
Battle of Mill Spring
"Battle of Mill Spring, on the Cumberland River, near Jamestown, between a confederate force, 8,000…

First Minnesota Regiment
"Fort built around the officer's quarters of the First Minnesota Regiment, Colonel Sully, near Fair…

Red Lemur
"This lemur is noted for its brillant colorings, the greater part of the body being covered with a vivid…

Douroucouli Monkey
"N. trivirgatus. Its generl color is gray: its body and head measure ten inches. It lives on…

Monk Saki
"The monkeys of this genus are marked by a short head, an angular muzzle, and a non-prehensile tail.…

Satanic Saki
"The monkeys of this genus are marked by a short head, an angular muzzle, and a non-prehensile tail.…

Galagos
"The head is large and round; the membranaceous ears remarkably large, and closed when the animal is…
Tupaias
"These are small animals, having somewhat the form and agility of squirrels. The head is long, the snout…

Raccoon
"The raccoon is about twenty-six inches long; the tail eight inches; the weight twenty to twenty-five…

Crab-Eating Raccoon
"The raccoon is about twenty-six inches long; the tail eight inches; the weight twenty to twenty-five…

Coati Mondi
"They are distinguished by a long body, a long head terminating in a long flexible snout, with which…

Pougonie
"P. typus, is of a yellowish brown, marked with three ranges of obscure spots on the back.;…

Cryptoprocta Ferox
"The only species, C. ferox, is but fifteen inches long, but its strength is great. Its disposition…

Fox Hound
"A cross between an old english hound and the greyhound. It is from twenty-two inches to two feet in…

Dingo
"This remarkable bred has the head elongated, the forehead flat, and the ears short and erect, or with…

Bull Dog
"The bull dog has a round, thick head, a turned-up nose, and thick and pendulous lips. He is of moderate…

Battle of Charles City
"Battle of Charles City Road- charge of the Jersey Brigade- the first New Jersey brigade, General Tayler,…

Battle of Gaines's Mill
"Battle of Gaines's Mill, Friday, June 27th, 1862. At eleven o'clock each division, brigade, regiment…

General Benjamin F. Butler
"General Butler was born in Deerfield, N. H., November 6th, 1818. At the time of President Lincoln's…

Strasburg Woods
"In the Shenandoah Valley- General Fremont's division marching through the woods to attack the Confederates.…

Blue Ridge Pass
"The victory at Blue Ridge Pass, Sunday, September 14th, 1862- infantry charge, and rout of the Confederates.…

Hilton Head
"Expedition to Port Royal- Government buildings erected on Hilton Head, S. C., by the Federal forces…
Hilton Head
"Expedition to Port Royal- Government buildings erected on Hilton Head, S. C., by the Federal forces…

Battle of Secessionville
"Battle of Secessionville, James Island, S. C.- bayonet charge of Federal troops, commanded by General…

Police Headquarters
"Interior of the outbuilding attached to Marshal Kane's Police Headquarters, Holliday Street, Baltimore-…

Battle of Savages Station
"Battle of Savages Station. Brigadier General Smith's division hotly engaged with the enemy, at noon,…

Battle of Cedar Mountain
"Battle of Cedar Mountain, fought Saturday, August 9th, 1862, between the Federal troops commanded by…

Commencement of Bull Run
"The Confederate forces under General Jackson advancing upon the Rapphannock Station at the river. Federal…

General Ormsby MacKnight Mitchel
"General Mitchel, born at Morganfield, Union County, Ky., August 28th, 1809, died at Hilton Head, S.…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Monitor
"Loss of the Monitor- gallant attempt of the officers and crew of the United States steamer…

Battle of Munfordville
"Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the Confederates charging through the abatis…
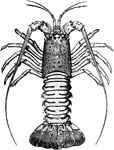
Crawfish
"Also known as Florida lobster. This Southern species, a "spiny" lobster, found off the southern Florida…

Army of the Potomac
"Advance of the Army of the Potomac. Occupation of Winchester, VA., and the abandoned Confederate Fortifications,…

Fort Thompson
"Bombardment and capture of Fort Thompson, thirteen guns, near New Berne, on the Neuse River, by the…

Battle of South Mountain
"Federal artillery taking up position at the Battle of South Mountain. The Federal movement was admirably…

Canada Lynx
"The Canada Lynx of the Indians, has a round, broad head, large eyes, strong teeth, ears acute and tipped…

Cape Ratel
"The hair is stiff and wiry; body above, from the top of the head to the root of the tail, dull ash-gray,…

Marten
"Its head is somewhat triangular , the muzzle pointed, the eyes prominent and lively; the body much…
Rabbit
"The difference between the hare and this animal is numerous and striking. In a state of nature, the…

Calling Hare
"It has a head loner than usual with hares, and thickly covered with cur, even the tip of the nose;…

Leopard Spermophile
"The leopard spermophile is one of the most beautiful of all striped species of spermophile. It resembles…

Capybara
"It measures three feet from muzzle to the hinder part, but has no tail. The general shape of the body…

Rock Cavy
"In this animal, the fur is soft, its general hue gray, tinted with rufous on the hinder art of the…

Black Agouti
"Is considerably smaller than the common agouti, being about the size of a rabbit, while the species…

Crested Nelomys
"In its size and hte form of its tail it bears no inconsiderable resemblance to the common rat, the…

Confederate Cavalry
"Confederate cavalry driving stragglers and skulkers back to their duty at the Battle of Antietam. One…

John Gilpin
Gilpin speaks to his horse. "I am in haste to dine; 'Twas for your pleasure you came here, You shall…











