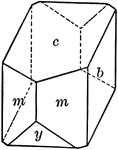
Orthoclase
"Monoclinic. Crystals are usually prismatic in habit and have as prominent forms, clinopinacoid, base,…
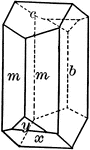
Orthoclase
"Monoclinic. Crystals are usually prismatic in habit and have as prominent forms, clinopinacoid, base,…
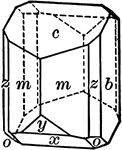
Orthoclase
"Monoclinic. Crystals are usually prismatic in habit and have as prominent forms, clinopinacoid, base,…
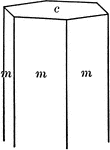
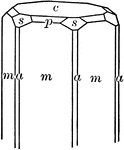
Beryl
"Hexagonal. Strong prismatic habit. Frequently vertically striated and grooved. Forms usually present…
Beryl
"Hexagonal. Strong prismatic habit. Frequently vertically striated and grooved. Forms usually present…
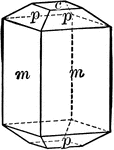
Vesuvianite
"Tetragonal. Prismatic in habit. Often vertically striated. Common forms are prisms of first and second…
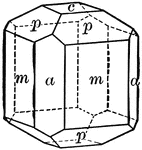
Vesuvianite
"Tetragonal. Prismatic in habit. Often vertically striated. Common forms are prisms of first and second…
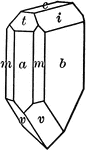
Calamine
"Orthohombic, hemimorphic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to the brachypinacoid. They show prism…
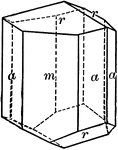
Tourmaline
"Hexagonal-rhombohedral; hemimorphic. Crystals usually prismatic, vertically striated. A triangular…
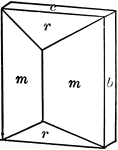
Staurolite
"Orthohombic. Habit prismatic, showing usually a combination of prism with large angle, brachypinacoid,…
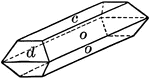
Barite
"Orthohombic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to base; often diamond shaped because of the presence…
Barite
"Orthohombic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to base; often diamond shaped because of the presence…
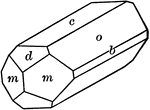
Celestite
"Orthorhombic. Crystals resemble closely those of barite. Commonly tabular parallel to the base or prismatic…
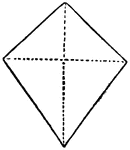
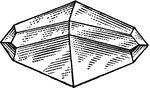
Deltoid
"A four-sided figure, formed of 2 unequal isosceles triangles on different sides of a common base."…
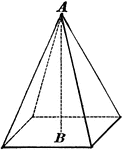
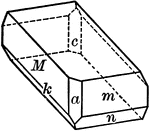
Pyramid
A pyramid is a solid whose base is a plan figure, and whose sides are triangles uniting at a common…
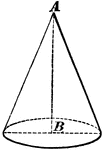
Cone
A cone is a solid whose base is a circle, and whose convex surface tapers uniformly to a point called…
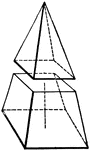
Frustum
If a pyramid be cut by a plan parallel to the base, so as to form two parts, the lower part is called…
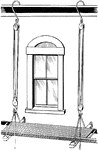
Swing Stage Scaffold
This shows the old fashioned rope stirrup rigging. The scaffold as a whole consists of a platform twenty…

Swing Stage Ladder Bracket
This is used on the upper end of two extension ladders in place of cornice hooks, where the building…

Rook
A species of crow. It differs from other birds of the crow family in having a naked spot at the base…
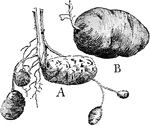
Tubers
This illustration shows the formation of tubers: A, old potato or tuber with two shoots reaching up…
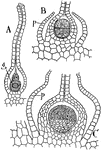
Gametospore
This illustration shows the germination of the gametospore: A, section of a mature archegonium with…
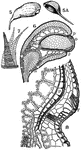
Funaria
This illustration shows the structure of capsule of Funaria: 5, capsule with calyptra, 5A, removed.…
Onion Magnified
This is an illustration of crystals from the base of an onion, one of them a hemitrope or double.
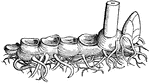
Diphylleia Cymosa
This illustration shows the rhizoma of Diphylleia cymosa, showing six years of growth, and a bud for…
White Lily
This illustration shows a radical leaf of the White Lily, with its base thickened into a bulb-scale,…

Mammillaria
The genus Mammillaria is one of the largest in the cactus family Cactaceae. the distinctive feature…
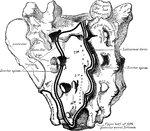
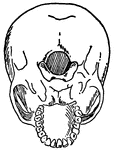
Sacrum
A large, triangular bone at the base of the vertebral column at the upper and back part of the pelvic…
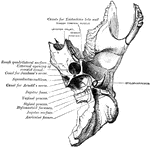
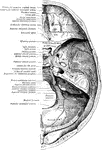
Temporal Bone
Bones situated at the sides and base of the skull. Each consists of five parts: the squama, the petrous,…
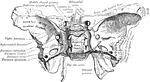
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
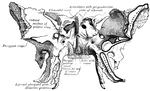
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
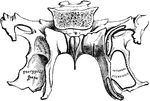
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.

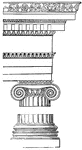
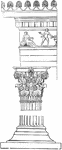
Base
A portion of the ornament which runs along the base of the rows of figures on the monolithic doorway.…
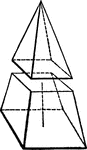
Pyramid
"If a pyramid be cut by a plane, parallel to the base, so as to form two parts, the lower part is called…
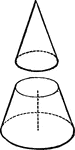
Cone
"If a cone be cut by a plane, parallel to the base, so as to form two parts, the lower part is called…

Saxifrage
"A genus of plants of the natural order Saxifrangeae. This order has a calyx, usually of five sepals…

Temple, Tanjore
"The great pagoda at Tanjore is by far the grandest temple in India, resting on a base 83 feet suare,…

Piping Plover
A small ring necked plover of North America. It is of a pale gray color above and white below, with…
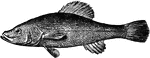
Pirate Perch
This fish is of a dark olive color heavily dotted with black, and has two dark bars at the base of the…