
The Star of the West
The Star of the West was a civilian ship hired by the United States government to transport…

Frederick Steele
Frederick Steele (January 14, 1819 – January 19, 1868) was a career military officer in the United…

Alexander Hamilton Stephens
Alexander Hamilton Stephens (February 11, 1812 – March 4, 1883) was an American politician from Georgia.…

General George Stoneman
George Stoneman, Jr. (August 22, 1822 – September 5, 1894) was a career United States Army officer,…

Samuel Davis Sturgis
Samuel Davis Sturgis (June 11, 1822 – September 28, 1889) was an American military officer who…

Jasminum grandiflorum
Jasminum grandiflorum (chameli in Hindi) is a species of jasmine native to South Asia. In India, its…

Juniper
An illustration of a juniper branch, vertical section of fruit (1), and male catkin (2). Junipers are…

Red-Legged Seriema
The Red-Legged Seriema (Cariama cristata) is a predatory terrestrial bird in the Cariamidae family of…
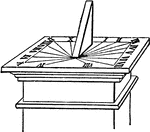
Sundial
A sundial is a device that measures time by the position of the Sun. In common designs such as the horizontal…
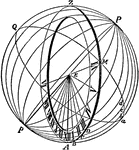
Vertical South Dial
In the common vertical dial, the shadow-receiving plane is aligned vertically; as usual, the gnomon's…
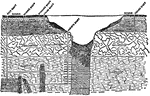
Kimberley Mine Section
An illustration of section of mine from the Kimberley Mine located in South Africa.

Fort Sumter
The fort is best known as the site where the shots initiating the American Civil War were fired, at…

Major Anderson's Headquarters
The headquarters of Major Robert Anderson at Fort Sumter, South Carolina during the American Civil War.

Fort Sumter in 1864
The fort is best known as the site where the shots initiating the American Civil War were fired, at…

Inside the Walls of Fort Sumter
The fort is best known as the site where the shots initiating the American Civil War were fired, at…

Fort Sumter Medal (Front)
The Fort Sumter medal executed by order of the New York Chamber of Commerce in recognition of the Battle…

Fort Sumter Medal (Back)
The Fort Sumter medal executed by order of the New York Chamber of Commerce in recognition of the Battle…

Gold Box Presented to Anderson
The gold box presented to Major Robert Anderson for his command of Fort Sumter during the American Civil…

Swamp Angel
One of the most famous Parrott rifles is the Swamp Angel, an 8-inch (200 mm) gun used by federal Brigadier…

Ladybug
Coccinellidae is a family of beetles, known variously as ladybirds (British English, Australian English,…

Hispid Cotton Rat
The Hispid Cotton Rat (Sigmodon hispidus) is a small rodent in the Cricetidae family of New World rats…
Silver Fir Cone and Foliage
An illustration of a silver fir cone and a small branch. Silver Fir or European Silver Fir (Abies alba)…
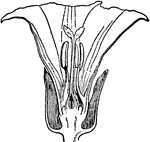
Calystegia Sepium
Calystegia sepium (Larger Bindweed, Hedge Bindweed, or Rutland beauty) is a species of bindweed, with…

Calystegia Sepium Bud
An illustration of a Calystegia sepium bud. Calystegia sepium (Larger Bindweed, Hedge Bindweed, or Rutland…
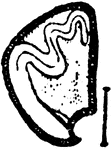
Calystegia Sepium Seed
An illustration of a Calystegia sepium seed cut lengthwise showing the embryo. Calystegia sepium (Larger…
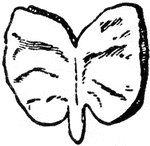
Calystegia Sepium Embryo
An illustration of a Calystegia sepium embryo. Calystegia sepium (Larger Bindweed, Hedge Bindweed, or…
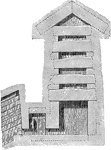
Great Pyramid of Giza, King's Chamber
The King's Chamber is lined with red granite brought from Aswan 935 km (580 miles) to the south, of…
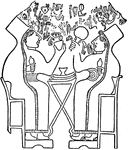
Hittite Women
An illustration of two Hittite women sitting. The Hittites were an ancient Anatolian people who spoke…
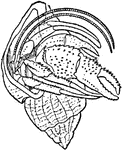
Hermit Crab
Pagurus bernhardus is the common marine hermit crab of Europe's Atlantic coasts. It is sometimes referred…

