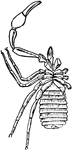
Garypus Litoralis
"Garypus litoralis, one of the Pseudoscorpiones. Ventral view. I to VI, Prosomatic appendages. o, Sterno-coxal…
Garypus Litoralis
"Garypus litoralis, one of the Pseudoscorpiones. Dorsal view. I to VI, The prosomatic appendages. o,…
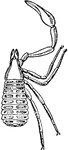
Garypus Litoralis
"Garypus litoralis, one of the Pseudoscopions. Lateral view. I to VI, Basal segments of the six prosomatic…
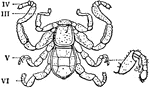
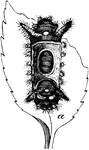
Cryptostemma Karschii
"Cryptostemma Karschii, one of the Podogona. Dorsal view of male. III to VI, The third, fourth, fifth…
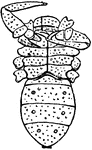
Cryptostemma Karschii
"Cryptostemma Karschii, one of the Podogona. Vental view. I to VI, The six pairs of appendages of the…
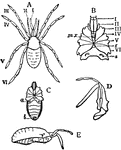
Stylocellus Sumatranus
"Stylocellus sumatranus, one of the Opiliones; after Thorell. Enlarged. A, Dorsal view; I to VI, the…
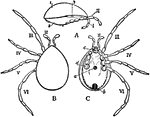
Holothyrus Nitidissimus
"Holothyrus nitidissimus, one of the Acari; ater Thorell. A, Lateral view with appendages III to VI…

Hagia Sophia
Cross section of Hagia Sophia in Istanbul (historically Constantinople). The Greek name Hagia Sophia…

Basilica
"Interior view of trajan's Basilica (Basilica Ulpia), as restored by Canina." — The Encyclopedia…

Basilica
"Sectional view of the old Basilica of St. Peter, before its destruction in the 16th century." —…

Bee Heiroglyph
"Sign of the king of Lower Egypt; from the coffin of Mykerinos, 1633 B.C." — The Encyclopedia…
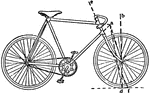
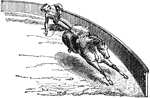
Road-Racer
"Road-racer. A full roadster would have the handles a little higher relatively to the saddle, and would…
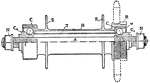
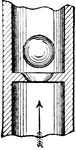
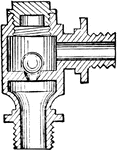
Ball-bearing Hub
"A ball-bearing hub with outward cups. The hub-shell H is turned out of mild steel, and the cups C are…

Buddha
"The sacred name of the founder of Buddhism, an Indian sage who appears to have lived in the 5th century…

Murillo
"Murillo, Bartolomeo Esteban, the greatest of Spanish painters, was born at Seville in 1618. He received…

Jasmine
"Botanically Jasminum, a genus of shrubs or climbers constituting the principal part of the natural…

Center of Gravity
"Why does a person carrying a weight upon his back stoop forward? In order to bring the center of gravity…
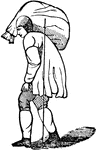
Center of Gravity
"Why does a person carrying a weight upon his back stoop forward? In order to bring the center of gravity…

Griffin Pendent
"A griffin having the uppet part of the body of an eagle and the lower parts of a lion, with wings decorated…
Gold Plate
"It is of gold plate, so thick as to require no "piping" at the back to sustain it; but in general the…
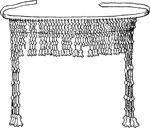
Diadem
"Diadems or head fillets of pure hammered gold cut into thin plates, attached to rings by double gold…
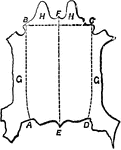
Hide Divisions
"The hides now come to be trimmed and prepared for tanning in the shape in which they are intended ultimately…
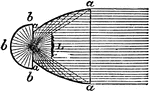
Catadioptric Holophote
"Catadioptric Holophote.—Part of the anterior hemisphere of rays is intercepted and at once parallelized…
Catadioptric Holophote
"Catadioptric Holophote.—Part of the anterior hemisphere of rays is intercepted and at once parallelized…

Dioptric Holophote
"Perfect Form of Dioptric Holophote for an Oil Flame.—By combining the back prisms ga, hc just described…
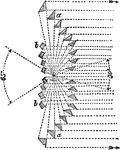
Swans Designs
"Professor Swan's Designs.—Among several ingenious arrangements and new forms of agents proposed by…

Rudd
A fish with a red eye. Sometimes refered to as a pest in parts of the world because of its impact on…
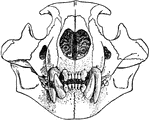
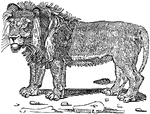
Lion Skull
"The internal structure of the lion, except in slight details, resembles that of the other Felidae,…

Rose Ryal
The front of a Rose Royal coin. It is a very rare English gold coin in the righ of King James 1. Worth…

Rose Ryal
The rear of a Rose Royal coin. It is a very rare English gold coin in the righ of King James 1. Worth…
Atmospheric Pressure
"The pressure of the atmosphere may be easily shown by the tube and piston. suppose there is an orifice…
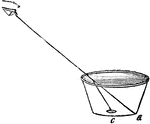
Cup and Shilling
"The refraction of water is beautifully proved by the following simple experiment. Place an empty cup,…
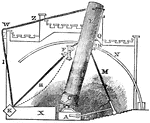
Telescope
"The following description of a section of Lord Rosse's telescope, though not so perfect as could be…
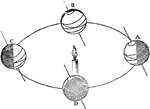
Earth Axis
"Now it is the inclination of the Earth's axis, as above described, which causes the lengths of the…
Earth Axis
"Now it is the inclination of the Earth's axis, as above described, which causes the lengths of the…
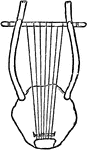
Chelys
"Chelys, from a vase in the British Museum, where also are fragments of such an instrument, the back…
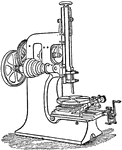
Slotting Machine
"The slotting machine also cuts grooves and slots, but in an entirely different manner. Those who are…
Femur
Section of the femur. 1: External view; 2: Cellular portion at end; 3: Hollow in middle; 4: Thick shell…

Bone Section
Longitudinal section of bone, a microscopic view. 1: Cells; 2: Canals; 3: Intercellular substance.

Bone Section
Cross-section of bone, a microscopic view. 1: Cells; 2: Canals; 3: Intercellular substance.
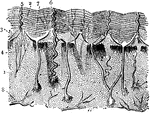
Skin
Vertical section of the skin, a microsopic view. 1: Cutis; 2: Cuticle in layers; 3: Papilla; 4: Nerves…
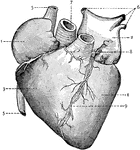
Heart
External view of the Heart. 1: Right Auricle; 2: Left Auricle; 3: Right Ventricle; 4: Left Ventricle;…
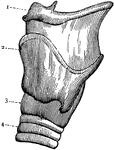
Larynx
External view of the left side of Larynx. 1: Front portion of hyoid bone; 2: Upper edge of larynx; 3:…
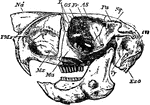
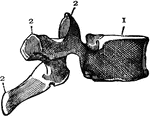
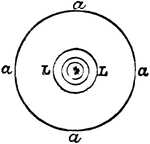
Cape Jumping Hare
"Side view of skull of Cape Jumping Hare. Pmx, premaxilla; Mx, maxilla; Ma, malar; Fr, frontal; L, lachrymal;…