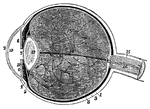
Human Eye
1, the sclerotic thicker behind than in front; 2, the cornea; 3, the choriod; 6, the iris; 7, the pupil;…
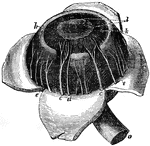
Human Eye
c, ciliary nerves going to be distributed in iris; d, smaller ciliary nerve; e, veins known as vasa…
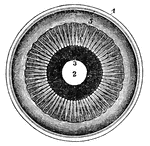
Human Eye
The iris and adjacent structures seen from behind. 1, the divided edge of the three coats, the choroid…
Talus
"Talus. The huckle-bones of sheep and goats were used to play with from the earliest times, principally…

Scourge
"The Furies are generally represented with a scourge, with which to punish the wicked in Tartarus. It…
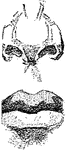
Teeth
The series of small bones attached to the jaws of animals, or human beings, which serve the purpose…
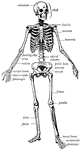
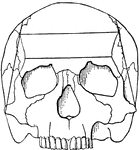
Human skeleton
"The human body, like a great building, has a framework which gives the body its shape and provides…
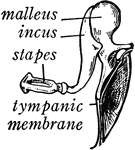
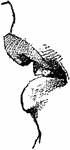
Bones of the Ear
"Across the middle ear a chain of three small bones stretches from the tympanic membrane to the inner…
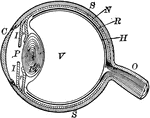
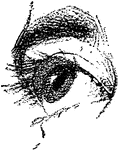
Eyeball
"The most essential parts of human vision are contained in the eyeball, a nearly spherical body, about…
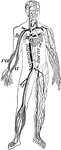
Veins and arteries
"Chief veins and arteries of the body. a, place of the heart; the veins are in black. On the right side…
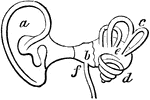
Ear
Interior of the ear. There is external to the head a wide-mouthed tube, or ear-trumpet (a), for catching…

Side View of the Body
A side view of the two great cavities of the body and their organs. 1: The mouth. 2: The thorax. 3:…
Spinal Column
The spinal column. 1, 2, and 3: Vertebrae. 4 and 5: The sacrum and cocyx bones of the pelvis. 6: Processes.
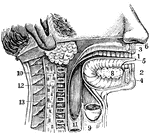
Mouth and Neck
The mouth and neck laid open. 1: The teeth. 3 and 4: Upper and lower jaws. 5: The tongue. 7: Parotid…
Oats
A genus of grasses including about sixty species, valuable alike for the production of hay and for their…