Great Temple at the Island of Philæ
The Temple of Debod is an ancient Egyptian temple which was rebuilt in Madrid, Spain. The temple was…
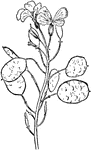
Annual Honesty
Annual Honesty (Lunaria annua) is a tall (height about 1 m), hairy-stemmed biennial plant found throughout…
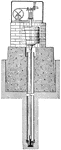
Pendulum Seismograph
"inverted Vertical Pendulum Seismograph. Marvin System. A stiff vertical tube, pivoted at its bottom…
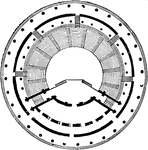
Ground Plan of the Theatre of Herodes Atticus
The Odeon of Herodes Atticus is a stone theatre structure located on the south slope of the Acropolis…

Oxalis
Oxalis is the largest genus in the wood sorrel family Oxalidaceae. Of the approximately 900 known species…

Dianthus
Dianthus is a genus of about 300 species of flowering plants in the family Caryophyllaceae, native mainly…

Yuca
The cassava, yuca, manioc, mogo or mandioca (Manihot esculenta) is a woody shrub of the Euphorbiaceae…

Krak des Chevaliers
Krak des Chevaliers was the headquarters of the Knights Hospitaller during the Crusades. It was expanded…

Caerphilly Castle
Caerphilly Castle is a Norman castle that dominates the centre of the town of Caerphilly in south Wales.…

Guyenne Spiny Rat
The Spiny Rat (Echimys cayennensis) is a rodent in the Echimyidae family of spiny rats.

Fumitory
Fumaria is a genus of about fifty annual herbaceous flowering plants in the family Fumariaceae, native…
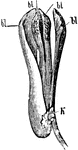
Fumitory (Side-view)
An illustration of the side-view of the fumitory flower Fumaria is a genus of about fifty annual herbaceous…
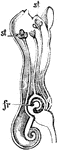
Fumitory Flower (Longitudinal Section)
An illustration of a longitudinal section of the fumitory flower. Fumaria is a genus of about fifty…
Fumitory Flower Anther
An illustration of a fumitory flower anther. Fumaria is a genus of about fifty annual herbaceous flowering…
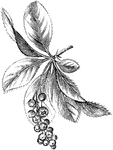
Berberis
An illustration of a berberis branch. Berberis (Bér-be-ris, barberry, pepperidge bush) a genus…
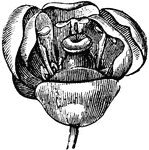
Berberis Flower
An illustration of the berberis flower. Berberis (Bér-be-ris, barberry, pepperidge bush) a genus…
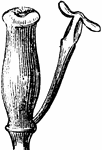
Pistil and Stamen of Burberis
An illustration of the a stamen and pistil of the berberis plant. Berberis (Bér-be-ris, barberry,…
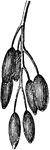
Fruit of Berberis
An illustration of the berberis fruit. Berberis (Bér-be-ris, barberry, pepperidge bush) a genus…

Mountain-laurel
Kalmia latifolia, commonly called Mountain-laurel or Spoonwood, is a flowering plant in the family Ericaceae,…

Escallonia
"Escallonia macrantha. Escallonia is a South American genus of trees or shrubs, of the natural order…
Dakota Artesian System
East-west section across South Dakota to show the Dakota artesian system. The Dakota sandstone is composed…

General Philip Henry Sheridan
(1831-1888) Philip Sheridan was a United States Army officer and Union General in the Civil War.

Fenestella in the Church of Norrey
"Fenestella. In Roman Catholic churches, a niche on the south side of an altar, containing the piscina,…
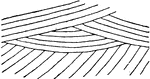
Eolian Cross-bedding
Eolian type of cross-bedding in ancient limestones, formed of uniform lime-sand grains south of St.…
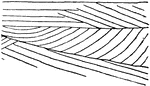
Eolian Cross-bedding
Eolian type of cross-bedding in ancient limestones, formed of uniform lime-sand grains south of St.…
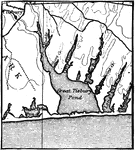
Bay-bar
A Bay-bar, with narrow inlet which leaves the water of the bay salty. South Shore of Marthas Vineyard.

Bay-bar
A Bay-bar completely cutting off a bay and converting it into a closed shore-pond. South Shore of Marthas…

Southern Literary Messenger Building
The Southern Literary Messenger was a periodical published in Richmond, Virginia, from 1834 until June…
St. Gothard Massif, Switzerland
North-south cross-section of the St. Gothard Massif, Switzerland, showing the fan-folds.
West Alps, South of Lake Geneva
Cross-section of a part of the West Alps, south of Lake Geneva, mainly in France.

Cuestas and Lowlands
Block diagram illustrating the formation of three cuestas and lowlands by normal drainage on the peneplaned…