typical…
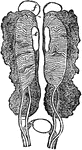
Male Uro-genital Organ
"Uro-genital organs of male embryo bird; from Owen, after Muller. a, kidneys: b, ureters; c, wolffian…
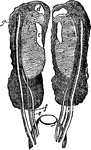
Female Uro-genital Organ
"Uro-genital organs of female embryo bird; from Owen, after Muller. a, kidneys: b, wolffian bodies;…
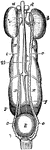
Female Uro-genital Organ
"Uro-genital organs of female embryo bird; from Owen, after Muller. a, testis; b, epididymis; c, sperm-duct…