Bust of Homer
"Of the Homeric poems the Iliad and the Odyssey were the most distinguished and have alone come down…

Bust of Pindar
"Pindar, though the contemporary of Simonides, was considerably his junior. He was born either at, or…

Bust of Herodotus
"The first writer who deserves the name of a historian is Herodotus, hence called the Father of History.…

Sophocles
"Sophocles, the younger rival and immediate successor of Aeschylus in the tragic art, was born at Colonus,…

Euripides
"Euripides was born in the island of Salamis, in B.C. 480, his parents having been among those who fled…

Aristotle
"Aristotle was born in 384 B.C., at Stagira, a seaport town of Chalcidice, whence he is frequeently…
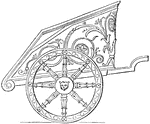
Chariot
"Arms and a chariot are here assigned to June through not properly a warlike goddess. The idea itself,…

Juno
"The following cut is taken from the Vatican Juno found in the ruins of Lorium." — Anthon, 1891

Venus and Diana
"Venus and Diana are generally represented with their hair dressed in the simple style of the young…
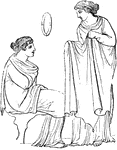
Peplus
"The peplus was a shawl which commonly formed part of the dress of females. It was often fastened…
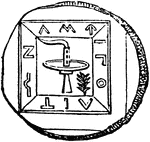
Lampadephoria
"Lampadedromia, torch-race, and often simply, Lampas, was a game common throughout Greece. At Athens…

Herculaneum
"In the following we have back and front views of the heads of statues from Herculaneum, on which we…

Tombstone of a cultrarius
"The preceding cut represents the tombstone of a cultrarius, or the individual who slew the…
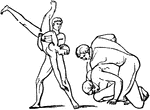
Pancratium
"An athletic game, in which all the powers of the fighter were called into action. The pancratium was…
Pons Cestius
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
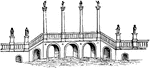
Pons Aelius
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
Pons Ariminum
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
Pons Trajan
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…

Stadium
"A Greek measure of length, and the chief one used for itinerary distances. It was equal to 600 Greek…

Diomede
"The following cut, from an ancient gem, represents Diomede in the act of bearing away the Palladium."…
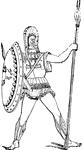
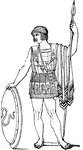
Greek soldier
"The early Greeks used a very short sword, as may be seen from the preceding cut. The ancient Homeric…
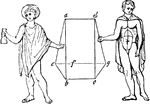
Chlamys
"The chlamys was a species of cloak or scarf, oblong instead of square, its length being generally about…

Carchesium
"The carchesium was a beaker, or drinking-cup, which was used by the Greeks in very early times. It…
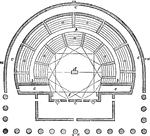
Theatrum
"Theatrum, a theatre. The Athenians before the time of Aeschylus had only a wooden scaffolding on which…

Greek Boat
"The masts were usually taken down when the vessel arrived in port, and raised again when it was about…
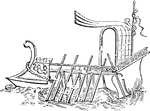
Ship with rudder
"The following cut represents a ship with its rudder. The pole by which it is fastened to the ship's…

Litmus
"This instrument was long, and curved at the end. From the similarity of form the original staff received…

Tunica
"Tunica, an under-garment. Greek. The chiton was the only kind of under-garment, worn by the Greeks.…

Tunica
"Tunica, an under-garment. Greek. The chiton was the only kind of under-garment, worn by the Greeks.…

Tunica
"Tunica, an under-garment. Greek. The chiton was the only kind of under-garment, worn by the Greeks.…
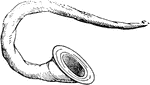
Curved buccina
"The buccina is curved for the convenience of the performer, with a very wide mouth, to diffuse…
Straight buccina
"A copy of an ancient sculpture taken from Blanchini's work, it still retains the original form of the…
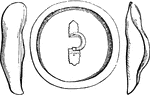
Greaves and shield
"Represents the interior view of a bronze shield and a pair of greaves. These greaves are made right…

George I, King of Greece
George I (born Prince William of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg; 24 December 1845 – 18…

Founding of Argos
"Navigation for the purpose of commerce, and the art of writing, are said to have originated with the…

Young Hercules
"Hercules, a Theban prince, was another of the descendants of Pelops. The numerous and extraordinary…

Phryxsus and ram
"When Phryxsus arrived in Colchis, he sacrificed his winger ram to Jupiter, in acknowledgement of the…

Theseus and Helen
"In the year 1234 B.C., Theseus came to the throne of Athens. He was one of the most renowned characters…

Trojan horse
"According to the poets, it was by stratagem that this famous city was at last overcome. They tell us…

Xerxes surveying his army
"About the year 480 B.C., Xerxes, an Asiatic king, assailed the country with an army of several millions.…

Victors at the Olympic Games
"From a very remote period, the Greeks had been accustomed to engage in contests of strength and agility…

Greek
"The Greeks belong to the great Indo-European race, who from the earliest times have been the conquerers…

Minerva
"On Minerva's side Varro tells us that Cecrops found an olive tree and a fountain, and that on consulting…

The Dioscuri
"Castor and Pollux were the offspring of Leda and the Swan, under which disguise Jupiter had concealed…
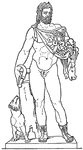
Sylvanus
"Sylvanus and Faunus were Latin divinities, whose characteristics are so nearly the same as Pan that…

Miltiades
Celebrated general of Athens, born in the latter part of the 6th century B.C. His skill and bravery…

Still Life Painting from Pompeii
"Painting of still life. On a wall of a house at Pompeii." —D'Anvers, 1895